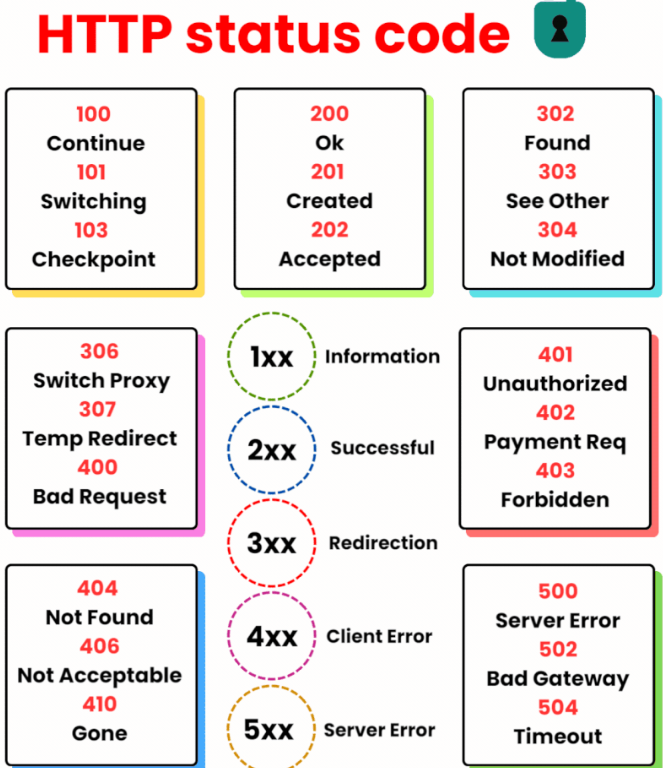
Here is a table of common HTTP status codes with their explanations:
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 100 | Continue – The server has received the request headers, and the client should proceed to send the request body. |
| 101 | Switching Protocols – The requester has asked the server to switch protocols, and the server is acknowledging that it will do so. |
| 200 | OK – The request has succeeded. The information returned with the response is dependent on the method used in the request. |
| 201 | Created – The request has been fulfilled and has resulted in one or more new resources being created. |
| 202 | Accepted – The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information – The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified response. |
| 204 | No Content – The server successfully processed the request and is not returning any content. |
| 205 | Reset Content – The server successfully processed the request, but is not returning any content, and requires that the requester reset the document view. |
| 206 | Partial Content – The server is delivering only part of the resource due to a range header sent by the client. |
| 300 | Multiple Choices – There are multiple options for the resource that the client may follow. |
| 301 | Moved Permanently – This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. |
| 302 | Found – The requested resource resides temporarily under a different URI. |
| 303 | See Other – The response to the request can be found under another URI using a GET method. |
| 304 | Not Modified – The resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers. |
| 305 | Use Proxy – The requested resource is available only through a proxy, whose address is provided in the response. |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect – In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. |
| 400 | Bad Request – The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error. |
| 401 | Unauthorized – Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. |
| 402 | Payment Required – Reserved for future use. |
| 403 | Forbidden – The request was valid, but the server is refusing action. |
| 404 | Not Found – The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed – A request method is not supported for the requested resource. |
| 406 | Not Acceptable – The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required – The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy. |
| 408 | Request Timeout – The server timed out waiting for the request. |
| 409 | Conflict – The request could not be processed because of conflict in the request, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates. |
| 410 | Gone – The resource requested is no longer available and will not be available again. |
| 411 | Length Required – The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource. |
| 412 | Precondition Failed – The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request. |
| 413 | Payload Too Large – The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. |
| 414 | URI Too Long – The URI provided was too long for the server to process. |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type – The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. |
| 416 | Range Not Satisfiable – The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. |
| 417 | Expectation Failed – The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field. |
| 418 | I’m a teapot – This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol. |
| 421 | Misdirected Request – The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response. |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity – The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors. |
| 423 | Locked – The resource that is being accessed is locked. |
| 424 | Failed Dependency – The request failed due to failure of a previous request. |
| 425 | Too Early – Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed. |
| 426 | Upgrade Required – The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.0. |
| 428 | Precondition Required – The origin server requires the request to be conditional. |
| 429 | Too Many Requests – The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. |
| 431 | Request Header Fields Too Large – The server is unwilling to process the request because its header fields are too large. |
| 451 | Unavailable For Legal Reasons – The user requests an illegal resource, such as a web page censored by a government. |
| 500 | Internal Server Error – A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable. |
| 501 | Not Implemented – The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfill the request. |
| 502 | Bad Gateway – The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable – The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout – The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server. |
| 505 | HTTP Version Not Supported – The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request. |
| 506 | Variant Also Negotiates – Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference. |
| 507 | Insufficient Storage – The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request. |
| 508 | Loop Detected – The server detected an infinite loop while processing a request. |
| 510 | Not Extended – Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfill it. |
| 511 | Network Authentication Required – The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. |
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
