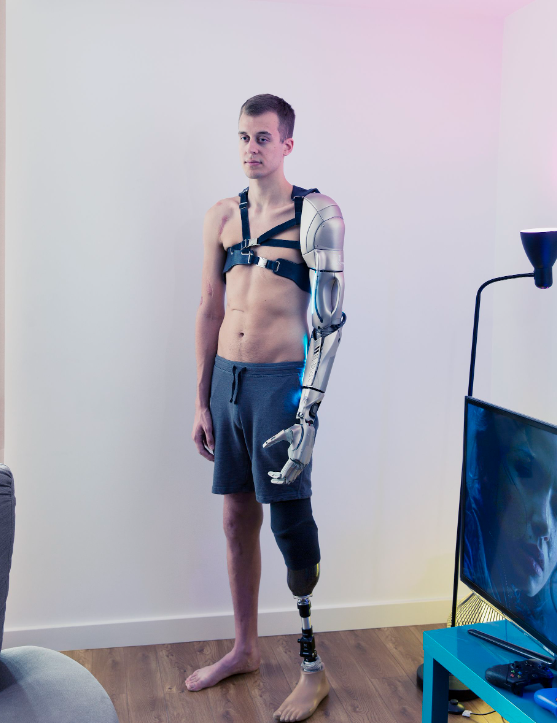
Transhumanism is an intellectual and cultural movement that advocates for the use of advanced technologies to enhance human physical and cognitive abilities and improve the human condition. It aims to transcend the biological limitations of humans by applying science and technology to expand our capabilities, improve health, and potentially extend lifespan. Transhumanism envisions a future where humans can evolve into “posthumans” with capabilities far beyond those we possess today, allowing for a significant transformation in the human experience.
Key Concepts of Transhumanism
- Human Enhancement: Transhumanism promotes the use of technologies such as genetic engineering, artificial intelligence, robotics, and nanotechnology to enhance human abilities. This includes improving physical capabilities, cognitive functions, emotional well-being, and extending lifespan.
- Technological Singularity: Many transhumanists anticipate a future point known as the “singularity,” where technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in transformative changes to civilization. This could involve the emergence of superintelligent AI and rapid advancements in human enhancement technologies.
- Posthumanism: Transhumanism envisions a transition from human to “posthuman,” where individuals possess capabilities that far exceed current human abilities. Posthumans might enjoy increased intelligence, strength, emotional stability, and longevity, fundamentally altering the human experience.
- Ethical and Social Considerations: Transhumanism raises important ethical questions about the nature of humanity, identity, equity, and access to enhancement technologies. The movement advocates for the responsible and equitable development of technologies to ensure that their benefits are widely distributed and do not exacerbate existing inequalities.
- Life Extension and Longevity: One of the central goals of transhumanism is to significantly extend human lifespan and improve health through advances in biotechnology, such as anti-aging therapies and regenerative medicine. Transhumanists seek to combat age-related diseases and enhance the quality of life as individuals age.
Philosophical Foundations
Transhumanism builds on humanist principles by emphasizing reason, science, and progress as means to improve the human condition. It encourages the exploration of new technologies to address fundamental human challenges and enhance well-being. Transhumanists believe in the potential for humans to take control of their evolution and shape their future through technological innovation.
Historical Background
The modern transhumanist movement began to take shape in the late 20th century, influenced by the rapid advancements in science and technology. Notable figures such as Julian Huxley, who coined the term “transhumanism” in the 1950s, and futurists like F.M. Esfandiary (FM-2030) and Max More, have played key roles in developing transhumanist thought. The publication of seminal works like “The Singularity is Near” by Ray Kurzweil has further popularized transhumanism, highlighting the potential of exponential technological growth to transform human life.
Transhumanism in Practice
Transhumanism encompasses a wide range of technologies and applications, including:
- Genetic Engineering: Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 enable precise modifications to DNA, allowing for genetic enhancements and the treatment of genetic disorders.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning enhance cognitive functions, personalize user experiences, and optimize decision-making processes.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: BCIs facilitate direct communication between the brain and external devices, offering potential for cognitive enhancement and assistive technologies.
- Nanotechnology: Nanobots and smart materials offer possibilities for medical treatments, environmental monitoring, and enhanced human capabilities.
Criticisms and Challenges
Transhumanism faces several criticisms and challenges, including concerns about the ethical implications of enhancement technologies, the potential for social inequality, and the risk of unintended consequences. Critics argue that transhumanism may overlook the importance of social and cultural factors and underestimate the complexity of biological systems.
- Best AI tools for Software Engineers - November 4, 2024
- Installing Jupyter: Get up and running on your computer - November 2, 2024
- An Introduction of SymOps by SymOps.com - October 30, 2024

