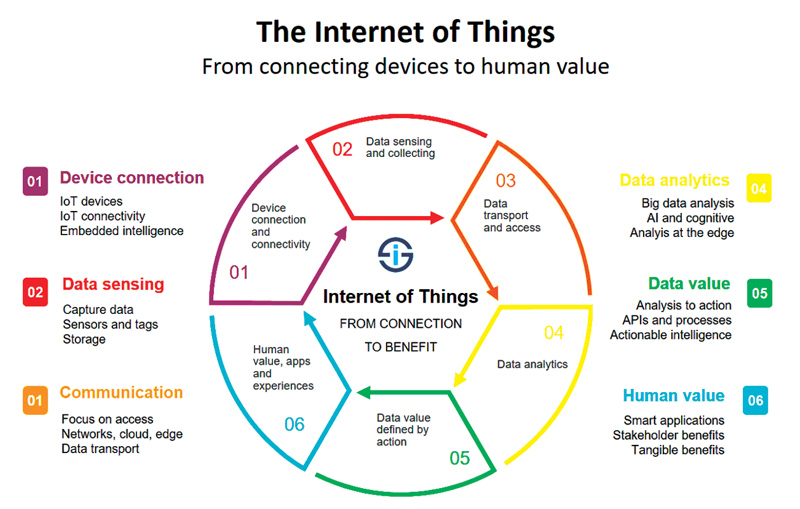
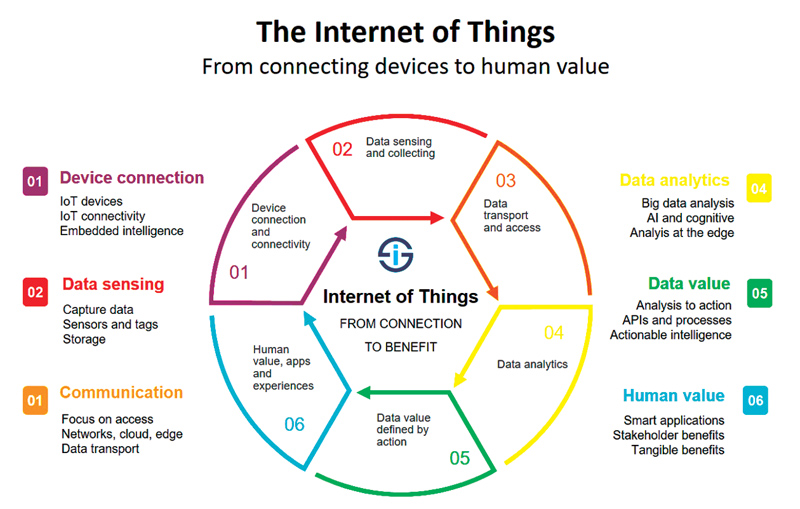
What is Internet of things?
The Internet of things describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the Internet.
IoT Operating Systems
RIOT
RIOT is a free operating system developed by a community consisting of companies, academia and hobbyists. RIOT supports most low-power devices and microcontroller architecture. It implements all relevant standards to ensure that the Internet of Things is connected, secure, durable and provides privacy protection.
Contiki
Contiki is an open-source operating system for the Internet of Things created by a worldwide team of developers. It provides powerful low-power Internet communication, supports fully standard IPv6 and IPv4, along with the recent low-power wireless standards: 6lowpan, RPL and CoAP. Contiki runs on a range of low-power wireless devices; its applications are written in standard C, and development with Contiki is easy and fast.
ARM mbed OS
ARM mbed OS is an open-source embedded operating system. It includes all the necessary features to develop a connected product. Mbed OS provides multilayer security and a wide range of communication options with drivers for Bluetooth Low Energy, Thread, 6LoWPAN, Ethernet and WiFi. What’s more, necessary libraries are included automatically on your devices to facilitate code writing.
ThingBox
The ThingBox is a set of software already installed and configured on an SDCard. The ThingBox allows anyone to graphically create new unlimited applications interacting with connected objects from a simple web-browser. This OS is suitable and easy-to-use for both technical people and users with no technical background.
LiteOS
Huawei LiteOS is a lightweight, low energy, efficient operating system. It starts up within milliseconds and responds within microseconds. LiteOS coordinates multiple sensors and supports long- and short-distance communication.
Raspbian
Raspbian is one of the most widely used platforms for the Internet of Things. It is a free system optimized for the Raspberry Pi hardware. Raspbian includes basic programs and utilities to make the hardware run, but it also compiles more than 35,000 packages and pre-compiled software for easy installation.
Android Things
Android Things is an operating system from Google. It lets you build professional, mass-market products on a trusted platform, without previous knowledge of embedded system design. Android Things provides you with leverage for the existing Android development tools, APIs, resources and regular security updates. Android Things ensures the development of IoT products at scale.
Open-Source Tools for the Internet of Things
- Arduino Starter Kit a cloud-based system that offers both software and hardware. It can be used even by beginner programmers.
- Home Assistant — the tool aimed is at the smart home market and is great for interaction with smart sensors in your house. The downside is that it doesn’t have a cloud component.
- Zetta — a cloud-based platform built on Node.js. Zetta is perfect for turning devices into API.
- Device Hive — this tool functions as an M2M communications framework. Device Hive is quite popular for the development of smart homes.
- ThingSpeak — one of the oldest and most effective tools for IoT applications in the market. ThingSpeak can process huge sums of data, it is used in web design applications and location tracking tasks. This tool is able to work with other open-source tools.
Best IoT Development Kits
- ARM mBed
- Relayr
- Microsoft Azure IoT Starter Kits
- BrickPi
- VERVE2
- Kinoma Create
- Ninja Sphere
- AWS IoT Starter Kits
- Helium Development Kit
Industry consortiums
- AllSeen Alliance
- Open Interconnect Consortium (OIC)
- COMPOSE
- Eclipse
- Open Source Hardware Association (OSHWA)
Protocols
- Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP)
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)
- Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)
- OASIS Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT)
- Very Simple Control Protocol (VSCP)
Operating systems (OS)
- ARM mbed
- Canonical Ubuntu and Snappy Ubuntu Core
- Contiki
- Raspbian
- RIOT
- Spark
- webinos
APIs
- BipIO
- Qeo Tinq
- Zetta
- 1248.io
Horizontal platforms
- Canopy
- Chimera IoT
- DeviceHive
- Distributed Services Architecture (DSA)
- Pico Labs (Kynetx open source assigned to Pico Labs)
- M2MLabs Mainspring
- Nimbits
- Open Source Internet of Things (OSIOT)
- prpl Foundation
- RabbitMQ
- SiteWhere
- webinos
- Yaler
Middleware
- IoTSyS
- OpenIoT
- OpenRemote
- Kaa
Node flow editors
- Node-RED
- ThingBox
Toolkits
- KinomaJS
- IoT Toolkit
Data visualization
- Freeboard
- ThingSpeak
Search
- Thingful
Hardware
- Arduino Ethernet Shield
- BeagleBone
- Intel Galileo
- openPicus FlyportPro
- Pinoccio
- WeIO
- WIZnet
In-memory data grids
- Ehcache
- Hazelcast
Home automation
- Home Gateway Initiative (HGI)
- Ninja Blocks
- openHAB
- Eclipse SmartHome
- PrivateEyePi
- RaZberry
- The Thing System
Robotics
- Open Source Robotics Foundation
Mesh networks
- Open Garden
- OpenWSN
Health
- e-Health Sensor Platform
Air pollution
- HabitatMap Airbeam
Water
- Oxford Flood Network
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com