What is Juniper Networks?

Juniper Networks is an American multinational company headquartered in Sunnyvale, California. It elaborates and markets networking products, including routers, switches, network management software, network security products, and software-defined networking technology. Founded in 1996, Juniper Networks has grown to become a major player in the networking industry, with a wide range of products and services that are used by businesses of all sizes around the world.
Top 10 use cases of Juniper Networks?
Here are the top 10 use cases of Juniper Networks products and services:
- Enterprise Routing and Switching: Juniper Networks offers a wide range of routers and switches that are designed for use in enterprise networks. These products provide high performance, scalability, and reliability, making them ideal for mission-critical applications.
- Data Center Networking: Juniper Networks offers a variety of products and services that are designed for use in data centers. These products help to ensure that data centers are running efficiently and securely.
- Service Provider Networking: Juniper Networks offers a wide range of products and services that are designed for use by service providers. These products help service providers to deliver high-quality network services to their customers.
- Cloud Networking: Juniper Networks offers a variety of products and services that are designed for use in cloud environments. These products help businesses to take advantage of the benefits of the cloud, such as scalability and agility.
- Security: Juniper Networks offers a wide range of security products and services that help businesses to protect their networks from cyberattacks. These products include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
- Automation: Juniper Networks offers a variety of automation tools that help businesses to automate their network operations. These tools can help businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve agility.
- Management: Juniper Networks offers a variety of network management tools that help businesses to manage their networks effectively. These tools provide businesses with visibility into their networks, and help them to troubleshoot problems and make informed decisions.
- Analytics: Juniper Networks offers a variety of analytics tools that help businesses to gain insights into their network data. These tools can help businesses to improve network performance, identify security threats, and make better business decisions.
- AI and Machine Learning: Juniper Networks is investing in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to develop new and innovative networking products and services. These products and services will help businesses to automate tasks, improve network performance, and make better decisions.
- Edge Computing: Juniper Networks is a leader in edge computing, which is the practice of processing data closer to the source where it is generated. Edge computing can help businesses to improve performance, reduce costs, and gain new insights from their data.
What are the feature of Juniper Networks?
Juniper Networks offers a wide range of features across its diverse product portfolio, catering to various network needs and environments. Here’s a breakdown of some key areas and features:
Routing:
- High-performance routing: Supports high bandwidth and packet forwarding rates for demanding applications.
- Scalability: Adapts to growing network demands with modular designs and high port densities.
- Advanced routing protocols: Supports BGP, MPLS, OSPF, and other protocols for efficient routing across diverse topologies.
- Security features: Integrated firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption capabilities for enhanced network security.
- Automation: Supports automation tools and APIs for streamlined configuration and management.
Switching:
- High-density switching: Provides numerous ports to connect various devices and cater to dense network environments.
- Advanced features: Supports layer 2/layer 3 switching, VLANs, QoS, and multicast for flexible network segmentation and traffic management.
- Security features: Integrates security functionalities like MAC address filtering, access control lists (ACLs), and port security for network protection.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): Delivers power and data over a single cable, simplifying deployments and reducing cabling costs.
- Software-defined networking (SDN): Supports SDN controllers for programmatic network management and automation.
Security:
- Firewalls: Offers next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) with deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and advanced threat detection capabilities.
- Unified Threat Management (UTM): Combines multiple security functions like firewall, intrusion detection, antivirus, and content filtering in a single appliance.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): Delivers cloud-based security services for remote users and branch offices.
- Encryption: Supports various encryption protocols like IPsec, VPN, and TLS to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Provides granular access control and user authentication for enhanced security.
Automation and Management:
- Junos Space Network Management Platform: Comprehensive platform for configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting across your network.
- Junos Automation Suite: Offers tools and APIs for automating network tasks and configuration management.
- Contrail Network Controller: SDN controller for centralized network management and policy enforcement.
- Mist Cloud Networking Platform: AI-powered platform for managing cloud-native and distributed networks.
- Integration with industry-standard tools: Supports integration with third-party management tools for unified visibility and control.
How Juniper Networks works and Architecture?
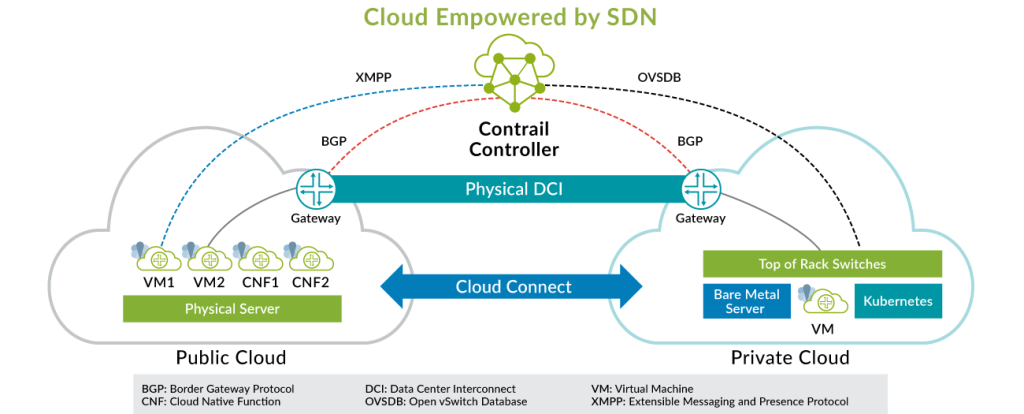
Juniper Networks operates through a combination of hardware, software, and architecture designed to deliver high-performance, secure, and scalable networking solutions. Here’s a breakdown of key elements:
Hardware:
- Routers: Juniper offers a wide range of routers optimized for specific needs, from branch offices to large data centers. These routers feature high-performance processors, modular designs, and extensive port densities.
- Switches: Similarly, Juniper provides various switches catering to different environments, offering layer 2 and layer 3 switching capabilities, advanced features like QoS, and support for PoE+.
- Security Appliances: Dedicated appliances for firewalls, UTM, and other security functions deliver comprehensive protection and network visibility.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Controllers: Centralized control points for managing and automating network infrastructure through software programming.
Software:
- Junos Operating System (Junos OS): The core software platform powering Juniper devices, offering robust routing, switching, security, and management functionalities.
- Junos Space Network Management Platform: Provides centralized configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting capabilities for your entire network.
- Contrail Network Controller: An SDN controller enabling programmatic network management and policy enforcement across diverse environments.
- Mist Cloud Networking Platform: Cloud-based platform leveraging AI for managing and optimizing cloud-native and distributed networks.
- Junos Automation Suite: Tools and APIs for automating network tasks and configuration management, streamlining operations.
Architecture:
- Modular Architecture: Juniper devices often feature modular designs, allowing flexible expansion and adaptation to changing network demands.
- Distributed Architecture: Certain solutions like Junos Space and Contrail operate with distributed components for scalability and resilience.
- Hierarchical Architecture: For large networks, a hierarchical architecture with core, aggregation, and access layers optimizes routing and traffic flow.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN principles enable centralized control and programmability of the network infrastructure, enhancing agility and automation.
How it Works:
- Network devices (routers, switches) run Junos OS for core functionalities.
- Management platforms like Junos Space or Contrail provide centralized configuration and control.
- Security appliances offer dedicated protection layers like firewalls and intrusion detection.
- SDN controllers allow programmatic network management and policy enforcement.
- Network devices communicate and forward data packets based on configured routing protocols and policies.
- Management platforms collect data and provide insights for monitoring, troubleshooting, and optimization.
Understanding Juniper Networks’ architecture and functionality empowers you to:
- Effectively deploy and manage your network infrastructure.
- Select the right products and features for your specific needs.
- Simplify network administration and automate tasks.
- Enhance network security and performance.
Remember, specific details and configurations will vary depending on your chosen products and network environment.
How to Install Juniper Networks it?
Installing Juniper Networks solutions involves several steps and considerations depending on the specific product and deployment scenario. Here’s a general overview to guide you:
1. Identify your needs and chosen product:
- What are you trying to achieve (e.g., routing, switching, security)?
- Which Juniper Networks product best suits your requirements (e.g., router model, switch series)?
2. Choose your deployment method:
- Physical appliance: On-premises hardware installation.
- Virtual appliance: Deployed on your virtualization platform (e.g., VMware, KVM).
- Cloud-based deployment: Managed through cloud services (e.g., Juniper Contrail Cloud).
3. Gather necessary information and resources:
- Product documentation: Specific installation guides and manuals for your chosen product.
- Software downloads: Obtain the appropriate software image or package from Juniper Networks.
- Hardware requirements: Ensure you have compatible hardware specifications for physical deployments.
- Network configuration details: Understand your existing network topology and IP addressing scheme.
4. Follow the installation guide:
- Each Juniper Networks product comes with detailed installation instructions specific to its model and deployment method.
- These guides typically cover:
- Hardware installation (if applicable)
- Software configuration
- Initial network setup
- Security configuration
- Verification and testing
5. Additional considerations:
- Licensing: Ensure you have the necessary licenses for your chosen product and features.
- Configuration customization: Tailor the settings to your specific network environment and policies.
- Post-installation tasks: Update firmware, integrate with management tools, and monitor performance.
Important notes:
- Due to the diverse product range and potential complexity, I cannot provide specific installation instructions without knowing your chosen product and deployment method.
- Consider seeking professional assistance for complex deployments or if you lack technical expertise.
Remember, installation is just the first step. Optimizing configuration, security, and ongoing management are crucial for a successful Juniper Networks deployment.
Basic Tutorials of Juniper Networks : Getting Started

Juniper Networks provides networking solutions, including routers, switches, and security devices. Below are step-by-step basic tutorials to help you get started with Juniper Networks devices running the Junos operating system.
Prerequisites:
- Access to a Juniper Device:
- Have physical or virtual access to a Juniper router, switch, or security device.
2. Junos Software:
- Ensure that the device is running the Junos operating system.
Step 1: Basic Configuration
- Access the Juniper Device:
- Connect to the device using the console port or SSH.
2. Enter Operational Mode:
- Log in with the default credentials (typically
rootfor the username, and no password).
3. Enter Configuration Mode:
- Enter configuration mode to make changes:
configure
4. Set Hostname:
- Set the hostname of the device:
set system host-name <hostname>
5. Configure Interfaces:
- Configure interfaces with IP addresses:
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address <ip_address>/<subnet_mask>
6. Set Default Route:
- Set a default route:
set routing-options static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop <next_hop_ip_address>
7. Commit Configuration:
- Commit the changes:
commit
Step 2: OSPF Configuration
- Enter OSPF Configuration Mode:
- Enter OSPF configuration mode:
edit protocols ospf
- Configure OSPF Area:
- Configure OSPF area and assign interfaces:
set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
- Set OSPF Router ID:
- Set the OSPF router ID:
set router-id <router_id>
- Exit Configuration Mode:
- Exit OSPF configuration mode:
top
- Commit Configuration:
- Commit the changes:
commit
Step 3: BGP Configuration
- Enter BGP Configuration Mode:
- Enter BGP configuration mode:
edit protocols bgp
2. Configure BGP Peer:
- Configure a BGP peer:
set group my-bgp-group type internal set group my-bgp-group local-address <local_ip_address> set group my-bgp-group neighbor <neighbor_ip_address>
3. Set BGP Router ID:
- Set the BGP router ID:
set group my-bgp-group export my-export-policy
4. Exit Configuration Mode:
- Exit BGP configuration mode:
top
5. Commit Configuration:
- Commit the changes:
commit
Step 4: Security Policies Configuration
- Enter Security Configuration Mode:
- Enter security configuration mode:
edit security
2. Configure Security Policies:
- Configure security policies to control traffic:
set policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-all match source-address any set policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-all match destination-address any set policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-all match application any set policies from-zone trust to-zone untrust policy allow-all then permit
3. Exit Configuration Mode:
- Exit security configuration mode:
top
4. Commit Configuration:
- Commit the changes:
commit
These tutorials provide a basic introduction to configuring Juniper Networks devices running Junos, covering initial setup, basic configuration, OSPF, BGP, and security policies.
Say goodbye to the hassles of bike ownership! MotoShare.in offers affordable rentals, whether you need a scooter for errands, a bike for a road trip, or a reliable ride to explore new cities.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
