
 1. What is Cloud Storage?
1. What is Cloud Storage?
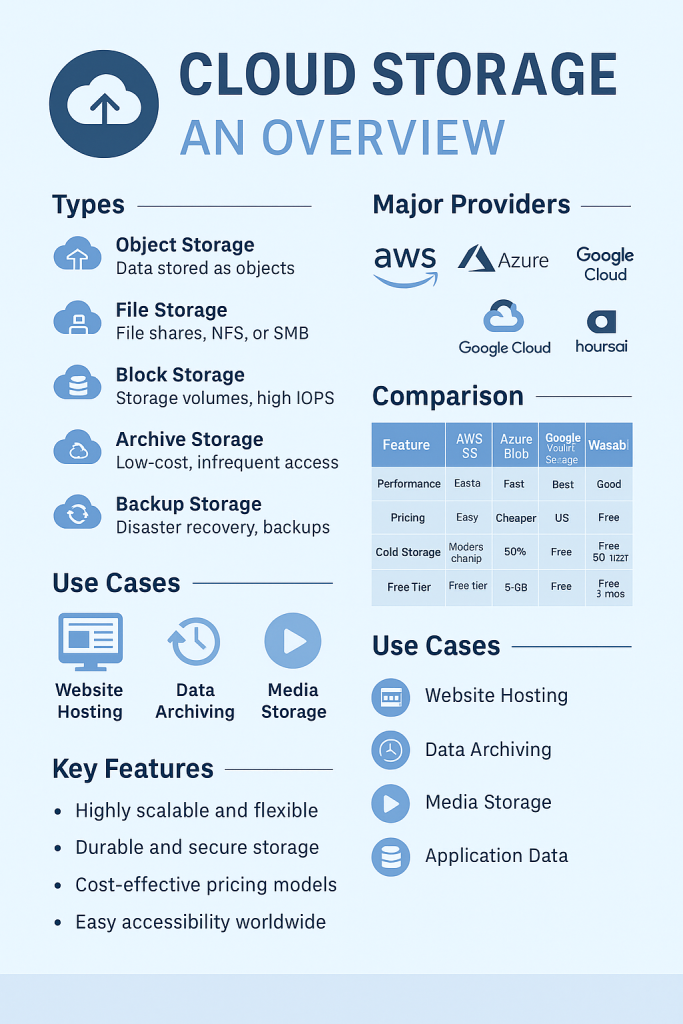
Cloud Storage refers to the service model where data is stored, managed, and accessed remotely over the internet instead of being stored locally on physical hard drives or servers.
It allows users and organizations to save files, databases, media, backups, and application data on highly secure and scalable off-premises infrastructure operated by cloud providers. Applications access cloud storage through traditional storage protocols or directly via an API. Many vendors offer complementary services designed to help collect, manage, secure and analyze data at massive sc.

- Accessible anytime, anywhere with internet connection.
- Scalable — store a few megabytes to exabytes of data easily.
- Durable — often designed for 99.999999999% (11 nines) data durability.
- Secure — with encryption at rest and in transit.
- Cost-Effective — pay-as-you-go models, no upfront hardware costs.
- Redundant — automatically replicated across multiple servers/data centers.
 2. Types of Cloud Storage
2. Types of Cloud Storage
There are several types of cloud storage services depending on use cases and data access needs:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Object Storage | Data stored as objects (files + metadata) in flat namespaces. Highly scalable, ideal for unstructured data. | Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage |
| File Storage (File Shares) | Hierarchical storage (folders/files) using standard protocols like NFS, SMB. Feels like a network drive. | Amazon EFS, Azure Files, Google Filestore |
| Block Storage | Storage volumes attached to compute instances (like virtual hard drives). High IOPS for databases, apps. | Amazon EBS, Azure Disk Storage, Google Persistent Disk |
| Cold Storage / Archive Storage | Extremely low-cost storage optimized for infrequent access. Long retrieval times. | Amazon Glacier, Azure Archive Storage, Google Archive Storage |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery Storage | Specialized for data backups, snapshots, recovery workflows. | Veeam Cloud Connect, AWS Backup, Azure Backup |

 3. Major Cloud Storage Providers (2025)
3. Major Cloud Storage Providers (2025)
Here are the major players offering world-class cloud storage services:
| Provider | Main Storage Services |
|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | S3 (Object Storage), EBS (Block), EFS (File), Glacier (Archive) |
| Microsoft Azure | Blob Storage (Object), Azure Files (File), Disk Storage (Block), Archive Storage |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Cloud Storage (Object), Persistent Disk (Block), Filestore (File), Archive |
| IBM Cloud | IBM Cloud Object Storage |
| Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) | OCI Object Storage, Block Volumes, File Storage |
| Wasabi | Low-cost S3-compatible object storage (popular for backup/archiving) |
| Backblaze B2 | Very affordable S3-like object storage for personal and business use |
| DigitalOcean Spaces | Simple, scalable object storage for developers and startups |
| Alibaba Cloud OSS | Object Storage Service, widely used in Asia-Pacific markets |
 4. Cloud Storage Providers — Detailed Comparison (2025)
4. Cloud Storage Providers — Detailed Comparison (2025)
| Feature | AWS S3 | Azure Blob | Google Cloud Storage | Wasabi | Backblaze B2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Industry-leading, ultra-scalable | Excellent for hybrid cloud | Fast, especially in AI/ML pipelines | Good for backups | Good for backups |
| Durability | 99.999999999% (11 9’s) | 99.999999999% | 99.999999999% | 99.999999999% | 99.999999% |
| Global Reach | Widest (250+ PoPs) | Strong Azure network | Strong Google fiber backbone | U.S., Europe mainly | U.S. focus |
| Pricing | Moderate (complex tiers) | Moderate | Slightly cheaper than AWS | Cheapest (predictable) | Very cheap |
| Cold Storage | Glacier, Glacier Deep Archive | Archive Storage | Archive Storage Class | Not specialized, but cheap | Not specialized |
| Free Tier | 5 GB (12 months) | 5 GB (12 months) | 5 GB (always free) | No free tier | 10 GB always free |
| Compliance | HIPAA, GDPR, FedRAMP, ISO | HIPAA, GDPR, ISO | HIPAA, GDPR, ISO | HIPAA, GDPR | HIPAA, GDPR |
| Ease of Use | Advanced (more complex) | Better integration with Microsoft ecosystem | Developer-friendly APIs | S3-compatible APIs | S3-compatible APIs |
 5. Common Use Cases of Cloud Storage
5. Common Use Cases of Cloud Storage
| Use Case | Description | Common Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Website Hosting (Static Websites) | Hosting static assets (HTML, CSS, JS) directly from object storage. | AWS S3, Azure Blob Static Websites, Google Cloud Storage |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery | Storing backups, disaster recovery copies with redundancy. | AWS Backup, Azure Backup, Wasabi, Backblaze |
| Big Data Storage | Storing massive datasets (logs, IoT, clickstreams) for analytics and ML. | AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage |
| Media Storage and Distribution | Storing and streaming videos, music, images at scale. | AWS S3 + CloudFront, GCP Media CDN |
| Application Data Storage | Application uploads, user-generated content storage. | Azure Blob Storage, AWS S3 |
| Archival and Compliance Storage | Long-term archive (e.g., healthcare, financial records). | AWS Glacier, Azure Archive, GCP Coldline |
| Hybrid Cloud Storage | On-premises + Cloud integrations (e.g., backup appliances synced with cloud). | AWS Storage Gateway, Azure File Sync |
| SaaS Application Backend | Storing app data (e.g., Dropbox, Netflix use object storage at scale). | AWS S3, GCP Storage |
 Bonus: Trends in Cloud Storage (2025 and Beyond)
Bonus: Trends in Cloud Storage (2025 and Beyond)
- AI + Storage: AI-based optimization of storage classes and smart archiving (auto-move data between hot/cold classes).
- Multi-Cloud Storage: Companies using storage across AWS + Azure + GCP simultaneously.
- Ransomware Resilience: Immutable backups, object lock features (S3 Object Lock, Azure Immutable Blob Storage).
- Serverless Storage Access: Direct integration with serverless applications and event-driven processing (e.g., S3 + Lambda).
- Green Cloud Storage: Focus on energy-efficient, carbon-neutral storage infrastructures (GCP Carbon-Free Cloud initiative).
 Pro Tip When Choosing a Cloud Storage Provider
Pro Tip When Choosing a Cloud Storage Provider

- High-read/write = Block Storage or Hot Object Storage.
- Infrequent access = Cold/Archive Storage.

- Latency, compliance needs, redundancy zones, API ecosystem matter.

- Prefer providers with S3-compatible APIs if flexibility matters (Wasabi, Backblaze).
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Cloud Storage has revolutionized how individuals and enterprises manage data, offering scalability, security, and global availability at an unprecedented scale.
With many powerful options available in 2025 — from AWS S3 and Azure Blob to newer players like Wasabi and Backblaze — the right choice depends heavily on your needs, data access patterns, and long-term strategy.
“In the era of AI, IoT, and decentralized applications, Cloud Storage isn’t just a utility — it’s a competitive advantage.“
Stay updated, stay secure, and leverage the right storage strategy to power your digital future.
 Quick Summary
Quick Summary
| Section | Quick Takeaway |
|---|---|
| What is Cloud Storage? | Online, scalable, durable data storage managed by providers |
| Types of Storage | Object, File, Block, Cold Storage, Backup |
| Popular Providers | AWS, Azure, GCP, Wasabi, Backblaze |
| Comparison | AWS S3 = best flexibility; GCP = best developer experience; Wasabi = best low-cost |
| Use Cases | Website hosting, backups, big data, media, compliance |
| Trends | AI optimization, multi-cloud, ransomware resilience |
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com

Great post! I thoroughly enjoyed reading your article. The points you raised are insightful and thought-provoking. I particularly appreciated your analysis of the topic and how you supported your arguments with evidence. The way you structured the post made it easy to follow and understand. It’s evident that you have a deep understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, your writing style is engaging and captivating, which kept me hooked from start to finish. Overall, this post was both informative and enjoyable to read. Thank you for sharing your expertise and I look forward to reading more of your work in the future!