
SysOps (Systems Operations) refers to the practice of managing and maintaining an organization’s IT systems and infrastructure, including servers, networks, databases, and other components. SysOps professionals are responsible for ensuring the reliability, availability, and performance of IT systems to support business operations.
SysOps involves tasks such as system configuration, monitoring, performance optimization, security management, troubleshooting, and ensuring compliance with best practices and industry standards. The role of SysOps is crucial in maintaining a stable and efficient IT environment that meets the needs of the organization.
Key Aspects of SysOps:
- System Configuration: SysOps professionals configure and set up IT systems, including hardware, software, and network components.
- Monitoring and Alerting: SysOps monitors system performance and health, using alerts to detect and respond to issues promptly.
- Performance Optimization: SysOps optimizes system performance by adjusting settings and resources to achieve optimal efficiency.
- Security Management: SysOps implements security measures to protect systems from threats, vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access.
- Troubleshooting: SysOps troubleshoots and resolves technical issues that arise in IT systems, minimizing downtime.
- Backup and Recovery: SysOps establishes backup and recovery processes to ensure data integrity and facilitate disaster recovery.
- Patch and Update Management: SysOps applies patches, updates, and software upgrades to keep systems secure and up-to-date.
Why Do We Need SysOps?
- System Reliability: SysOps ensures that IT systems are reliable and available to support business operations.
- Performance Optimization: SysOps optimizes system performance, enhancing the efficiency and responsiveness of IT resources.
- Security: SysOps implements security measures to protect systems and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Problem Resolution: SysOps identifies and resolves technical issues to minimize disruptions and downtime.
- Resource Management: SysOps manages resources like servers, storage, and network bandwidth to ensure efficient utilization.
- Data Integrity: SysOps establishes backup and recovery processes to ensure data integrity and facilitate disaster recovery.
- Compliance: SysOps ensures that systems adhere to industry standards and compliance requirements.
- Cost Efficiency: SysOps optimizes resource utilization to reduce IT infrastructure costs.
- User Experience: SysOps contributes to a positive user experience by maintaining responsive and reliable IT systems.
- Innovation Support: SysOps provides a stable platform for innovation by maintaining a reliable IT environment.
- Scaling: SysOps facilitates the scaling of IT systems to accommodate growing demands.
- Integration: SysOps integrates different components and services to ensure seamless functioning.
SysOps plays a critical role in managing and maintaining IT systems to ensure their reliability, security, and performance. It supports business operations, mitigates risks, and contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s IT environment.
What is the Advantage of SysOps?
- System Reliability: SysOps ensures that IT systems are reliable and available to support business operations, reducing downtime and disruptions.
- Performance Optimization: SysOps optimizes system performance, enhancing the efficiency and responsiveness of IT resources.
- Security: SysOps implements security measures to protect systems and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Problem Resolution: SysOps identifies and resolves technical issues to minimize disruptions and downtime, ensuring smooth operations.
- Resource Management: SysOps efficiently manages resources like servers, storage, and network bandwidth, reducing costs and optimizing utilization.
- Data Integrity: SysOps establishes backup and recovery processes to ensure data integrity and facilitate disaster recovery.
- Compliance: SysOps ensures that systems adhere to industry standards and compliance requirements, avoiding regulatory issues.
- User Experience: SysOps contributes to a positive user experience by maintaining responsive and reliable IT systems.
- Innovation Support: SysOps provides a stable platform for innovation by maintaining a reliable IT environment that supports new initiatives.
- Scaling: SysOps facilitates the scaling of IT systems to accommodate growing demands, ensuring performance remains consistent.
- Integration: SysOps integrates different components and services to ensure seamless functioning and communication.
What is the feature of SysOps?
- System Configuration: SysOps professionals configure and set up hardware, software, and network components to ensure proper functioning.
- Monitoring and Alerting: SysOps monitors system performance and health, using alerts to detect and respond to issues promptly.
- Performance Optimization: SysOps optimizes system performance by adjusting settings, resources, and configurations.
- Security Management: SysOps implements security measures, including firewalls, access controls, and encryption, to protect systems and data.
- Troubleshooting: SysOps troubleshoots and resolves technical issues, using diagnostic tools and expertise to maintain system integrity.
- Backup and Recovery: SysOps establishes backup and recovery processes to ensure data is protected and can be restored in case of failures.
- Patch and Update Management: SysOps applies patches, updates, and software upgrades to keep systems secure and up-to-date.
- Automation: SysOps employs automation to streamline routine tasks, reducing manual intervention and improving operational efficiency.
- Capacity Planning: SysOps performs capacity planning to ensure IT resources can handle expected workloads and demands.
- Change Management: SysOps manages changes to systems and infrastructure to minimize risks and ensure stability.
- Configuration Management: SysOps maintains consistent and up-to-date configurations to prevent inconsistencies and drift.
- Scalability: SysOps designs systems to be scalable, allowing for growth without compromising performance.
- Security Auditing: SysOps conducts regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
- Vendor Management: SysOps manages relationships with vendors and third-party providers for hardware, software, and services.
- Documentation: SysOps maintains thorough documentation of systems, configurations, and procedures.
SysOps offers various advantages by ensuring the reliability, security, and performance of IT systems and infrastructure. Its features encompass a range of practices and processes that support efficient and effective IT operations, ultimately contributing to the success of an organization’s business objectives.
What is the Top 10 Use cases of SysOps?
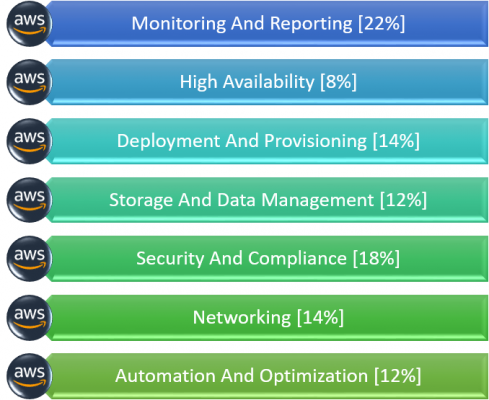
Here are some of the top 10 use cases of SysOps:
- System administration: SysOps engineers can use their skills to administer systems, such as servers, storage, and networks. This can help to ensure that systems are up and running and that they are secure.
- DevOps: SysOps engineers can use their skills to support DevOps teams. This can involve automating tasks, managing infrastructure, and monitoring systems.
- Cloud computing: SysOps engineers can use their skills to manage cloud computing environments. This can involve provisioning and configuring resources, monitoring performance, and troubleshooting problems.
- Security: SysOps engineers can use their skills to secure systems. This can involve implementing security controls, monitoring for threats, and responding to incidents.
- Compliance: SysOps engineers can use their skills to ensure that systems comply with regulations. This can involve implementing compliance controls, monitoring for compliance violations, and responding to audits.
- Capacity planning: SysOps engineers can use their skills to plan for the capacity needs of systems. This can involve forecasting demand, sizing resources, and managing costs.
- Performance tuning: SysOps engineers can use their skills to tune the performance of systems. This can involve optimizing configurations, configuring caching, and monitoring performance metrics.
- Backup and disaster recovery: SysOps engineers can use their skills to implement backup and disaster recovery solutions. This can involve backing up data, testing recovery procedures, and monitoring for failures.
- Monitoring and alerting: SysOps engineers can use their skills to monitor systems and generate alerts. This can involve monitoring performance metrics, detecting anomalies, and notifying stakeholders.
- Change management: SysOps engineers can use their skills to manage changes to systems. This can involve planning changes, communicating changes, and testing changes.
The following are the steps involved in implementing SysOps:
- Define your goals: The first step is to define your goals for SysOps. What do you want to achieve by implementing SysOps? Do you want to improve efficiency, reliability, security, or compliance?
- Assess your current state: The next step is to assess your current state of SysOps. What are your strengths and weaknesses? What are your biggest challenges?
- Choose the right tools and technologies: There are a number of tools and technologies available for SysOps. Choose the tools and technologies that are right for your needs and that will help you achieve your goals.
- Implement the tools and technologies: The next step is to implement the tools and technologies that you have chosen. This may involve training your staff on how to use the new tools and technologies.
- Monitor and improve: The final step is to monitor and improve your SysOps practices. This involves collecting data on the performance of SysOps and using this data to identify areas for improvement.
Implementing SysOps can be a complex and challenging undertaking, but it can be very rewarding. By following these steps, you can implement SysOps and achieve your goals.
How to Get certified in SysOps?
- DevOpsSchool.com
- scmGalaxy.com
- BestDevOps.com
- Cotocus.com

Here are some of the ways to get certified in SysOps:
- Take a course: There are many online and in-person courses available that teach the fundamentals of SysOps. These courses can help you learn the key concepts and principles of SysOps, as well as the tools and technologies used in this field.
- Get certified by a vendor: There are a number of vendors that offer SysOps certifications. These certifications can be a good way to demonstrate your skills and knowledge to potential employers.
- Contribute to an open source project: There are many open source projects that are related to SysOps. Contributing to these projects can help you learn about the practical application of SysOps concepts and technologies.
- Get a job in SysOps: One of the best ways to learn SysOps is to get a job in this field. This will give you the opportunity to work with experienced SysOps professionals and learn from them.
Here are some of the resources that you can consider for learning SysOps:
- Books and articles: There are many books and articles available that discuss SysOps. These resources can help you learn more about the history of SysOps, the different approaches to SysOps, and the challenges and opportunities that SysOps presents.
- Online courses: There are many online courses available that teach the fundamentals of SysOps. These courses can help you learn the key concepts and principles of SysOps, as well as the tools and technologies used in this field.
- Conferences and meetups: There are many conferences and meetups that focus on SysOps. These events can be a great way to learn about the latest trends in SysOps, network with other SysOps professionals, and get hands-on experience with SysOps tools and technologies.
- Get involved in open source projects: There are many open source projects that are related to SysOps. Getting involved in these projects can help you learn about the practical application of SysOps concepts and technologies.
- Contribute to a SysOps community: There are many online communities and forums where SysOps professionals discuss their work. Joining these communities can be a great way to learn from others, get help with your own work, and stay up-to-date on the latest developments in SysOps.
How to Learn SysOps?
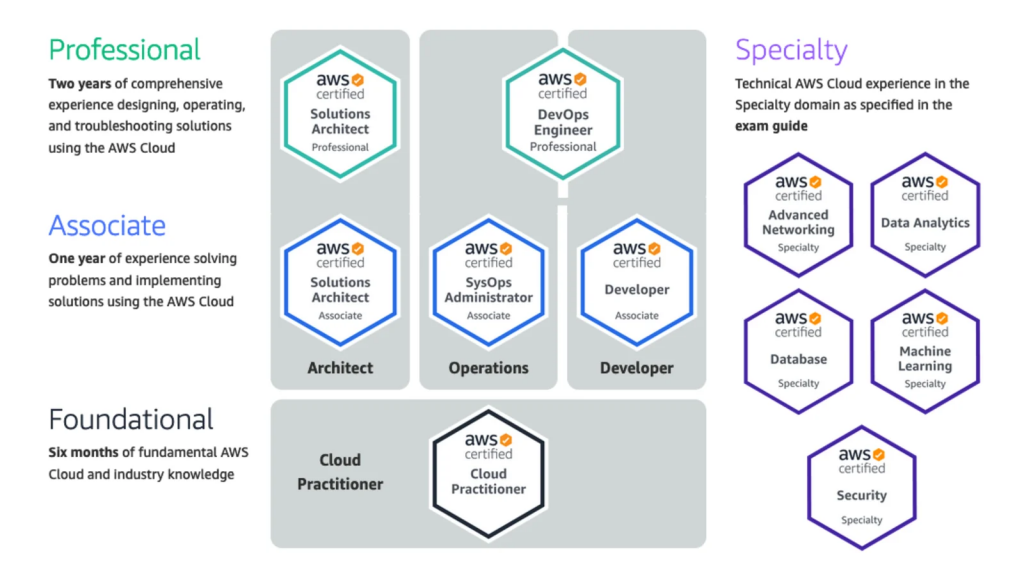
The best way to learn SysOps is to find a combination of methods that works for you. Some people prefer to take courses, while others prefer to read books and articles. Some people prefer to attend conferences and meetups, while others prefer to get involved in open source projects or contribute to SysOps communities. The most important thing is to find a way to learn that is engaging and that helps you retain the information.
The following are the additional tips for learning SysOps:
- Start with the basics: Before you dive into the more advanced topics, make sure you understand the basics of system administration, such as operating systems, networking, and storage.
- Find a mentor: A mentor can be a great way to learn SysOps. A mentor can give you better assistance and guide support, and they can aid you in troubleshooting issues.
- Be patient: Learning SysOps takes time and effort. Don’t get discontinued if you don’t understand everything in a true manner. Just keep learning and practicing, and you will eventually master the concepts and technologies of SysOps.
Email- contact@devopsschool.com

 Starting: 1st of Every Month
Starting: 1st of Every Month  +91 8409492687
+91 8409492687  Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
Contact@DevOpsSchool.com
