What is Exabeam?

Exabeam is a security intelligence platform that helps organizations detect, investigate, and respond to security threats across their IT infrastructure. It acts as a central hub, ingesting data from various security tools and devices, then applying advanced analytics and machine learning to identify suspicious activity and prioritize potential threats.
Here’s a simplified analogy: Imagine Exabeam as a high-tech security detective. It gathers clues (security data) from different sources, analyzes them with its keen intelligence (advanced analytics), and presents you with a clear picture of potential criminal activity (security threats) so you can take swift action.
Top 10 use cases of Exabeam?
Top 10 Use Cases of Exabeam:
- Threat Detection and Investigation: Exabeam excels at uncovering hidden threats lurking within your vast security data. It uses user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to identify anomalous activities, like privileged user access at odd hours or unusual data exfiltration attempts.
- Incident Response and Automation: When a security incident occurs, Exabeam helps you respond quickly and effectively. It streamlines the investigation process by providing contextual insights and automates routine tasks like containment and remediation.
- Security Compliance: Exabeam helps you comply with various security regulations, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS, by providing audit trails and reports demonstrating your proactive security posture.
- Insider Threat Detection: Exabeam’s UEBA capabilities can detect suspicious behavior by internal users, potentially indicating malicious intent or compromised accounts.
- Fraud Prevention: Exabeam can help combat financial fraud by identifying suspicious financial transactions and user activities related to known fraud patterns.
- IoT Security: Exabeam can monitor and secure Internet of Things (IoT) devices, detecting vulnerabilities and suspicious communication patterns within your IoT network.
- Cloud Security: Exabeam extends its security intelligence to cloud environments, providing visibility and threat detection across your cloud infrastructure.
- Endpoint Security: Exabeam integrates with endpoint security solutions to gain deeper insights into endpoint activity and identify potential malware or unauthorized access attempts.
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Optimization: Exabeam can centralize and streamline your SOC operations, enhancing team efficiency and threat response times.
- Threat Hunting and Proactive Security: Exabeam empowers your security team to proactively hunt for threats instead of waiting for them to surface. Its advanced analytics capabilities can uncover subtle indicators of compromise before they escalate into major security incidents.
These are just a few of the many ways Exabeam can bolster your organization’s security posture. Its comprehensive platform and advanced capabilities make it a valuable tool for any organization looking to proactively defend against evolving cyber threats.
What are the feature of Exabeam?
Exabeam comes packed with powerful features designed to empower your security team in detecting, investigating, and responding to threats. Here are some key highlights:
1. Security Data Collection and Management:
- Ingest data from diverse sources: Collects logs, events, and data from security tools, endpoints, cloud platforms, and more.
- Parsimonious parsing and storage: Efficiently parses and stores data in various formats, minimizing storage footprint.
- Hot, warm, and cold data access: Delivers fast search and analysis across hot, warm, and cold data archives.
2. Advanced Threat Detection and Analytics:
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Identifies anomalies in user behavior and entity activity, highlighting suspicious patterns.
- Machine Learning and Statistical Analysis: Leverages algorithms to detect subtle threats and prioritize suspicious events.
- Pre-built and custom analytics: Utilize pre-built correlations and threat models or create your own for tailored detection.
3. Streamlined Investigation and Response:
- Automated timelines: Visually reconstruct the chain of events for each incident, providing context and clarity.
- Alert enrichment and correlation: Enrich alerts with contextual data and link them to related events for faster investigation.
- Scripted actions and SOAR integration: Automate response actions and orchestrate workflows with security orchestration and automated response (SOAR) tools.
4. Reporting and Compliance:
- Customizable dashboards and reports: Create clear and insightful reports on security posture, threats, and incident response.
- Compliance reporting: Generate reports demonstrating compliance with industry regulations and audit requirements.
- Real-time threat intelligence integration: Feed in threat intelligence feeds to further enhance detection capabilities.
5. Scalability and Performance:
- Cloud-native architecture: Scales efficiently to handle large volumes of data and complex security environments.
- High-performance search and analysis: Offers rapid query response times and efficient data processing.
- Open and extensible platform: Integrates with existing security tools and workflows for seamless deployment.
How Exabeam works and Architecture?
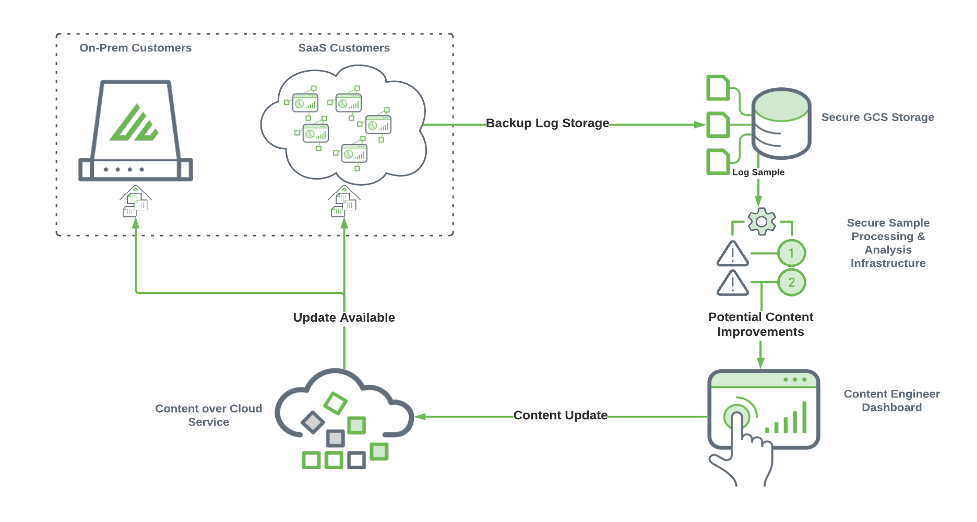
How Exabeam Works:
- Data Intake: Exabeam collects security data from various sources and parses it into a unified format.
- Normalization and Enrichment: Data is normalized and enriched with contextual information like user identities and device attributes.
- Behavioral Analytics and Threat Detection: Advanced algorithms analyze the enriched data to identify suspicious activity and potential threats.
- Alerting and Investigation: Exabeam triggers alerts for suspicious events, providing investigators with contextual information and automated timelines.
- Response and Remediation: Teams can take decisive action through automated response scripts, SOAR integrations, or manual intervention.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Exabeam learns from previous incidents and new threat intelligence to refine its detection algorithms and improve its effectiveness over time.
Exabeam Architecture:
- Data Collection Layer: This layer gathers data from various sources and feeds it into the platform.
- Normalization and Enrichment Layer: Data is cleansed, normalized, and enriched with additional context.
- Analytics and Detection Layer: Advanced analytics engines and machine learning algorithms identify suspicious activity and generate alerts.
- Investigation and Response Layer: This layer provides tools for investigating alerts, visualizing timelines, and orchestrating response actions.
- Reporting and Compliance Layer: Generates reports on security posture, incidents, and compliance requirements.
- Threat Intelligence Layer: Integrates with threat intelligence feeds to update detection rules and enhance threat awareness.
By understanding these features and how Exabeam works, you can see how it empowers security teams to effectively protect their systems and data from evolving cyber threats.
How to Install Exabeam it?
Installing Exabeam involves technical expertise and depends on your deployment environment. To guide you accurately, I need some additional information:
- Deployment Model: Do you want to install Exabeam on your own infrastructure (on-premises) or utilize the Exabeam Cloud Deployment service?
- Operating System: Which operating system will you be installing Exabeam on (e.g., Red Hat, Ubuntu, Windows)?
- License type: Do you have a subscription license for Exabeam and its components?
Once I have this information, I can provide detailed instructions and resources for your specific installation scenario.
Following is a general overview of the two main deployment models:
1. On-premises Deployment:
- Requires manual installation and configuration of Exabeam components on your server infrastructure.
- Offers greater control and flexibility but demands more technical expertise.
- Exabeam provides detailed documentation and installation guides for various operating systems.
2. Exabeam Cloud Deployment:
- Exabeam manages the infrastructure and software, requiring minimal setup on your end.
- Easier and faster to deploy but offers less customization options.
- Exabeam provides deployment instructions and support for their cloud service.
In addition to the deployment model, Exabeam has various components, each with its own installation requirements. These components include:
- Site Collector: Manages data collection and processing.
- Fusion Center: Provides user interface for investigation and analysis.
- Exabeam Collectors: Collect data from various security tools and devices.
Basic Tutorials of Exabeam: Getting Started

While providing full step-by-step tutorials for Exabeam would require tailoring to your specific environment and desired outcomes, I can offer a general framework to get you started with its basic functionalities:
1. Set Up Your Exabeam Environment:
- Deployment Model:
- On-premises: Follow Exabeam’s detailed installation guides for your chosen operating system (Red Hat, Ubuntu, Windows). Configure components like Site Collector and Fusion Center.
- Exabeam Cloud: Follow Exabeam’s cloud deployment instructions. Access the platform through your web browser.
- Integrations: Connect Exabeam with your existing security tools and services using available connectors.
2. Explore Data Ingestion and Management:
- Define data sources: Add the security tools, endpoints, and cloud platforms you want to gather data from.
- Configure data collection: Set up filters and schedules for data ingestion, balancing capture volume with performance.
- Monitor data flow: Use dashboards and reports to monitor data collection status and identify any issues.
3. Start Detecting Threats with Basic Analytics:
- Pre-built Correlations: Apply Exabeam’s pre-built correlation rules to detect common threat patterns and suspicious activities.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Define user baselines and monitor for anomalous behavior like unusual login times or data access patterns.
- Basic Alerting: Configure basic alerts to be triggered on specific events or exceeding certain thresholds.
4. Investigate and Respond to Detected Threats:
- Alert Investigation: View details of triggered alerts, including contextual information and timelines.
- Log Search and Filtering: Deep dive into logs to investigate suspicious activity and gather evidence.
- Automated Response Actions: Implement basic pre-defined actions like account lockouts or data quarantine for specific alerts.
5. Further Exploration and Learning:
- Advanced Analytics: As you gain familiarity, explore more complex analytics capabilities like custom correlation rules and machine learning models.
- Threat Hunting: Leverage Exabeam’s hunting tools to proactively search for specific threats or indicators of compromise (IOCs).
- Reporting and Compliance: Generate reports on security posture, incidents, and compliance requirements.
Say goodbye to the hassles of bike ownership! MotoShare.in offers affordable rentals, whether you need a scooter for errands, a bike for a road trip, or a reliable ride to explore new cities.

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
