Switches and routers are both critical components of networking infrastructure, but they serve different functions within a network. Understanding the difference between them is fundamental to grasping how networks handle data and connect devices. Here’s a comparison highlighting their primary differences:
1. Functionality:
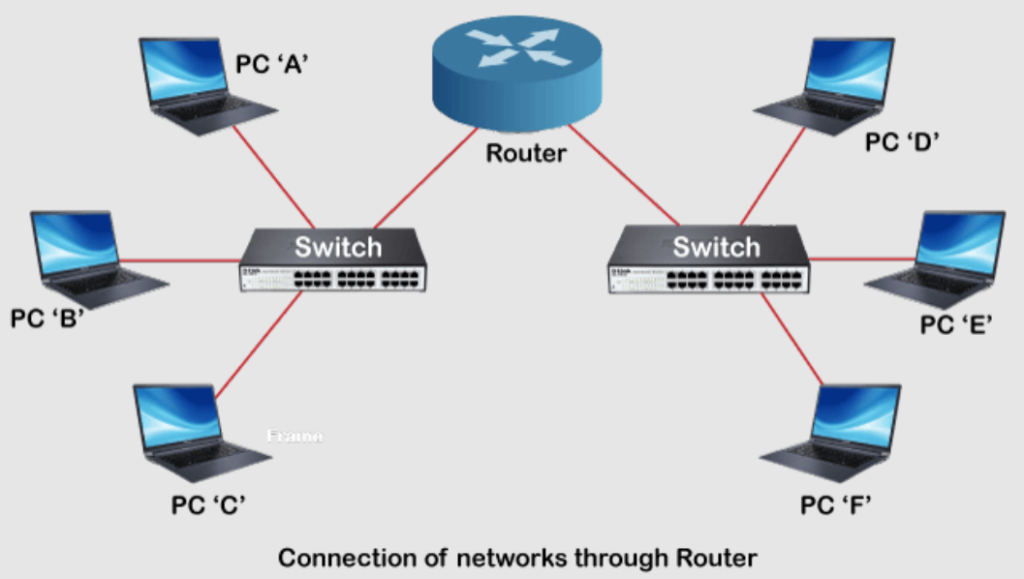
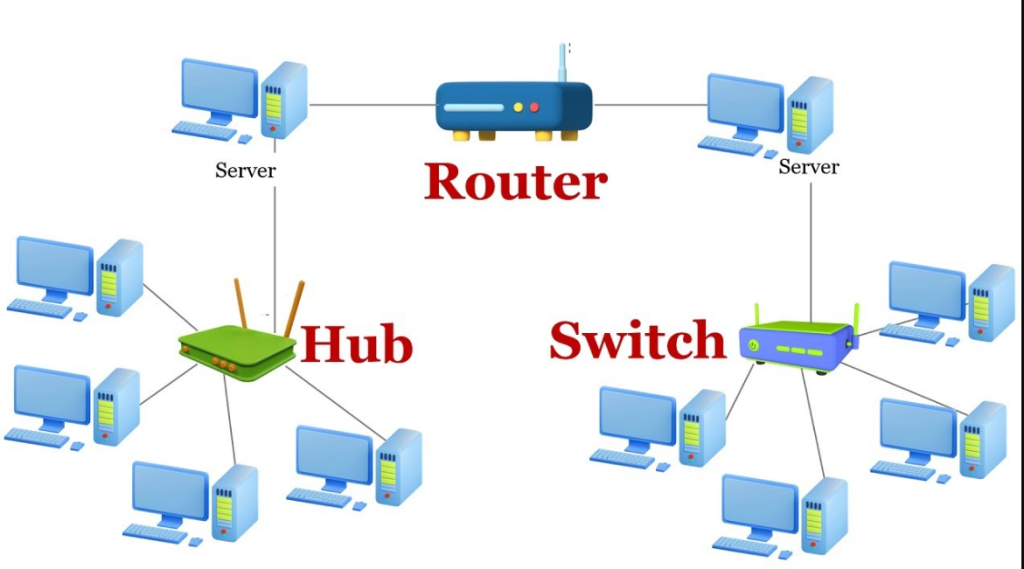
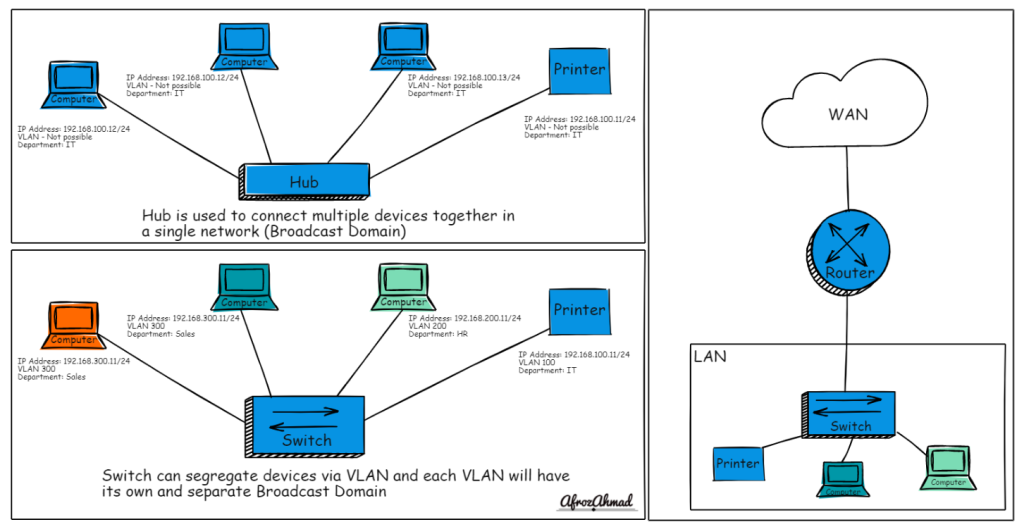
- Switches are networking devices that connect multiple devices together on a Local Area Network (LAN). They operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and use MAC addresses to forward data to the correct device within the LAN.
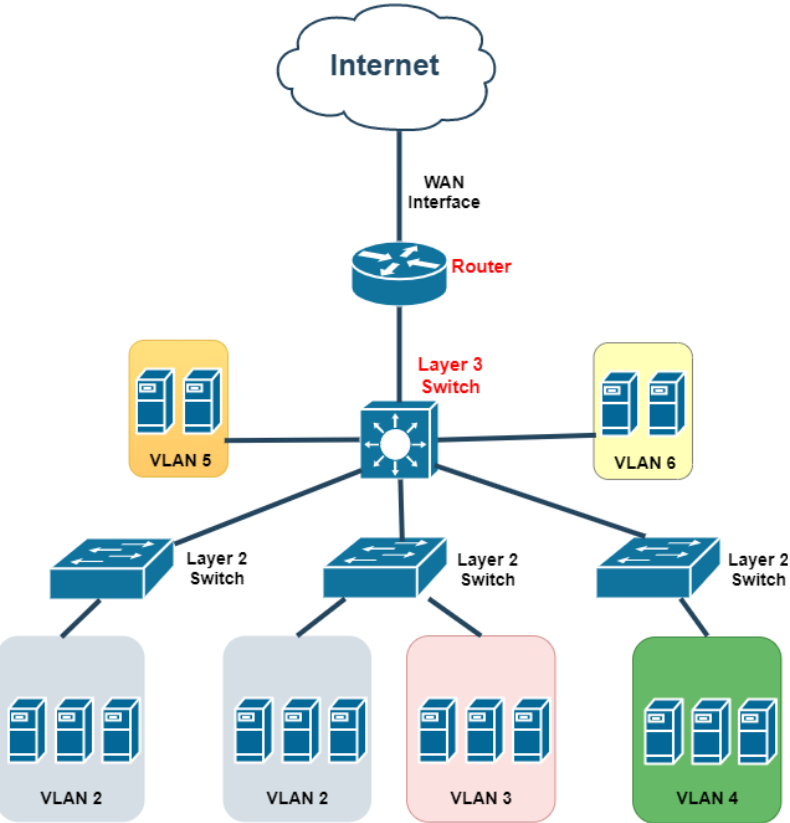
- Routers connect multiple networks together, such as a LAN to a Wide Area Network (WAN) or two LANs. They operate at the network layer (Layer 3) and use IP addresses to route data between networks, making decisions based on the most efficient path for data to travel.
2. Network Segments:
- Switches create a single network segment and work within a single network to manage and switch data packets among connected devices.
- Routers are used to segment and organize the network into different broadcast domains, preventing broadcasts from reaching every part of the network, which increases efficiency and security.
3. Traffic Handling:
- Switches handle traffic within the same network. They can significantly increase a network’s efficiency by sending data only to the intended recipient device within the LAN.
- Routers handle and direct outgoing and incoming traffic between different networks, managing data packets among devices that might not be on the same network.
4. Performance:
- Switches can enhance performance within a LAN by reducing unnecessary data transmission through packet switching, which sends data directly to the device it’s addressed to.
- Routers can affect the performance of a network based on the route it chooses for data packets. Advanced routing algorithms help in optimizing the speed and efficiency of data transmission across networks.
5. Security:
- Switches offer some level of security by segregating traffic between devices within the LAN. Managed switches provide advanced features like VLANs which can be used to further segment and secure the network.
- Routers play a significant role in network security. They can provide firewall protection, filter traffic, and perform network address translation (NAT), which hides the IP addresses of devices on a local network from the outside world.
6. Use Cases:
- Switches are used to build a network infrastructure within a home, office, or any establishment requiring multiple devices to connect within a single LAN.
- Routers are essential for connecting a LAN to the internet or other LANs, making them indispensable for any network that needs access to external networks.
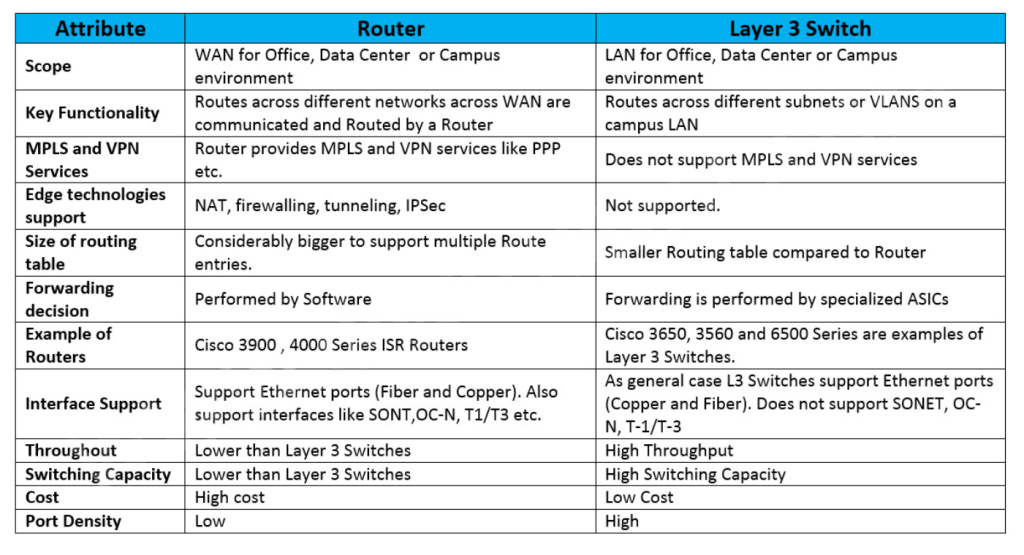
Switches vs Routers
| Feature | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|
| Area of Expertise | Connects devices within a single network | Connects multiple networks |
| Data Delivery Method | Uses MAC addresses | Uses IP addresses |
| OSI Model Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) | Layer 3 (Network Layer) |
| Function | Directs data packets to specific devices | Routes data packets between different networks |
| Analogy | Mailroom sorter within a building | Post office sending mail to different locations |
| Connectivity | Usually wired | Wired or wireless |
| Routing Table | No | Yes |
| Services | Limited (e.g., basic security) | More advanced (e.g., NAT, QoS) |
| Cost | Typically less expensive | Typically more expensive |
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
