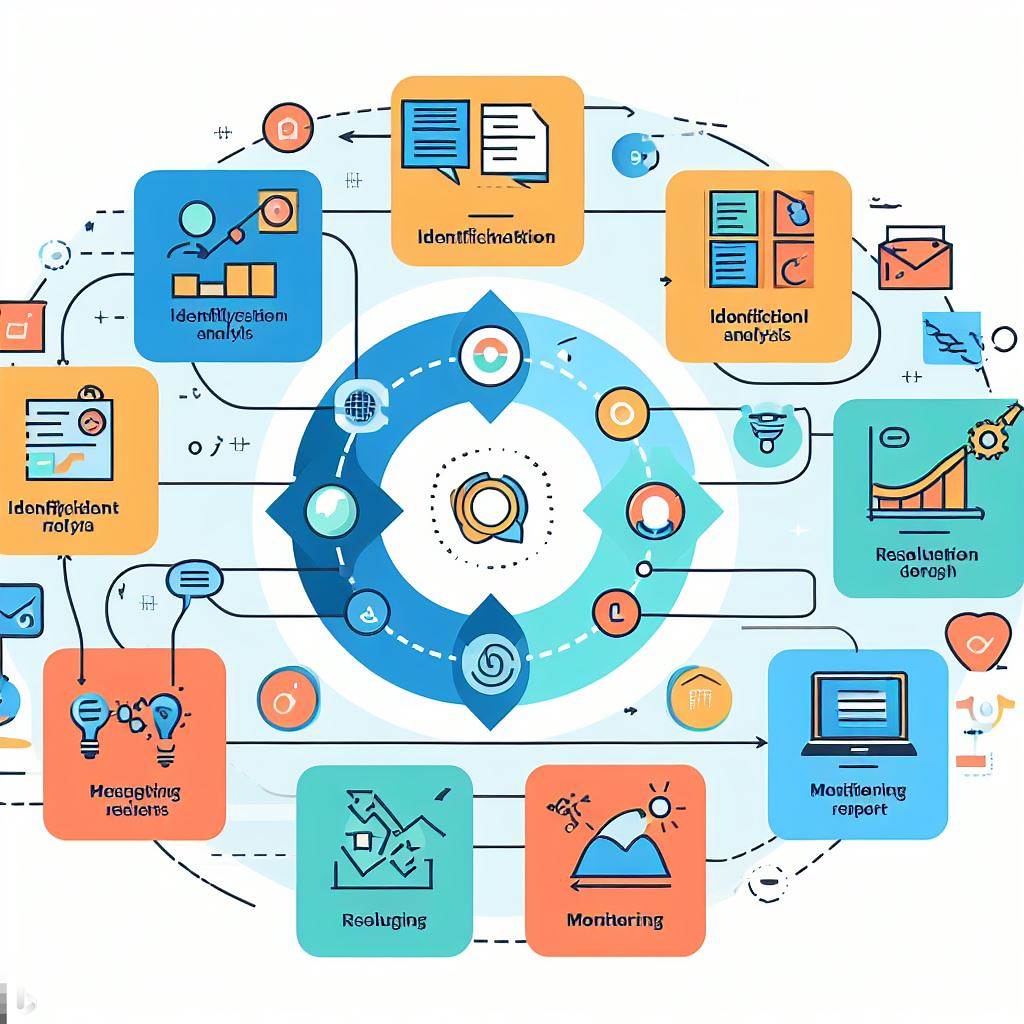
What is Problem management?
Problem management in terms of an organization is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and resolving the underlying causes of problems. It is a proactive process that helps organizations to prevent problems from recurring and to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their operations.
Problem management is typically seen as a key component of IT service management (ITSM), but it is also applicable to other areas of the organization, such as customer service, product development, and manufacturing.
The problem management process typically involves the following steps:
- Problem identification: Problems can be identified through a variety of mechanisms, such as incident reports, customer complaints, and employee feedback.
- Problem categorization and prioritization: Once a problem has been identified, it needs to be categorized and prioritized. This will help to ensure that the most important problems are addressed first.
- Problem investigation and analysis: The next step is to investigate and analyze the problem to determine its root cause. This may involve gathering data, interviewing stakeholders, and conducting root cause analysis (RCA) techniques.
- Problem resolution: Once the root cause of the problem has been identified, the next step is to develop and implement a solution to resolve the problem. This may involve making changes to processes, procedures, or systems.
- Problem closure: Once the problem has been resolved, it needs to be closed out. This involves documenting the solution and verifying that the problem has been resolved.
Types of Problem in Oranization to Manage?
Organizations encounter a wide range of problems and challenges that require effective management. These problems can vary in complexity, scope, and impact. Here are some common types of problems that organizations often need to manage:
- Operational Problems:
- Efficiency Issues: Challenges related to inefficient processes, workflow bottlenecks, or resource allocation problems.
- Quality Control: Problems related to maintaining consistent product or service quality.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Issues with procurement, inventory management, and supply chain disruptions.
- Financial Problems:
- Budgeting and Cost Control: Challenges in managing budgets, controlling costs, and ensuring financial stability.
- Revenue Generation: Difficulties in achieving revenue targets or expanding market share.
- Cash Flow Management: Issues related to cash flow, liquidity, and managing working capital.
- Human Resources and Personnel Issues:
- Employee Relations: Problems related to workplace conflicts, morale, and employee engagement.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: Challenges in recruiting, retaining, and developing a skilled workforce.
- Workplace Diversity and Inclusion: Issues related to fostering diversity and creating an inclusive workplace.
- Strategic Challenges:
- Market Competition: Problems related to market changes, competitive pressures, and industry disruptions.
- Strategic Planning: Challenges in defining and executing long-term strategies.
- Business Expansion: Issues associated with entering new markets, mergers, acquisitions, or diversification.
- Technology and IT Challenges:
- Cybersecurity: Problems related to data breaches, hacking, and IT security vulnerabilities.
- Legacy Systems: Challenges in upgrading or replacing outdated technology systems.
- Digital Transformation: Issues associated with adopting new technologies and digital strategies.
- Compliance and Regulatory Issues:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Problems related to adhering to industry-specific regulations and compliance standards.
- Ethical and Social Responsibility: Challenges in meeting ethical and social responsibility expectations.
- Customer Relations and Service Problems:
- Customer Satisfaction: Issues related to customer complaints, feedback, and service quality.
- Product or Service Defects: Challenges in managing and rectifying product defects or service failures.
- Change Management Challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Problems related to employee resistance when implementing organizational changes.
- Change Fatigue: Difficulties in managing multiple concurrent changes without overwhelming employees.
- Environmental and Sustainability Issues:
- Environmental Impact: Challenges related to environmental sustainability, waste reduction, and eco-friendly practices.
- Resource Conservation: Problems related to the responsible use of resources and energy efficiency.
- Crisis and Risk Management:
- Risk Mitigation: Challenges in identifying, assessing, and mitigating various risks, including financial, operational, and reputational.
- Crisis Response: Issues associated with managing crises such as natural disasters, public relations crises, or cybersecurity incidents.
- Ethical and Cultural Challenges:
- Organizational Culture: Problems related to aligning organizational culture with values and objectives.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Challenges in addressing ethical issues or dilemmas within the organization.
- Health and Safety Concerns:
- Workplace Safety: Problems associated with ensuring a safe and healthy work environment for employees.
Problem Workflow in Software Company
A problem workflow in a software company is the process by which problems are identified, investigated, resolved, and closed out. It is typically a collaborative process that involves multiple stakeholders, such as product managers, engineers, and support staff.
The following is a high-level overview of a common problem workflow in a software company:
- Problem identification: A problem can be identified through a variety of mechanisms, such as user feedback, bug reports, and performance monitoring. Once a problem has been identified, it is important to document it clearly and concisely.
- Problem triage: Once a problem has been identified, it needs to be triaged to determine its severity and impact. This will help to ensure that the most important problems are addressed first.
- Problem investigation: The next step is to investigate the problem to determine its root cause. This may involve gathering data, interviewing stakeholders, and debugging the code.
- Problem resolution: Once the root cause of the problem has been identified, the next step is to develop and implement a solution to resolve the problem. This may involve fixing bugs, changing the design of the software, or improving the documentation.
- Problem verification: Once the solution has been implemented, it is important to verify that the problem has been resolved. This may involve testing the software and gathering feedback from users.
- Problem closure: Once the problem has been resolved and verified, it needs to be closed out. This involves documenting the solution and updating the problem tracker.

Feature of Problem Management Software
Problem management software is designed to help organizations identify, track, manage, and resolve issues or problems efficiently and systematically. These tools offer a range of features to streamline the problem-solving process. Here are common features you can expect in problem management software:
- Ticketing System:
- Create and manage problem tickets or issues.
- Assign tickets to specific team members or groups.
- Set priorities and due dates for problem resolution.
- Problem Logging:
- Record detailed information about the problem, including its description, severity, and affected components.
- Attach files, documents, or screenshots to provide additional context.
- Problem Classification:
- Categorize problems based on type, department, or impact.
- Assign problem attributes to facilitate sorting and filtering.
- Workflow Automation:
- Automate the routing of problem tickets to the appropriate teams or individuals.
- Create predefined workflows for common types of problems.
- Collaboration Tools:
- Enable real-time collaboration among team members working on problem resolution.
- Allow for comments, discussions, and notifications within the software.
- Integration:
- Integrate with other IT service management (ITSM) tools, such as incident management, change management, and asset management systems.
- Connect to communication tools like email and messaging platforms.
- Reporting and Analytics:
- Generate reports and dashboards to track problem resolution progress.
- Analyze historical data to identify recurring problems and trends.
- Knowledge Base:
- Create and maintain a knowledge base of known problems and their solutions.
- Provide self-service options for users to find solutions to common issues.
- Problem Prioritization:
- Prioritize problems based on their impact on the organization, urgency, or business-criticality.
- Use predefined criteria or custom rules to assign priority levels.
- Root Cause Analysis:
- Facilitate the investigation and identification of root causes for problems.
- Link related incidents, changes, and known errors to problem records.
- Change Management Integration:
- Integrate with change management processes to ensure that problems are addressed during the change planning and execution phases.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management:
- Set SLAs for problem resolution and track adherence to these agreements.
- Automate notifications and escalations for SLA breaches.
- Auditing and Compliance:
- Maintain an audit trail of all problem-related activities and changes.
- Support compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards.
- User Self-Service Portal:
- Provide a self-service portal where users can report problems, check the status of their tickets, and access relevant knowledge articles.
- Customization and Configuration:
- Customize forms, fields, and workflows to align with specific organizational needs.
- Define business rules and triggers for automated actions.
- Mobile Accessibility:
- Offer mobile apps or responsive web interfaces to allow users and IT teams to access and manage problems on the go.
- User and Role Management:
- Define user roles and permissions to control access to sensitive problem data.
- Ensure proper segregation of duties.
- Notification and Alerts:
- Send automated notifications and alerts to relevant stakeholders when problem status changes or milestones are reached.
- SLA and KPI Tracking:
- Monitor and report on key performance indicators (KPIs) related to problem management, such as time to resolution and recurrence rates.
- Scalability:
- Accommodate the growth and changing needs of the organization as it scales.
Best software of Problem management?

The best software for problem management depends on the specific needs of your organization. However, some of the most popular and highly-rated problem management software solutions include:
Jira Service Management (JSM):
- JSM is a cloud-based ITSM platform that includes a comprehensive set of tools for problem management, including incident management, change management, and asset management. JSM is a good choice for organizations of all sizes, and it is especially well-suited for organizations that are already using other Jira products.
BMC Helix ITSM:
- BMC Helix ITSM is a comprehensive ITSM platform that offers a variety of features for problem management, including incident management, change management, and knowledge management. BMC Helix ITSM is a good choice for organizations of all sizes, and it is especially well-suited for organizations that need a highly customizable solution.
Ivanti Service Manager
- Ivanti Service Manager is an ITSM platform that offers a variety of features for problem management, including root cause analysis, knowledge management, and reporting. Ivanti Service Manager is a good choice for organizations of all sizes, and it is especially well-suited for organizations in the healthcare and financial services industries.
Freshservice
- Freshservice is a cloud-based ITSM platform that offers a variety of features for problem management, including incident management, change management, and asset management. Freshservice is a good choice for small and medium-sized businesses, and it is especially well-suited for organizations that are looking for an affordable and easy-to-use solution.
Wizbrand
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, adept problem management is a cornerstone of success. Enter Wizbrand, a powerful and versatile problem management software that transcends conventional solutions. Wizbrand is not just about identifying and resolving issues; it’s about elevating your organization’s capacity to adapt, learn, and grow.
What sets Wizbrand apart is its unwavering commitment to simplicity and adaptability. With a user-friendly interface that caters to both technical and non-technical users, Wizbrand ensures that problem management is a seamless and collaborative endeavor. It empowers teams to capture, classify, and prioritize issues swiftly, making way for prompt and effective resolutions.
Moreover, Wizbrand doesn’t merely provide a static solution. It evolves with your organization, scaling to meet the evolving demands of your problem management needs. Whether you’re a small business tackling everyday issues or a large enterprise addressing complex challenges, Wizbrand is your trusted partner in the quest for efficient and effective problem resolution.

With a rich array of features, including ticketing systems, automation tools, reporting and analytics, and knowledge base support, Wizbrand streamlines your problem management workflow. It allows you to focus on what matters most—resolving problems and ensuring the continuity of your operations.
In a world where every issue is an opportunity for improvement, Wizbrand is the software solution that transforms obstacles into stepping stones. Experience the difference—unlock efficient problem resolution, streamline operations, and drive continuous improvement with Wizbrand by your side.
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
