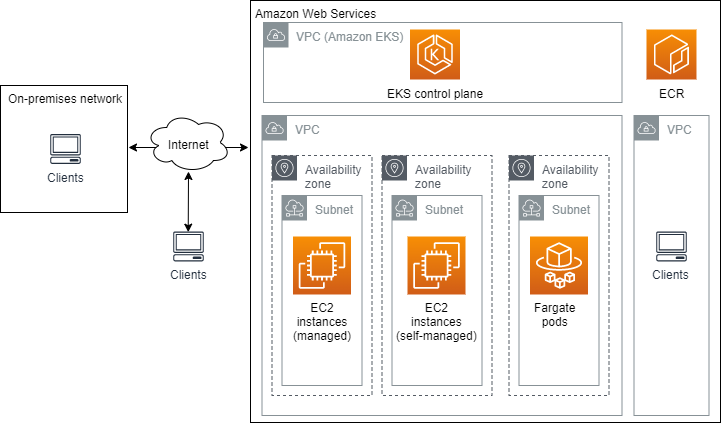
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) runs the Kubernetes management infrastructure for you across multiple AWS Availability Zones to eliminate a single point of failure. Amazon EKS is certified Kubernetes-conformant, so you can use existing tooling and plugins from partners and the Kubernetes community. Applications running on any standard Kubernetes environment are fully compatible and can be migrated to Amazon EKS.
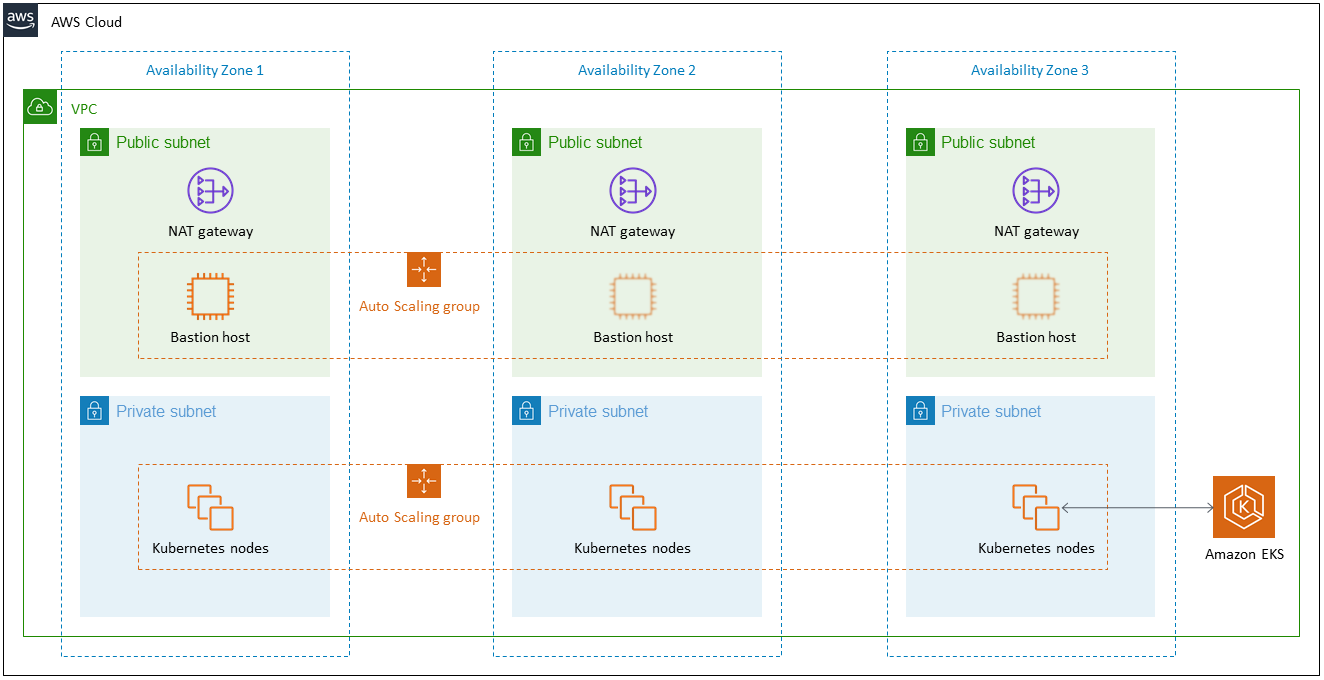
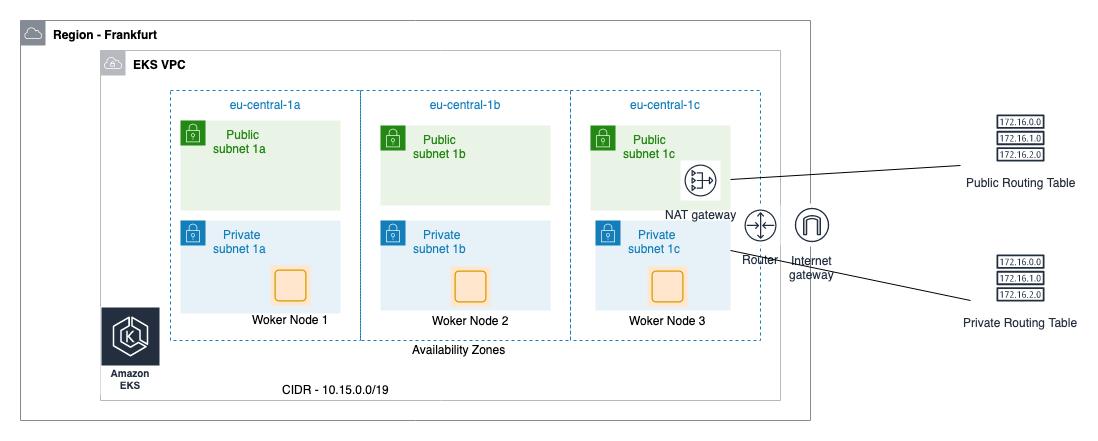
- A highly available architecture that spans three Availability Zones.*
- A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets according to AWS best practices, to provide you with your own virtual network on AWS.*
- In the public subnets, managed NAT gateways to allow outbound internet access for resources in the private subnets.*
- In one public subnet, a Linux bastion host in an Auto Scaling group to allow inbound Secure Shell (SSH) access to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances in private subnets. The bastion host is also configured with the Kubernetes kubectl command line interface for managing the Kubernetes cluster.
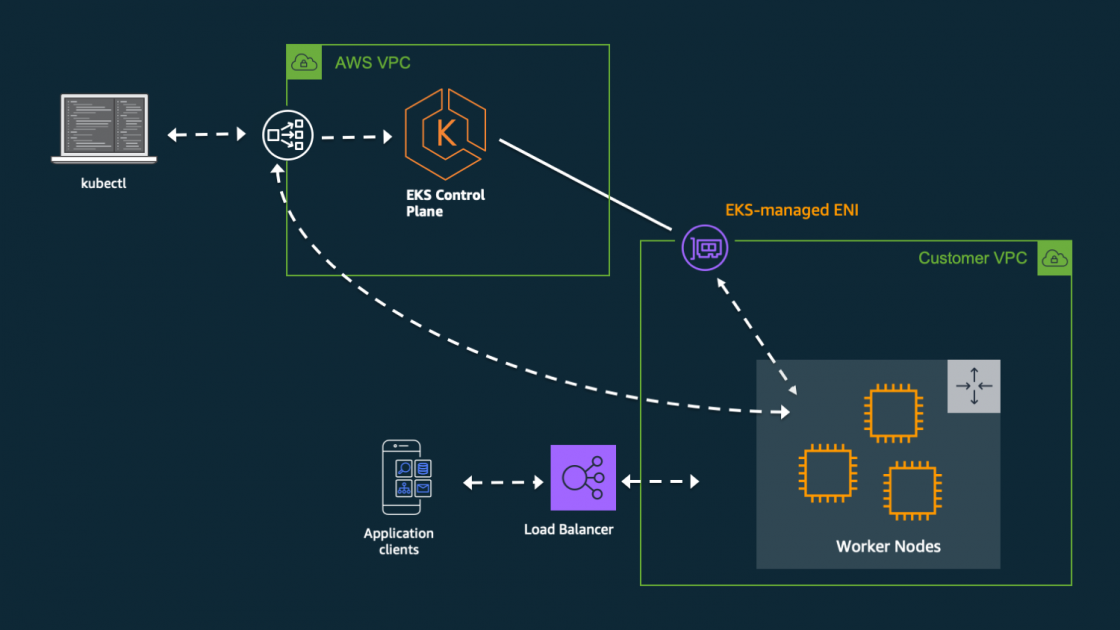
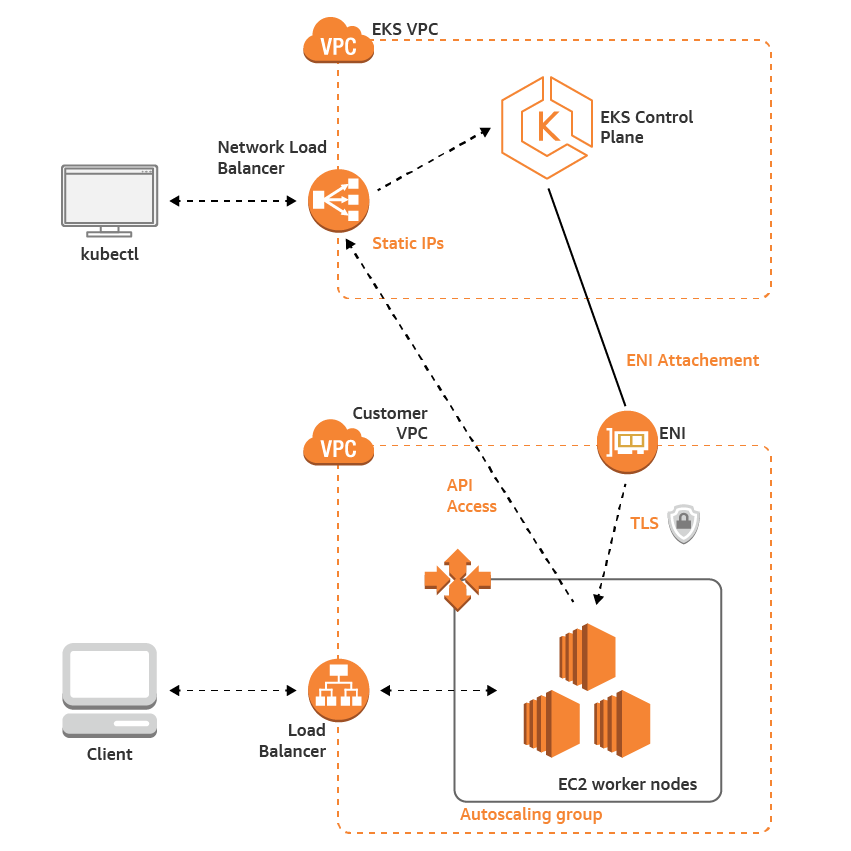
- An Amazon EKS cluster, which provides the Kubernetes control plane.
- In the private subnets, a group of Kubernetes nodes.
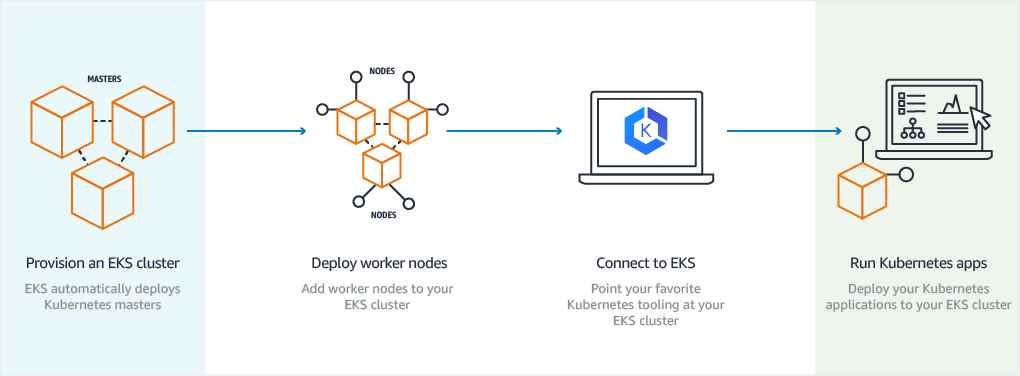
EKS Workflow
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
