
Before learning how to do search engine work, let us know what is a search engine?
Search Engines:
A search engine is a web-based tool that enables users to locate information on the World Wide Web. A popular example of a search engine is Google, Yahoo! and MSN search. Search engines use automated software applications that travel across the web as well as the link from page to page, site to site. Information gathered by the spider is used to create an index that is searchable by the web.
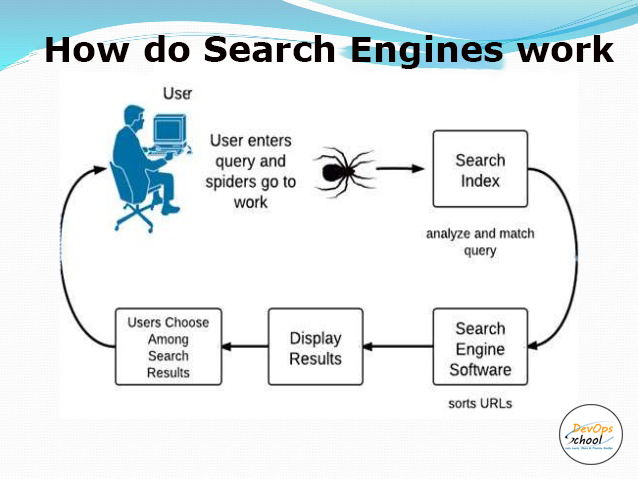
How do Search Engines work?
Each search engine uses various complex mathematical formulas to generate search results. The results of a specific query are displayed on the SERP. Search engine algorithms take the key elements of a web page, including the page title, content, and keyword density, and come up with a ranking where to place the results on the pages. The algorithm of each search engine is unique, hence a top ranking on Yahoo! Does not guarantee a major ranking on Google, and vice versa.
This means that the criteria to best optimize a site must be validated through observation, as well as trial and error – and not just once, but continuously.
A “search engine” is a number of interlinked mechanisms that work together to identify pieces of web content such as images, videos, website pages, etc. – based on the words you type in the search bar.
The Search Engines use three primary functions:
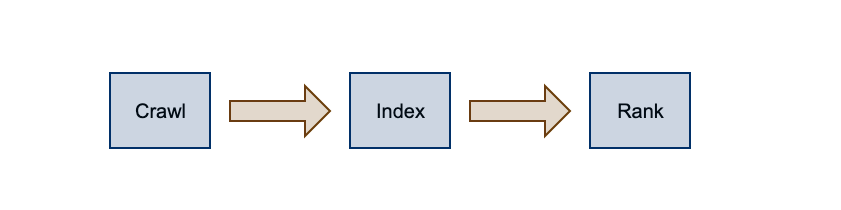
- Crawl: Search engines send out web crawlers, also known as bots or spiders, to review website content. Paying close attention to new websites and to existing content that has recently been changed, web crawlers look at data such as URLs, sitemaps, and code to discover the types of content being displayed.
- Index: After a website is crawled, search engines need to decide how to organize the information. The bot organizes this content into categories, including images, CSS and HTML, text, and keywords, etc. The indexing process occurs when they review website data for positive or negative ranking signals and store it in the correct location on their server.
- Rank: During the indexing process, search engines begin making decisions to display specific content on the results page (SERP). Rankings are accomplished by assessing several different factors based on the end user’s query for quality and relevance.
During this process to determine the value any website can potentially provide to end-user. Understanding how the algorithm works helps you create content that ranks better for each platform.
MotoShare.in provides the perfect two-wheeler for every occasion—daily commuting, weekend escapes, tourist exploration, or test-riding your dream bike. Simplify your mobility with us!

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
