
The Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a simple text-based arrangement for representing structured information documents, data, configuration, books, transactions, invoices, and much more. It was derived from an older normal format called SGML (ISO 8879), in order to be more appropriate for Web use.
The XML is one of the most widely-used formats for sharing structured info today between programs, amid people, between computers and people, both locally and across networks.
A short example:-
<part number="1976">
<name>Windscreen Wiper</name>
<description>The Windscreen wiper
automatically removes rain
from your windscreen, if it
should happen to splash there.
It has a rubber <ref part="1977">blade</ref>
which can be ordered separately
if you need to replace it.
</description>
</part>

If you are previously acquainted with HTML, you can see that XML is very comparable. Though, the syntax rules of XML are strict, XML tools will not procedure files that contain errors, but in its place will give you error messages so that you fix them. This means that almost all XML documents can be processed dependably by computer software.
Interview Questions and Answers:-
1. What is a markup language?

Markup languages are designed for presentation of text in different formats, and it can also be used for transporting and storing data. This markup language specifies the code for formatting, layout and style of data .This markup code is called Tag.
HTML and XML are examples of Markup Language.
2. What is XML?
XML is called Extensible Markup Language which is designed to carry or transport and store data. XML tags are not as predefined as HTML, but we can define our own user tags for simplicity. It mainly concentrates on storing of data, not on displaying of data.
3. What are the features of XML?
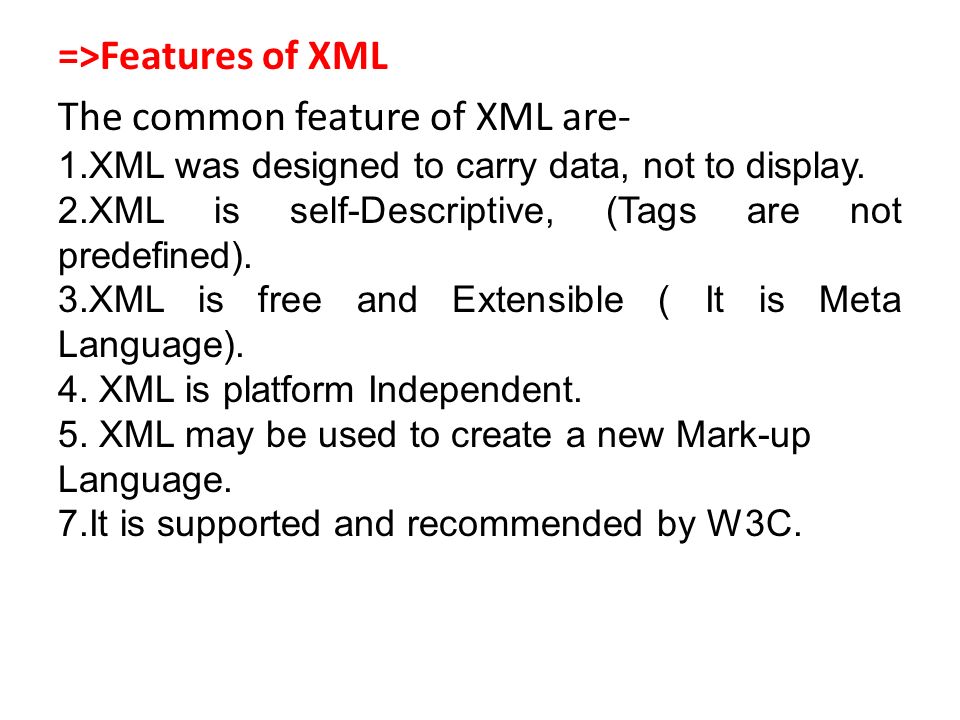
Main features of XML are:
- Very easy to learn and implement
- XML files are text files, and no editor is required
- Minimal and a limited number of syntax rules in XML
- It is extensible, and it specifies that structural rules of tags
5. Which tag is used to find the version of XML and the syntax? Declaring the XML version is very important for each XML document and platform needs to be specified in which it is running
<?xml version=”1.1” encoding=”|ISO-8859-1|”?>
xml-svg
6. What is XML DOM Document?
XML Document object represents the whole XML document, and it is the root of a document tree. It gives access to entire XML document – Nodes and Elements, and it has its own properties.
7. What is XPath?
XPath is used to find information in an XML document and contains standard functions. XPath is the major element in XSLT, and it is w3c recommendation.
8. What is an attribute?
An attribute provides more or additional information about an element than otherwise.
Example –
<Person name=”Peter”>Attribute name can be given to an element person.
9. Can we have empty XML tags?
Yes, we can have empty tags in XML. Empty tags are used to indicate elements that have no textual content. Empty tags can be represented as
<person></person>
<person/>
10. What are the advantages of XML DOM Document?
Advantages of XML DOM:
• XML structure is traversable, and it can be randomly accessed by traversing the tree.
• XML structure is modifiable, and values can be added, changed and removed
11. What are the basic rules while writing XML?
These are the basic rules while writing XML:
• All XML should have a root element
• All tags should be closed
• XML tags are case sensitive
• All tags should be nested properly
• Tag names cannot contain spaces
• Attribute value should appear within quotes
• White space is preserved
12. What is XML Element?
An XML document contains XML Elements, and it starts from an element’s start tag to end tag. It can contain:
• Other elements within main element
• An Attribute
• text
13. What is CDATA?
CDATA is unparsed character data that cannot be parsed by the XML parser. Character < and > are illegal in XML elements. CDATA section starts with <![CDATA[“ and end with “]]>”.
14. How comment can be represented in XML?

Comment can be represented as <! – – comments – -> as like HTML. This comment symbol is applicable for single or multiple lines.
15. What are XML Namespaces?
XML namespaces are used to avoid element name conflicts, and it can be avoided by using prefix before the name.
16. What is XML Parser?
XML Parser is used to convert from XML document into an XML DOM object which can be written in Javascript.
17. What is XSL?
XSL is a language used with XML for expressing style sheets as like CSS. It describes how to display an XML document for a given type.
18. Who is responsible for XML?
XML is a recommendation of the W3C – World Wide Web Consortium and the development are supervised by XML working group.
19. What is an XML Schema?
An XML schema gives the definition of an XML document, and it has following:
• Elements and attributes
• Elements that are child elements
• Order of child elements
• Data types of elements and attributes
20. What is well formed XML document?
A well-formed XML document must follow the following rules –
• Every start tag should end with an end tag
• XML tags are case sensitive
• Empty tags are necessary to close with a forward slash
• All tags should be properly nested
21. Why XML has been used for development?
XML is used for development for following reasons:
• Used for Database driven websites
• Used to store data for e-commerce websites
• Used to transport and store data on internet
• XML is used for database and flat files
• Generate dynamic content by applying different style sheets
22. What is SGML?
SGML is large and powerful Standard Generalized markup Language which is used to define descriptions of the structure of different types of electronic document.
23. Can I execute a XML?
No, we cannot execute XML, and it is not a programming language to execute. It is just a markup language to represent the data.
24. What are the special characters used in XML?
<, > and & are the special characters used in XML. Because these characters are used for making tags.
25. What software is available for XML?
There are thousands of programs available for XML and updated list will be present in
- Oxygen XML Editor
- Liquid XML Studio
- MadCap Flare
26. Whether graphics can be used in XML? If so, How?
Yes, Graphics can be included in XML by using XLink and XPointer specifications. It supports graphic file formats like GIF, JPG, TIFF, PNG, CGM, EPS and SVG.
XLink:
<description
xlink:type="simple"
xlink:href="http://show.com/Cinema.gif"
xlink:show="new">
</description>
XPointer:
<description
xlink:type="simple"
xlink:href="http://show.com/Cinema.gif#Shownumber"
xlink:show="new">
</description>
27. Can I replace HTML with XML?
No, XML is not a replacement of HTML. XML provides an alternative approach to define own set of markup elements, and it is used for processing and storing data.
28. How can I include conditional statements in XML?
We cannot include conditional statement as like programming language.
<foo if{DB}="A">bar</foo>
This can be done by using Document Type Definition(DTD).
<xsl:if test="@foo=’bar’">
<xsl:text>Hello, world!</xsl:text>
</xsl:if>
29. What are the benefits of XML?
Benefits of XML are
• Simple to read and understand
• XML can be done with a text editor
• Extensibility – No fixed tags
• Self – descriptive
• Can embed multiple data types
30. What are the disadvantages of XML?
Following are the disadvantages of XML:
• XML will be just a text file if elements and attributes are not defined properly.
• Overlapping markup is not permitted
31. What is DTD?
DTD is abbreviated as Document Type Definition and it is defined to build legal building blocks of an XML document. It defines the XML document structure with elements and attributes.
32. Why XSLT is important for XML?
XSLT is abbreviated as eXtensible Sytlesheet Language Transformation which is used to transform an XML document to HTML before it is displayed to the browser.
33. What are nested elements in XML?
If one or more elements are nested inside the root element is called nested element. Nesting can be easy to understand and also keeps order in an XML document.
34. What is XQuery?
XQuery was designed to query XML data which is nothing but SQL for database tables. XQuery is used to fetch the data from the XML file.
35. What is XLink and XPointer?
XLink is the standard way of creating hyperlinks in the XML files. Xpointer which allows those hyperlinks to point to more specific parts of the XML file or document.
36. Why XML editor is needed instead of Notepad?
XML editors are required to write error free XML documents, and it is used to validate against DTD or schema. Editors are able to check:
• Open and Close Tags
• XML against DTD
• XML against Schema
• Color code on XML Syntax
37. What is XML Encoding?
XML documents may contain Non-ASCII characters like French and Norwegian characters. XML Encoding is used to avoid errors and XML files have to be saved as Unicode.
38. Which XML is set to be valid XML?
When the XML file is validated against the Document Type Definition(DTD), then it is called valid XML. DTD is nothing but it defines the structure of an XML file.
39. What is Simple Element?
A simple element contain only text and following are the kinds of Simple Element:
- No attributes
- Doesn’t contain other elements
- It cannot be empty
40. What is Complex Element?
A complex element contain other elements or attributes and following are kinds of Complex Elements:
- It has empty elements
- It contain other elements
- It contain only text
- It contain both other elements and text
41. Is there a way to describe XML data?
Yes, XML uses Document Type Definition (DTD) to describe the data.
42. What are the three parts of XSL?
XSL consists of three parts:
XSLT – Used to transform XML documents
XPath – Used for navigating in XML documents
XSL-FO – Used for formatting XML documents
43. What is the correct syntax when we define XML version?
<?xml version=”1.0”/>
is the correct declarative syntax used to define XML version.
44. If XML attribute name itself has double quotes, then how it can be represented?
Attribute name can be represented within single quotes if double quotes are present in the attribute name.
Example –
<country city='Texas "US"'></country>45. What are the types of XML Parsers?
There are two types of parsers – Non-Validating and Validating Parsers. Name itself implies Non-Validating will not validate the XML and Validating parser will validate the XML with DTD.
46. Whether root element is required for XML? If so, how many root elements are required?
Yes, root element is required, and it can have only one root element in each XML.
47. What is XML Signature?
XML Signature is recommended by W3C, and it acts as a digital signature for XML documents. If the signature is contained outside the document, it is called detached signature. If it contains inside the XML document, then it is called Enveloping signature.
48. What is Data Island?
An XML Data island is XML data embedded into a HTML page. This works only with the Internet.
49. What is DiffGram in XML?
A DiffGram is an XML format which is used to find current and original versions of XML document.
50. What is SAX?
SAX is an interface processing XML documents using events.
Here is the video tutorial which will help you:-
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
