There are many methods for inserting data in database through Model. See below:-
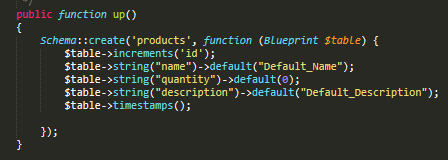
Migration is common in all methods in which we defined the table name and default value of all column’s. See below the migration code:-
Method 1: Through object.
We can insert data using Object in our controller. See the below code for help:-
| $product= new product(); | |
| $product->name="Sushant Kumar"; | |
| $product->quantity=12; | |
| $product->description="This is description"; | |
| $data = $product->save(); | |
| print_r("ID is "); | |
| print_r($product["id"]); |
Where, $project = Object.
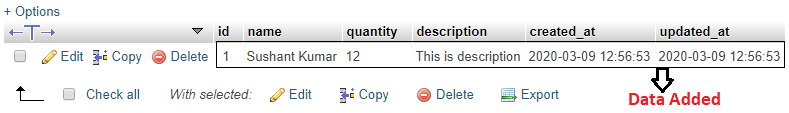
See Output below:-
Method 2: Through Controller
We can insert data by using constructor in our controller. See the below code for help:-
| $product= new product([ | |
| "name"=>"Sushant Kumar", | |
| "quantity"=>12, | |
| "description"=>"This is description"]); | |
| $data = $product->save(); | |
| print_r("ID is "); | |
| print_r($product["id"]); |
But, whenever we are inserting data by using controller then we need to use fillable or guarded property in model otherwise it returns an error.
See below how to use fillable:-
protected $fillable = [“key1″,”key2”];
Note:- We add value of key in fillable which we want to add in the database.
See below how to use guarded:-
protected $guarded = [“key1″,”key2”];
Note:- We add the value of key in guarded which we don’t want to add in the database.
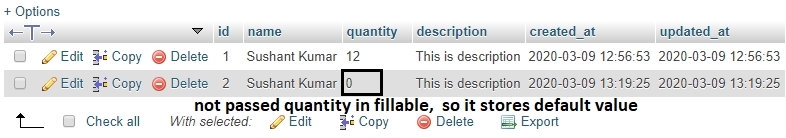
See the Output below:-
insertion by using fillable.
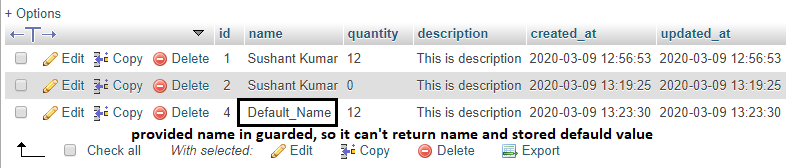
insertion by using guarded.
method 3: Through create() method
We can insert data using create() method in our controller. See the below code for help:-
| $product= product::create(["name"=>"Sushant Kumar","quantity"=>12,"description"=>"This is description"]); | |
| $data = $product->save(); | |
| print_r("ID is "); | |
| print_r($product["id"]); |
As above property, it also depends on fillable and guarded.
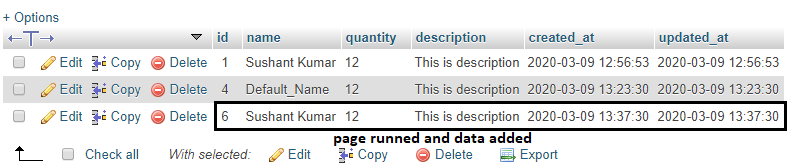
See the output below:-
With MotoShare.in, you can book a bike instantly, enjoy doorstep delivery, and ride without worries. Perfect for travelers, professionals, and adventure enthusiasts looking for a seamless mobility solution.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
 by
by 