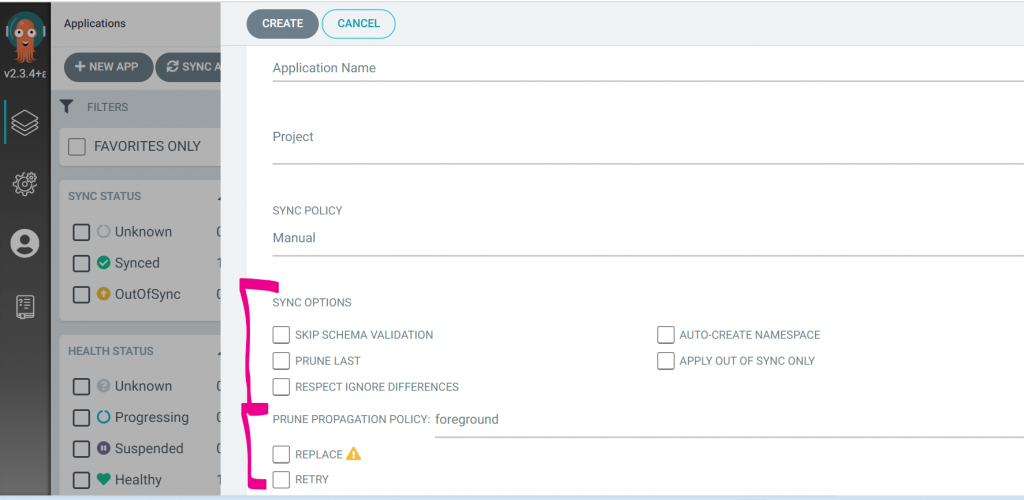
Common to both manual and automatic sync policies.
- Skip schema validation: When selected, bypasses validating the YAML schema.
- Auto-create namespace: When selected, automatically create the namespace if the specified namespace does not exist in the cluster.
- Prune last: When selected, removes those resources that do not exist in the currently deployed version during the final wave of the sync operation. See Prune last.
- Apply out of sync only: When selected, syncs only those resources in the application that have been changed and are OutOfSync, instead of syncing every resource regardless of their state. This option is useful to reduce load and save time when you have thousands of resources in an application.
- Selective sync: Currently when syncing using auto sync ArgoCD applies every object in the application. For applications containing thousands of objects this takes quite a long time and puts undue pressure on the api server. Turning on selective sync option which will sync only out-of-sync resources.
Prune propagation policy:
Defines how resources are pruned, applying Kubernetes cascading deletion prune policies. For more information, see Kubernetes – Cascading deletion.
- Foreground: The default prune propagation policy used by Argo CD. With this policy, Kubernetes changes the state of the owner resource to `deletion in progress`, until the controller deletes the dependent resources and finally the owner resource itself.
- Background: When selected, Kubernetes deletes the owner resource immediately, and then deletes the dependent resources in the background.
- Orphan: When selected, Kubernetes deletes the dependent resources that remain orphaned after the owner resource is deleted.
All Prune propagation policies can be used with:
Replace: When selected, Argo CD executes kubectl replace or kubectl create, instead of the default kubectl apply to enforce the changes in Git. This action will potentially recreate resources and should be used with care. See Replace Resource Instead Of Applying Change.
Retry: When selected, retries a failed sync operation, based on the retry settings configured:
- Maximum number of sync retries (Limit)
- Duration of each retry attempt in seconds, minutes, or hours (Duration)
- Maximum duration permitted for each retry (Max Duration)
- Factor by which to multiply the Duration in the event of a failed retry (Factor). A factor of 2 for example, attempts the second retry in 2 X 2 seconds, where 2 seconds is the Duration.
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

