Database Monitoring provides deep visibility into your Postgres databases by exposing query metrics, query samples, explain plans, database states, failovers, and events.
The Agent collects telemetry directly from the database by logging in as a read-only user. Do the following setup to enable Database Monitoring with your Postgres database:
Step 1 – Install Datadog Agent
Step 2 – Install and Configure postgresql
Step 3 – Prepare Postgres & Configurations
To get started with the PostgreSQL integration, create a read-only datadog user with proper access to your PostgreSQL server. Start psql on your PostgreSQL database
Connect to the chosen database as a superuser (or another user with sufficient permissions). For example, if your chosen database is postgres, connect as the postgres user using psql by running:
$ psql -h mydb.example.com -d postgres -U postgres
For PostgreSQL version 10 and above, run:
create user datadog with password '<PASSWORD>';
grant SELECT ON pg_stat_database to datadog;
# Create the following schema in every database:
CREATE SCHEMA datadog;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA datadog TO datadog;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO datadog;
GRANT pg_monitor TO datadog;
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_statements;
When generating custom metrics that require querying additional tables, you may need to grant the SELECT permission on those tables to the datadog user.
grant SELECT on <TABLE_NAME> to datadogTo verify the permissions are correct, run the following command:
psql -h localhost -U datadog postgres -c \
"select * from pg_stat_database LIMIT(1);" \
&& echo -e "\e[0;32mPostgres connection - OK\e[0m" \
|| echo -e "\e[0;31mCannot connect to Postgres\e[0m"
psql -h localhost -U datadog postgres -A \
-c "select * from pg_stat_database limit 1;" \
&& echo -e "\e[0;32mPostgres connection - OK\e[0m" \
|| echo -e "\e[0;31mCannot connect to Postgres\e[0m"
psql -h localhost -U datadog postgres -A \
-c "select * from pg_stat_activity limit 1;" \
&& echo -e "\e[0;32mPostgres pg_stat_activity read OK\e[0m" \
|| echo -e "\e[0;31mCannot read from pg_stat_activity\e[0m"
psql -h localhost -U datadog postgres -A \
-c "select * from pg_stat_statements limit 1;" \
&& echo -e "\e[0;32mPostgres pg_stat_statements read OK\e[0m" \
|| echo -e "\e[0;31mCannot read from pg_stat_statements\e[0m"
When it prompts for a password, enter the one used in the first command.Note: When generating custom metrics that require querying additional tables, you may need to grant the SELECT permission on those tables to the datadog user. Example: grant SELECT on <TABLE_NAME> to datadog;. Check the FAQ section for more information.
Step 4 – Host configure to check for an Agent for Metric collection
- Edit the postgres.d/conf.yaml file to point to your host / port and set the masters to monitor.
- Restart the Agent.
init_config:
instances:
- dbm: true
host: localhost
port: 5432
username: datadog
password: '<PASSWORD>'
## Optional: Connect to a different database if needed for `custom_queries`
# dbname: '<DB_NAME>'init_config:
instances:
## @param host - string - required
## The hostname to connect to.
## NOTE: Even if the server name is "localhost", the agent connects to
## PostgreSQL using TCP/IP, unless you also provide a value for the sock key.
#
- host: localhost
## @param port - integer - required
## Port to use when connecting to PostgreSQL.
#
port: 5432
## @param user - string - required
## Datadog Username created to connect to PostgreSQL.
#
username: datadog
## @param pass - string - required
## Password associated with the Datadog user.
#
password: "<PASSWORD>"
## @param dbname - string - optional - default: postgres
## Name of the PostgresSQL database to monitor.
## Note: If omitted, the default system postgres database is queried.
#
dbname: "<DB_NAME>"
# @param disable_generic_tags - boolean - optional - default: false
# The integration will stop sending server tag as is reduntant with host tag
disable_generic_tags: trueStep 5 – Configure Postgres settings
Configure the following parameters in the postgresql.conf file and then restart the server for the settings to take effect.
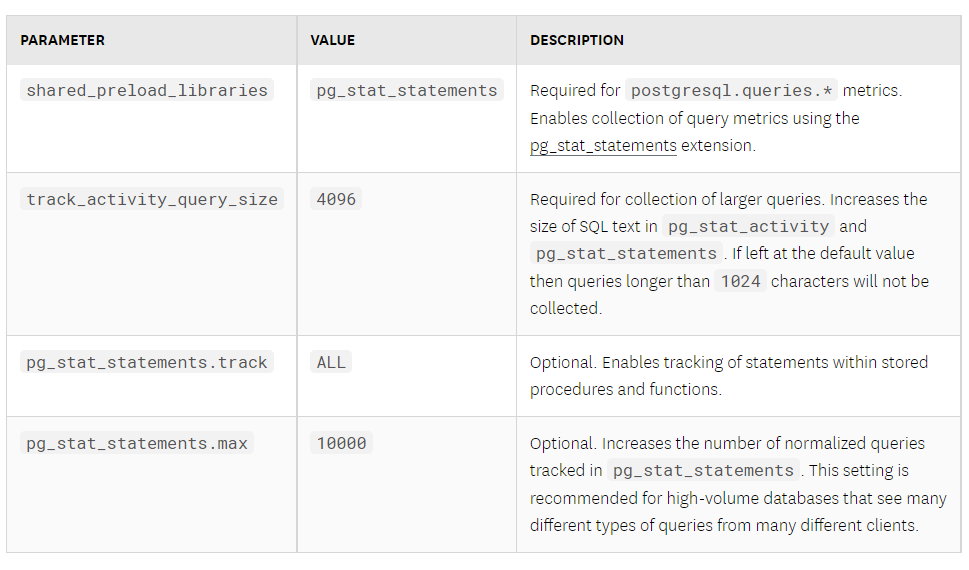
Step 6 – verify
Restart a agent Postgres
$ sudo datadog-agent status
Run the Agent’s status subcommand and look for postgres under the Checks section. Or visit the Databases page to get started!
Integrtion metrics
The following metrics will be tracked by this integration:
| Name | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| postgres.replication_delay_bytes | bytes | Deprecated please use postgresql.replication_delay_bytes instead |
| postgresql.active_queries | The number of active queries in this database. | |
| postgresql.active_waiting_queries | The number of waiting queries in this database in state active. | |
| postgresql.analyzed | The number of times this table has been manually analyzed. | |
| postgresql.autoanalyzed | The number of times this table has been analyzed by the autovacuum daemon. | |
| postgresql.autovacuumed | The number of times this table has been vacuumed by the autovacuum daemon. | |
| postgresql.before_xid_wraparound | transactions | The number of transactions that can occur until a transaction wraparound. |
| postgresql.bgwriter.buffers_alloc | The number of buffers allocated | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.buffers_backend | buffers | The number of buffers written directly by a backend. |
| postgresql.bgwriter.buffers_backend_fsync | The of times a backend had to execute its own fsync call instead of the background writer. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.buffers_checkpoint | The number of buffers written during checkpoints. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.buffers_clean | The number of buffers written by the background writer. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.checkpoints_requested | The number of requested checkpoints that were performed. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.checkpoints_timed | The number of scheduled checkpoints that were performed. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.maxwritten_clean | The number of times the background writer stopped a cleaning scan due to writing too many buffers. | |
| postgresql.bgwriter.sync_time | milliseconds | The total amount of checkpoint processing time spent synchronizing files to disk. |
| postgresql.bgwriter.write_time | milliseconds | The total amount of checkpoint processing time spent writing files to disk. |
| postgresql.buffer_hit | hits/second | The number of times disk blocks were found in the buffer cache, preventing the need to read from the database. |
| postgresql.commits | transactions/second | The number of transactions that have been committed in this database. |
| postgresql.connections | connections | The number of active connections to this database. If DBM is enabled, this metric is tagged with state, app, db and user |
| postgresql.database_size | bytes | The disk space used by this database. |
| postgresql.db.count | items | The number of available databases. |
| postgresql.dead_rows | rows | The estimated number of dead rows. |
| postgresql.deadlocks | The number of deadlocks detected in this database | |
| postgresql.disk_read | blocks/second | The number of disk blocks read in this database. |
| postgresql.function.calls | The number of calls made to a function. | |
| postgresql.heap_blocks_hit | hits/second | The number of buffer hits in this table. |
| postgresql.heap_blocks_read | blocks/second | The number of disk blocks read from this table. |
| postgresql.index_bloat | percent | The estimated percentage of index bloat. |
| postgresql.index_blocks_hit | hits/second | The number of buffer hits in all indexes on this table. |
| postgresql.index_blocks_read | blocks/second | The number of disk blocks read from all indexes on this table. |
| postgresql.index_rel_rows_fetched | rows/second | The number of live rows fetched by index scans. |
| postgresql.index_rel_scans | The overall number of index scans initiated on this table. | |
| postgresql.index_rows_fetched | rows/second | The number of live rows fetched by index scans. |
| postgresql.index_rows_read | rows/second | The number of index entries returned by scans on this index. |
| postgresql.index_scans | The number of index scans initiated on this table, tagged by index. | |
| postgresql.index_size | bytes | The total disk space used by indexes attached to the specified table. |
| postgresql.live_rows | rows | The estimated number of live rows. |
| postgresql.locks | locks | The number of locks active for this database. |
| postgresql.max_connections | connections | The maximum number of client connections allowed to this database. |
| postgresql.percent_usage_connections | fractions | The number of connections to this database as a fraction of the maximum number of allowed connections. |
| postgresql.queries.count | queries | The total query execution count per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.duration.max | nanoseconds | The age of the longest running query per user, db and app. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.duration.sum | nanoseconds | The sum of the age of all running queries per user, db and app. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.local_blks_dirtied | blocks | Total number of local blocks dirtied per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.local_blks_hit | blocks | Total number of local block cache hits per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.local_blks_read | blocks | Total number of local blocks read per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.local_blks_written | blocks | Total number of local blocks written per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.rows | rows | The total number of rows retrieved or affected per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.shared_blks_dirtied | blocks | Total number of shared blocks dirtied per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.shared_blks_hit | blocks | Total number of shared block cache hits per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.shared_blks_read | blocks | Total number of shared blocks read per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.shared_blks_written | blocks | Total number of shared blocks written per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.temp_blks_read | blocks | Total number of temp blocks read per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.temp_blks_written | blocks | Total number of temp blocks written per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.queries.time | nanoseconds | The total query execution time per query_signature, db, and user. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.replication.wal_flush_lag | seconds | Time elapsed between flushing recent WAL locally and receiving notification that this standby server has written and flushed it (but not yet applied it). This can be used to gauge the delay that synchronous_commit level on incurred while committing if this server was configured as a synchronous standby. Only available with postgresql 10 and newer. |
| postgresql.replication.wal_replay_lag | seconds | Time elapsed between flushing recent WAL locally and receiving notification that this standby server has written, flushed and applied it. This can be used to gauge the delay that synchronous_commit level remote_apply incurred while committing if this server was configured as a synchronous standby. Only available with postgresql 10 and newer. |
| postgresql.replication.wal_write_lag | seconds | Time elapsed between flushing recent WAL locally and receiving notification that this standby server has written it (but not yet flushed it or applied it). This can be used to gauge the delay that synchronous_commit level remote_write incurred while committing if this server was configured as a synchronous standby. Only available with postgresql 10 and newer. |
| postgresql.replication_delay | seconds | The current replication delay in seconds. Only available with postgresql 9.1 and newer |
| postgresql.replication_delay_bytes | bytes | The current replication delay in bytes. Only available with postgresql 9.2 and newer |
| postgresql.rollbacks | transactions/second | The number of transactions that have been rolled back in this database. |
| postgresql.rows_deleted | rows/second | The number of rows deleted by queries in this database |
| postgresql.rows_fetched | rows/second | The number of rows fetched by queries in this database |
| postgresql.rows_hot_updated | rows/second | The number of rows HOT updated, meaning no separate index update was needed. |
| postgresql.rows_inserted | rows/second | The number of rows inserted by queries in this database |
| postgresql.rows_returned | rows/second | The number of rows returned by queries in this database |
| postgresql.rows_updated | rows/second | The number of rows updated by queries in this database |
| postgresql.seq_rows_read | rows/second | The number of live rows fetched by sequential scans. |
| postgresql.seq_scans | The number of sequential scans initiated on this table. | |
| postgresql.table.count | tables | The number of user tables in this database. |
| postgresql.table_bloat | percent | The estimated percentage of table bloat. |
| postgresql.table_size | bytes | The total disk space used by the specified table. Includes TOAST, free space map, and visibility map. Excludes indexes. |
| postgresql.temp_bytes | bytes/second | The amount of data written to temporary files by queries in this database. |
| postgresql.temp_files | files/second | The number of temporary files created by queries in this database. |
| postgresql.toast_blocks_hit | hits/second | The number of buffer hits in this table’s TOAST table. |
| postgresql.toast_blocks_read | blocks/second | The number of disk blocks read from this table’s TOAST table. |
| postgresql.toast_index_blocks_hit | blocks/second | The number of buffer hits in this table’s TOAST table index. |
| postgresql.toast_index_blocks_read | blocks/second | The number of disk blocks read from this table’s TOAST table index. |
| postgresql.total_size | bytes | The total disk space used by the table, including indexes and TOAST data. |
| postgresql.transactions.duration.max | nanoseconds | The age of the longest running transaction per user, db and app. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.transactions.duration.sum | nanoseconds | The sum of the age of all running transactions per user, db and app. (DBM only) |
| postgresql.transactions.idle_in_transaction | transactions | The number of ‘idle in transaction’ transactions in this database. |
| postgresql.transactions.open | transactions | The number of open transactions in this database. |
| postgresql.vacuumed | The number of times this table has been manually vacuumed. | |
| postgresql.waiting_queries | The number of waiting queries in this database. | |
| postgresql.wal_age | seconds | The age in seconds of the oldest WAL file. |
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com

cd /etc/datadog-agent/conf.d/postgres.d/
where should this file exists postgres.d/conf.yaml?