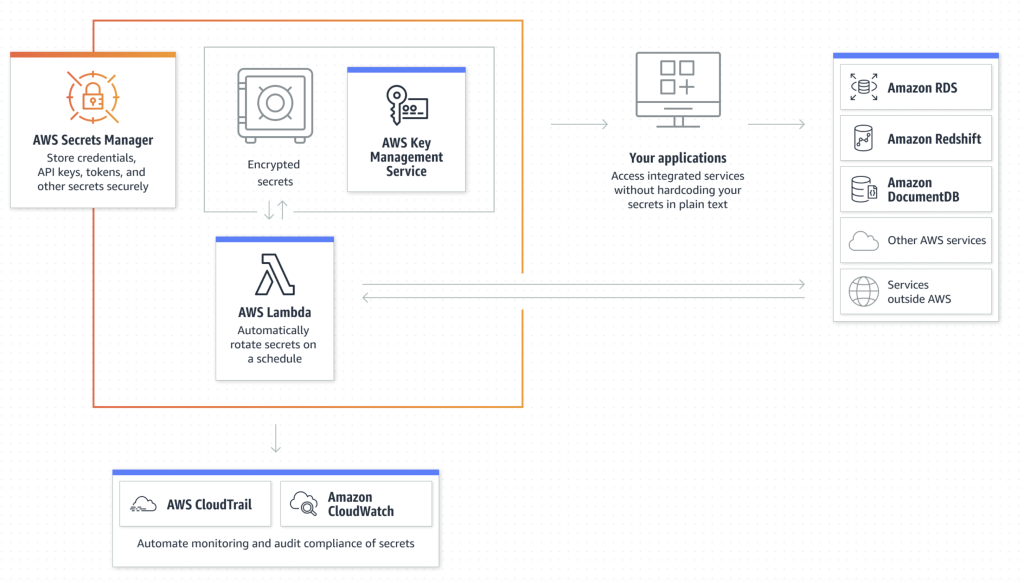
AWS Secrets Manager simplifies and enhances security by storing, managing, and rotating sensitive secrets. It integrates seamlessly with AWS services and provides automated secret rotation, secure retrieval, and fine-grained access control.
What is AWS Secrets Manager?
AWS Secrets Manager is a fully managed service that securely stores, retrieves, rotates, and manages sensitive information like:
- Database credentials
- API keys
- OAuth tokens
- Encryption keys
- Other application secrets
It provides automated secret rotation, fine-grained access control, and seamless integration with AWS services.
 Key Features of AWS Secrets Manager
Key Features of AWS Secrets Manager
 Secure Secret Storage
Secure Secret Storage
- Secrets are stored encrypted using AWS KMS (Key Management Service).
- Automatically rotates encryption keys periodically.
 Automatic Secret Rotation
Automatic Secret Rotation
- Supports automatic rotation of secrets without service downtime.
- Works with RDS, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Aurora, and custom scripts.
 Fine-Grained Access Control
Fine-Grained Access Control
- Uses AWS IAM policies and resource-based policies for controlled access.
- Supports integration with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
 Seamless AWS Service Integration
Seamless AWS Service Integration
- Works with AWS Lambda, AWS RDS, DynamoDB, EC2, and ECS.
- SDK & API support for fetching secrets securely.
 Versioning and History
Versioning and History
- Maintains multiple versions of a secret.
- Supports rollback to previous versions if needed.
 Secure Access & Retrieval
Secure Access & Retrieval
- Secrets can be retrieved using:
- AWS SDK
- AWS CLI
- Terraform, CloudFormation
 How AWS Secrets Manager Works
How AWS Secrets Manager Works
- Create a Secret
- Store credentials, API keys, or other sensitive information.
- Retrieve the Secret
- Applications fetch secrets securely using AWS SDK or CLI.
- Rotate Secrets Automatically
- Secrets are automatically rotated without affecting applications.
- Control Access with IAM Policies
- Use IAM roles and policies to grant access only to authorized resources.
 AWS Secrets Manager vs Parameter Store vs KMS
AWS Secrets Manager vs Parameter Store vs KMS
| Feature | AWS Secrets Manager | AWS SSM Parameter Store | AWS KMS (Key Management) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secret Storage |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |  No No |
| Automatic Rotation |  Yes Yes |  No No |  No No |
| Encryption |  Yes (KMS) Yes (KMS) |  Yes (KMS) Yes (KMS) |  Yes Yes |
| Access via IAM |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |
| Integration |  Yes (Lambda, RDS, etc.) Yes (Lambda, RDS, etc.) |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |
| Versioning |  Yes Yes |  Yes Yes |  No No |
 How to Use AWS Secrets Manager
How to Use AWS Secrets Manager
 Creating a Secret Using AWS CLI
Creating a Secret Using AWS CLI
aws secretsmanager create-secret \
--name MySecret \
--secret-string '{"username":"admin", "password":"mypassword"}' \
--region us-east-1
 Retrieving a Secret
Retrieving a Secret
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id MySecret --region us-east-1
 Updating a Secret
Updating a Secret
aws secretsmanager put-secret-value \
--secret-id MySecret \
--secret-string '{"username":"admin", "password":"newpassword"}' \
--region us-east-1
 Deleting a Secret
Deleting a Secret
aws secretsmanager delete-secret --secret-id MySecret --force-delete-without-recovery
 Using AWS Secrets Manager in Terraform
Using AWS Secrets Manager in Terraform
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret" "example" {
name = "my-secret"
}
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "example" {
secret_id = aws_secretsmanager_secret.example.id
secret_string = jsonencode({username = "admin", password = "mypassword"})
}
 Common Use Cases
Common Use Cases





Secrets Manager using Kubernetes
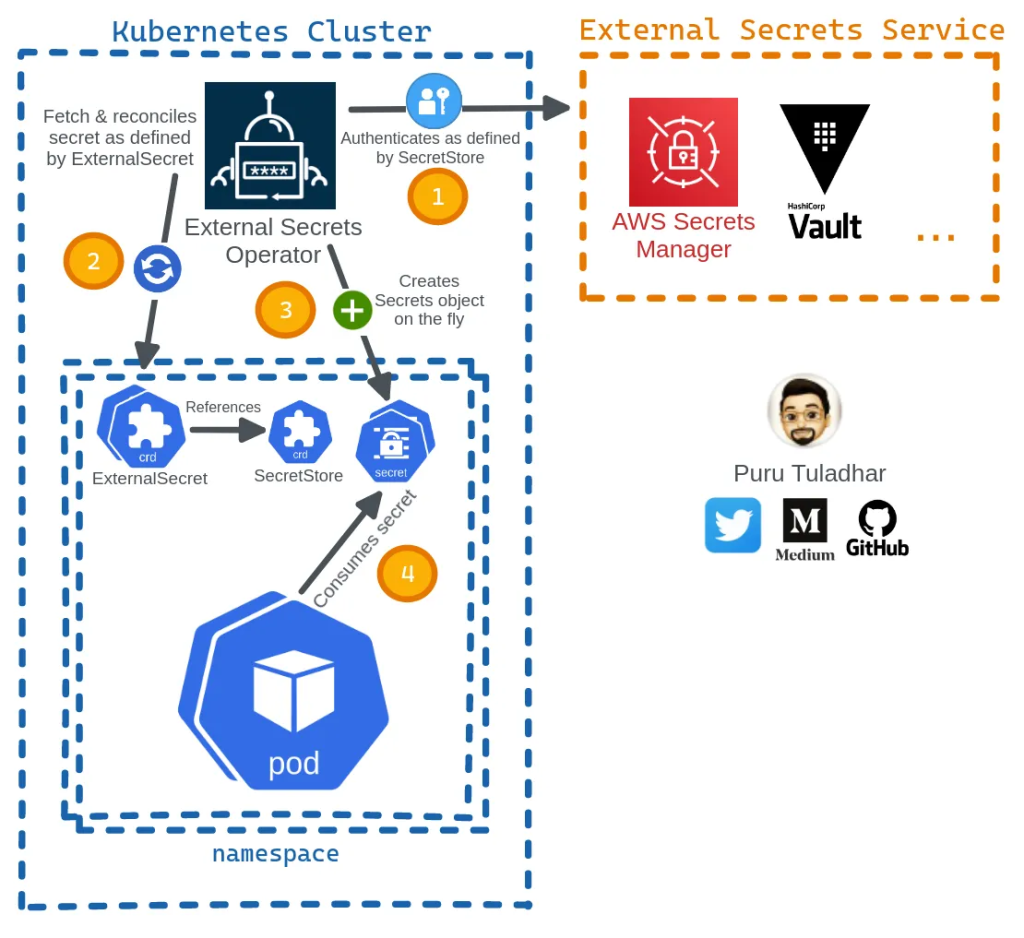
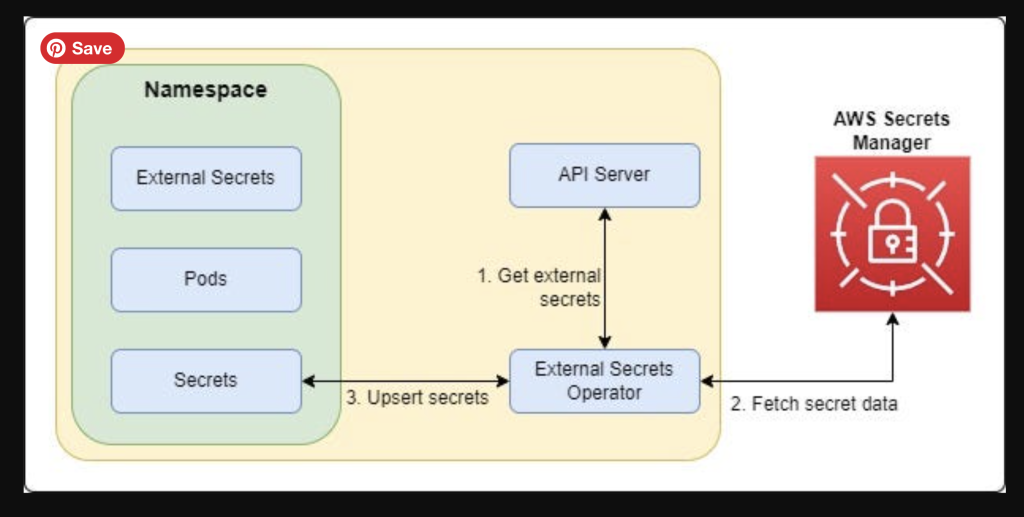
Secret Types in AWS Secrets Manager
AWS Secrets Manager supports storing various types of secrets based on use cases such as database credentials, API keys, OAuth tokens, encryption keys, and custom application secrets. Below are the most common secret types:
 Summary Table: AWS Secrets Manager Secret Types
Summary Table: AWS Secrets Manager Secret Types
| Secret Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| AWS RDS Credentials | Store database usernames and passwords securely. |
| API Keys & Tokens | Store API authentication tokens securely. |
| SSH Keys | Store private SSH keys for authentication. |
| Encryption Keys & Certs | Store SSL certificates and encryption keys securely. |
| JSON Configuration | Store app configurations like database connection details. |
| AWS IAM Access Keys | Store AWS access keys securely (though IAM roles are preferred). |
| Kubernetes Secrets | Store Kubernetes API authentication tokens securely. |
| Custom Application Secrets | Store other sensitive app secrets. |
 1. AWS RDS Database Credentials
1. AWS RDS Database Credentials
- Use Case: Store RDS credentials securely and allow automatic rotation.
- Supported Databases:
- Amazon RDS: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server
- Amazon Aurora (MySQL & PostgreSQL)
- Example JSON Format:
{ "username": "admin", "password": "mypassword" } - Terraform Example:
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret" "db_secret" { name = "my-db-secret" } resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "db_secret_version" { secret_id = aws_secretsmanager_secret.db_secret.id secret_string = jsonencode({username = "admin", password = "mypassword"}) }
 2. API Keys & Tokens
2. API Keys & Tokens
- Use Case: Store third-party API keys, OAuth tokens, and application credentials securely.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "api_key": "1234567890abcdef", "api_secret": "abcdef1234567890" } - AWS CLI Example:
aws secretsmanager create-secret --name MyAPIKey \ --secret-string '{"api_key":"1234567890abcdef","api_secret":"abcdef1234567890"}'
 3. SSH Keys & Private Keys
3. SSH Keys & Private Keys
- Use Case: Store SSH private keys used for server authentication.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "private_key": "-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEpQIBAAKCAQE...\n-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----" } - Retrieving the Secret in CLI:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id MySSHKey
 4. Encryption Keys & Certificates
4. Encryption Keys & Certificates
- Use Case: Store SSL/TLS certificates or encryption keys securely.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "certificate": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nMIIBIjANBgkqh...\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----", "private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nMIIEvQIBADANBg...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----" } - Terraform Example:
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret" "ssl_secret" { name = "my-ssl-cert" } resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "ssl_secret_version" { secret_id = aws_secretsmanager_secret.ssl_secret.id secret_string = jsonencode({certificate = "CERT_HERE", private_key = "KEY_HERE"}) }
 5. JSON Configuration Data
5. JSON Configuration Data
- Use Case: Store application config settings like database connection details, email server settings, etc.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "db_host": "mydb.example.com", "db_port": 3306, "email_server": "smtp.example.com" } - AWS CLI Example:
aws secretsmanager create-secret --name MyAppConfig \ --secret-string '{"db_host":"mydb.example.com","db_port":3306,"email_server":"smtp.example.com"}'
 6. AWS IAM Access Keys
6. AWS IAM Access Keys
- Use Case: Store AWS IAM user access keys securely.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "aws_access_key_id": "AKIAXXXEXAMPLE", "aws_secret_access_key": "wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY" } - Best Practice: Rotate IAM keys automatically and grant access via IAM roles instead.
 7. Kubernetes Secrets
7. Kubernetes Secrets
- Use Case: Store Kubernetes cluster API tokens securely for authentication.
- Example JSON Format:
{ "kube_api_server": "https://k8s.example.com", "kube_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1Ni..." }
 8. Custom Application Secrets
8. Custom Application Secrets
- Use Case: Store any sensitive data used by applications (e.g., session tokens, encryption keys, auth tokens).
- Example JSON Format:
{ "app_secret": "super_secure_value", "app_id": "my-app" } - Retrieving the Secret in Python (Boto3 SDK):
import boto3 client = boto3.client('secretsmanager') response = client.get_secret_value(SecretId='my-app-secret') print(response['SecretString'])
 Best Practices for Managing Secrets in AWS Secrets Manager
Best Practices for Managing Secrets in AWS Secrets Manager





Would you like a step-by-step guide on implementing AWS Secrets Manager in an application?
Comparison: AWS Secrets Manager vs. AWS SSM Parameter Store vs. AWS KMS
AWS provides three services for managing secrets and sensitive data: AWS Secrets Manager, AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Parameter Store, and AWS Key Management Service (KMS). Each service has different features, use cases, and pricing models.
AWS Secrets Manager vs. AWS SSM Parameter Store vs. AWS KMS
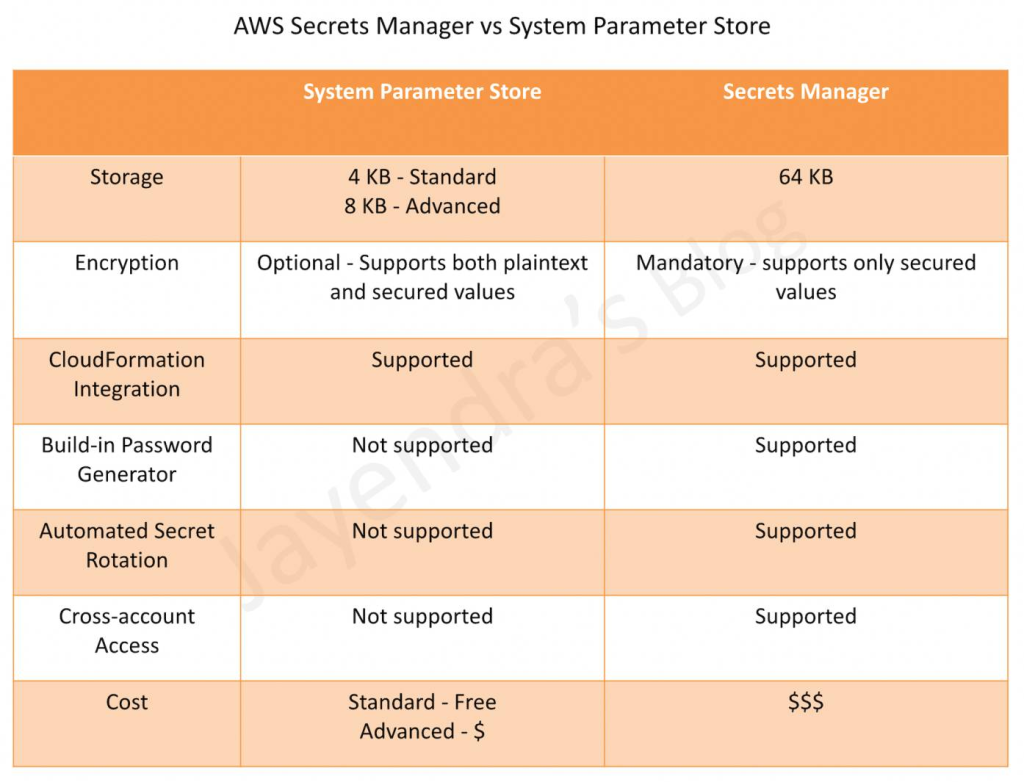
| Feature | AWS Secrets Manager | AWS SSM Parameter Store | AWS KMS (Key Management Service) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Securely store, manage, and rotate secrets like passwords, API keys, and DB credentials. | Store plaintext or encrypted configuration values & secrets. | Manage and encrypt/decrypt encryption keys. |
| Secret Types | API keys, database credentials, passwords, OAuth tokens, and certificates. | Any text-based parameter (config settings, secrets, database URLs). | Encryption keys for data, S3, EBS, databases. |
| Secret Encryption | Encrypted using AWS KMS (AES-256) by default. | Can be encrypted using AWS KMS (optional). | Uses AWS KMS for encryption key storage. |
| Automated Secret Rotation |  Yes (for RDS, Aurora, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) Yes (for RDS, Aurora, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) |  No (manual rotation required). No (manual rotation required). |  No (manages encryption keys, not secrets). No (manages encryption keys, not secrets). |
| API Access | AWS SDK, CLI, IAM policies, and Lambda integration. | AWS SDK, CLI, IAM policies. | AWS SDK, CLI, IAM, integrated into S3, RDS, EBS, DynamoDB. |
| IAM Access Control | Fine-grained access via IAM roles. | Fine-grained access via IAM roles. | Highly restrictive access via IAM policies. |
| Versioning |  Yes (Secret versioning is supported). Yes (Secret versioning is supported). |  Yes (Parameter versioning is supported). Yes (Parameter versioning is supported). |  No (Only key rotation, no versioning). No (Only key rotation, no versioning). |
| Multi-Region Support |  Yes (Automatic replication across AWS regions). Yes (Automatic replication across AWS regions). |  Yes (Can store multi-region values). Yes (Can store multi-region values). |  Yes (Can replicate keys across AWS regions). Yes (Can replicate keys across AWS regions). |
| Logging & Auditing | AWS CloudTrail logs secret access. | AWS CloudTrail logs parameter access. | AWS CloudTrail & CloudWatch logs key usage. |
| Pricing | $0.40 per secret per month + $0.05 per 10,000 API calls. | Standard Parameters: Free; Advanced Parameters: $0.05 per parameter per month. | $1 per key per month + $0.03 per 10,000 API calls. |
| Best Use Case | Secrets rotation & high security (RDS, API keys, passwords). | Storing config settings & parameters (without rotation). | Encrypting sensitive data & managing encryption keys. |
 1. AWS Secrets Manager
1. AWS Secrets Manager
 When to Use AWS Secrets Manager?
When to Use AWS Secrets Manager?
- You need automatic secret rotation (for databases, API keys, etc.).
- You need fine-grained access control to manage who can access secrets.
- You require audit logs & versioning to track secret changes.
 Pros
Pros




 Cons
Cons


 2. AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Parameter Store
2. AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Parameter Store
 When to Use AWS SSM Parameter Store?
When to Use AWS SSM Parameter Store?
- You need free storage for configuration parameters.
- You want to store encrypted secrets with basic IAM control.
- You don’t need automatic secret rotation.
 Pros
Pros



 Cons
Cons


 3. AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
3. AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
 When to Use AWS KMS?
When to Use AWS KMS?
- You need to encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- You need secure key management for S3, RDS, EBS, DynamoDB, etc.
- You require fine-grained key access control.
 Pros
Pros



 Cons
Cons


 Choosing the Right AWS Secret Management Service
Choosing the Right AWS Secret Management Service
| Use Case | Best AWS Service |
|---|---|
| Securely storing and rotating database credentials & API keys | AWS Secrets Manager |
| Storing application configuration settings & non-rotated secrets | AWS SSM Parameter Store |
| Encrypting sensitive data in S3, EBS, RDS, Lambda | AWS KMS |
| Low-cost, simple secret storage | AWS SSM Parameter Store (Standard) |
| Fine-grained access control & audit logging | AWS Secrets Manager or KMS |
 Pricing Comparison
Pricing Comparison
| Service | Cost |
|---|---|
| AWS Secrets Manager | $0.40 per secret per month + $0.05 per 10,000 API calls |
| AWS SSM Parameter Store (Standard) | Free |
| AWS SSM Parameter Store (Advanced) | $0.05 per parameter per month |
| AWS KMS | $1 per key per month + $0.03 per 10,000 API calls |
 Conclusion: Which One Should You Use?
Conclusion: Which One Should You Use?
- Use AWS Secrets Manager
if you need automated secret rotation, fine-grained IAM access control, and audit logs.
- Use AWS SSM Parameter Store
if you need a cost-effective way to store configuration parameters and static secrets.
- Use AWS KMS
if you need to manage encryption keys for AWS services like S3, RDS, EBS, and DynamoDB.
 Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts



I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND
 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
