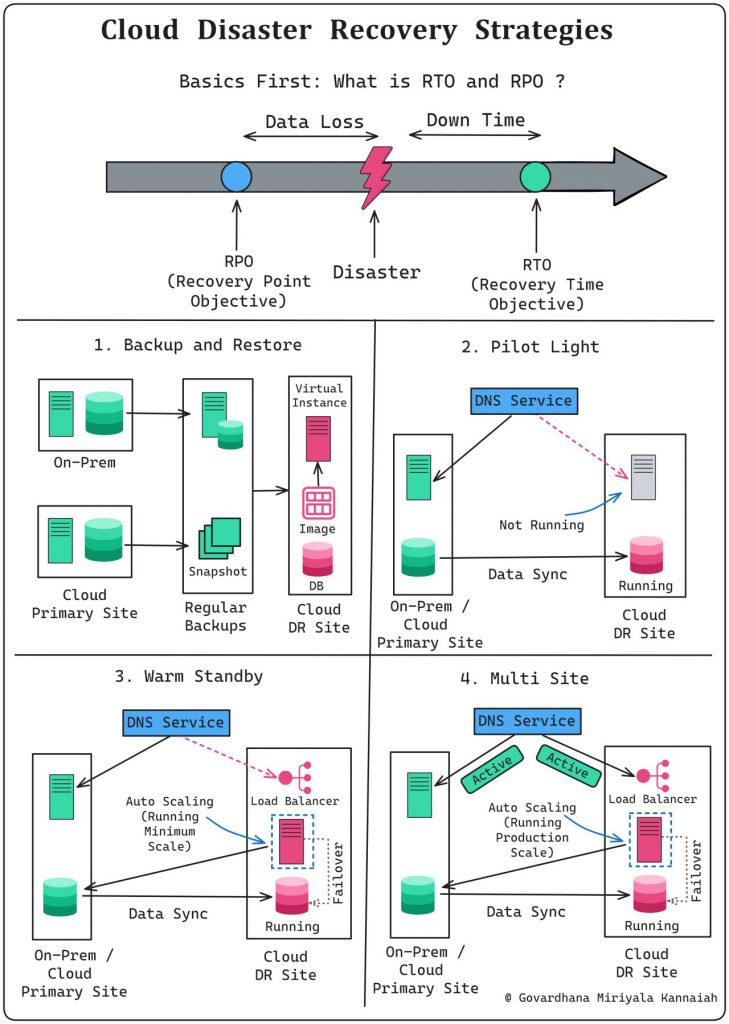
Any DR strategy starts with finalizing:
𝟭. 𝗥𝗧𝗢 (𝗥𝗲𝗰𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝗧𝗶𝗺𝗲 𝗢𝗯𝗷𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲):
How much downtime one can accept ?
𝟮. 𝗥𝗣𝗢 (𝗥𝗲𝗰𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝗣𝗼𝗶𝗻𝘁 𝗢𝗯𝗷𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲):
How much data loss one can accept ?
Disaster Recovery Strategies:
𝟭. 𝗕𝗮𝗰𝗸𝘂𝗽 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗼𝗿𝗲:
Creating copies of data and systems periodically to be used for recovery in case of a disaster
Typical,
𝘙𝘛𝘖: Several hours to days
𝘙𝘗𝘖: Can vary from several hours to the last successful backup
𝟮. 𝗣𝗶𝗹𝗼𝘁 𝗟𝗶𝗴𝗵𝘁:
Maintaining essential components in a standby state to quickly scale up the infrastructure during a disaster
Typical,
𝘙𝘛𝘖: Mins to a few hours
𝘙𝘗𝘖: How frequently data is synchronized
𝟯. 𝗪𝗮𝗿𝗺 𝗦𝘁𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗯𝘆:
Preparing a partially operational environment with up-to-date data to minimize downtime during recovery
Typical,
𝘙𝘛𝘖: Mins to a few hours
𝘙𝘗𝘖: Within the last few minutes or hours
𝟰. 𝗛𝗼𝘁 𝗦𝗶𝘁𝗲 / 𝗠𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗶 𝗦𝗶𝘁𝗲:
Running a fully redundant, active production environment in parallel with the primary system, ensuring continuous business operations
Typical,
𝘙𝘛𝘖: Near-zero or a few minutes
𝘙𝘗𝘖: Very minimal, often within the last few seconds
Disaster recovery (DR) strategies in the cloud aim to ensure the availability, integrity, and resilience of data and applications in the event of a disaster. Cloud-based disaster recovery offers several advantages, including flexibility, scalability, cost-efficiency, and reduced maintenance. Here are some common cloud disaster recovery strategies:
- Backup and Restore: This is the most basic and commonly used strategy. It involves regularly backing up critical data and applications to a separate location (cloud storage) and restoring them when needed. Cloud storage solutions offer reliable and scalable options for storing backup data.
- Pilot Light: In this strategy, a minimal version of the production environment is continuously running in the cloud. When a disaster occurs, additional resources and data are quickly scaled up to restore full functionality. This approach allows for faster recovery times but keeps costs lower during normal operations.
- Warm Standby: In a warm standby approach, a partially functional replica of the production environment is pre-provisioned in the cloud. This standby environment is kept up-to-date with data and configurations, ready to be fully activated in case of a disaster. It provides faster recovery times than the pilot light approach but is more expensive as resources are partially allocated.
- Hot Standby: A hot standby strategy involves maintaining a fully replicated and active version of the production environment in the cloud at all times. This approach ensures the highest level of availability and minimal downtime during a disaster. However, it is the most expensive option since you are paying for active resources continuously.
- Cloud-to-Cloud Disaster Recovery: This approach involves replicating data and applications from one cloud provider to another. It provides an extra layer of redundancy and ensures that even if one cloud provider experiences an outage, services can still be restored from the backup in the secondary cloud.
- Hybrid Cloud Disaster Recovery: In this strategy, critical workloads are distributed across both on-premises infrastructure and cloud infrastructure. It allows organizations to maintain control over sensitive data on-premises while leveraging the cloud for additional scalability and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): DRaaS is a comprehensive disaster recovery solution provided by a third-party cloud service provider. It offers automated backup, failover, and failback processes, ensuring minimal downtime and simplified management. DRaaS solutions are often scalable and can be tailored to the specific needs of businesses.
When implementing a cloud disaster recovery strategy, it’s essential to consider factors such as Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), as they determine how much data loss and downtime are acceptable during a disaster. The choice of strategy depends on the organization’s budget, the criticality of applications, and the desired level of resilience. Regular testing and updates to the disaster recovery plan are crucial to ensure its effectiveness when needed.
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
