HTTP vs WebSocket Vs REST
HTTP vs WebSocket Vs REST
Comparison: HTTP vs WebSocket vs REST
When designing APIs or communication protocols for applications, developers often choose between HTTP, WebSocket, and REST based on use case, efficiency, and scalability. Below is a detailed comparison:
 Quick Overview
Quick Overview
| Feature | HTTP | WebSocket | REST |
|----------|---------|--------------|---------|
| Type | Request-Response | Persistent, Full-Duplex | Request-Response |
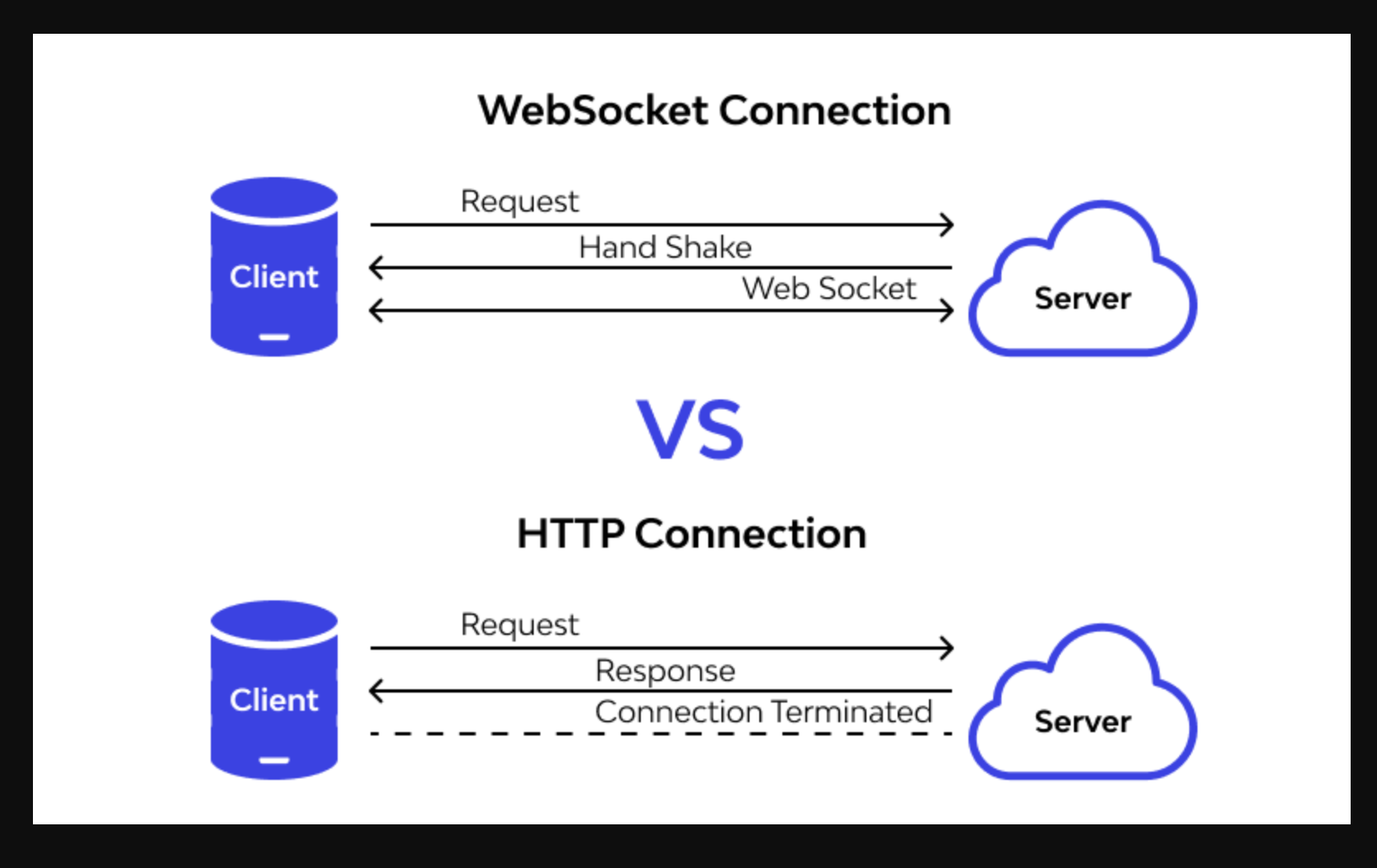
| Communication Model | Client sends request, server responds | Real-time bidirectional communication | Stateless API using HTTP |
| Connection | Opens & closes with each request | Persistent connection | Stateless (new connection per request) |
| Performance | Latency due to handshaking | Low latency, efficient | Moderate performance |
| Data Format | Plain text, JSON, XML | JSON, Binary, Text | JSON, XML, HTML |
| Best Use Cases | Web pages, file downloads | Chat apps, live feeds, gaming | APIs, microservices |
| Security | HTTPS (SSL/TLS) | WSS (SSL/TLS) | HTTPS (SSL/TLS) |
| Scalability | High but may require caching | Requires WebSocket support | Highly scalable with caching |
 What is HTTP?
What is HTTP?
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a request-response protocol used for communication between clients (browsers, mobile apps, APIs) and servers.
 Key Features of HTTP
Key Features of HTTP
- Stateless → Every request is independent and does not retain session state.
- Client-initiated → The client always sends a request, and the server responds.
- Uses TCP → Runs over port 80 (HTTP) or port 443 (HTTPS).
- Text-based format → Uses JSON, XML, or HTML for requests and responses.
 When to Use HTTP?
When to Use HTTP?
 Web pages, form submissions.
Web pages, form submissions.
 RESTful APIs and Microservices.
RESTful APIs and Microservices.
 File downloads and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
File downloads and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
 What is WebSocket?
What is WebSocket?
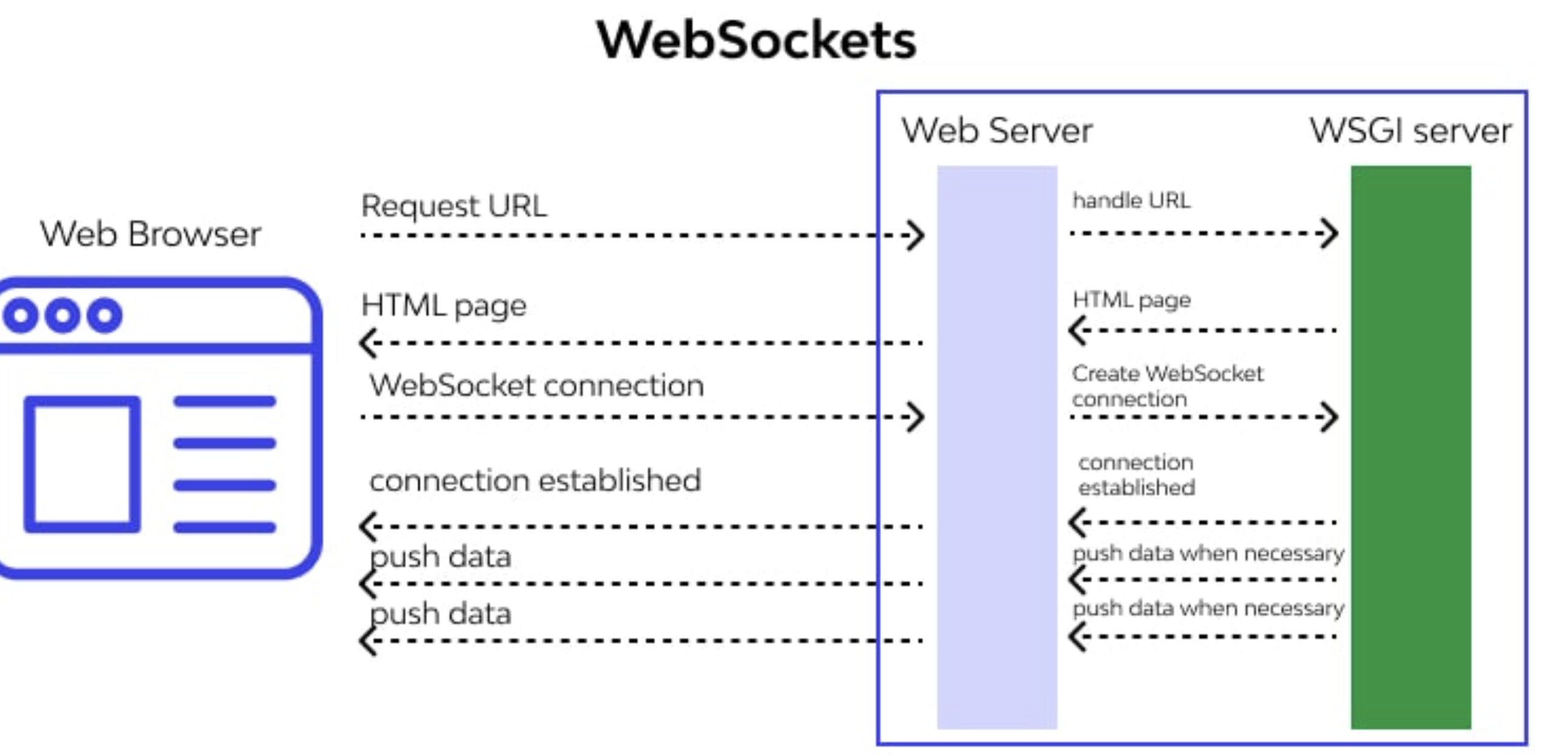
WebSocket is a full-duplex, bidirectional protocol that allows real-time communication between clients and servers.
 Key Features of WebSocket
Key Features of WebSocket
- Persistent connection → The connection remains open after handshake.
- Low latency → Ideal for real-time applications.
- Push-capable → The server can send messages without waiting for a request.
- Uses TCP (Port 80/443) → Upgrades HTTP to ws:// or wss://.
 When to Use WebSocket?
When to Use WebSocket?
 Live chat applications (WhatsApp, Slack).
Live chat applications (WhatsApp, Slack).
 Stock market tickers & financial dashboards.
Stock market tickers & financial dashboards.
 Online gaming (real-time player updates).
Online gaming (real-time player updates).
 Live notifications and collaborative apps.
Live notifications and collaborative apps.
 What is REST?
What is REST?
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for designing web APIs that communicate over HTTP.
 Key Features of REST
Key Features of REST
- Stateless → Each request from a client contains all necessary information.
- Standardized methods → Uses GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH.
- Scalable & flexible → Can be cached and used with load balancers.
- Uses JSON/XML → Common for web APIs.
 When to Use REST?
When to Use REST?
 Web applications (CRUD operations).
Web applications (CRUD operations).
 Mobile apps consuming backend APIs.
Mobile apps consuming backend APIs.
 Microservices architecture (communication between services).
Microservices architecture (communication between services).
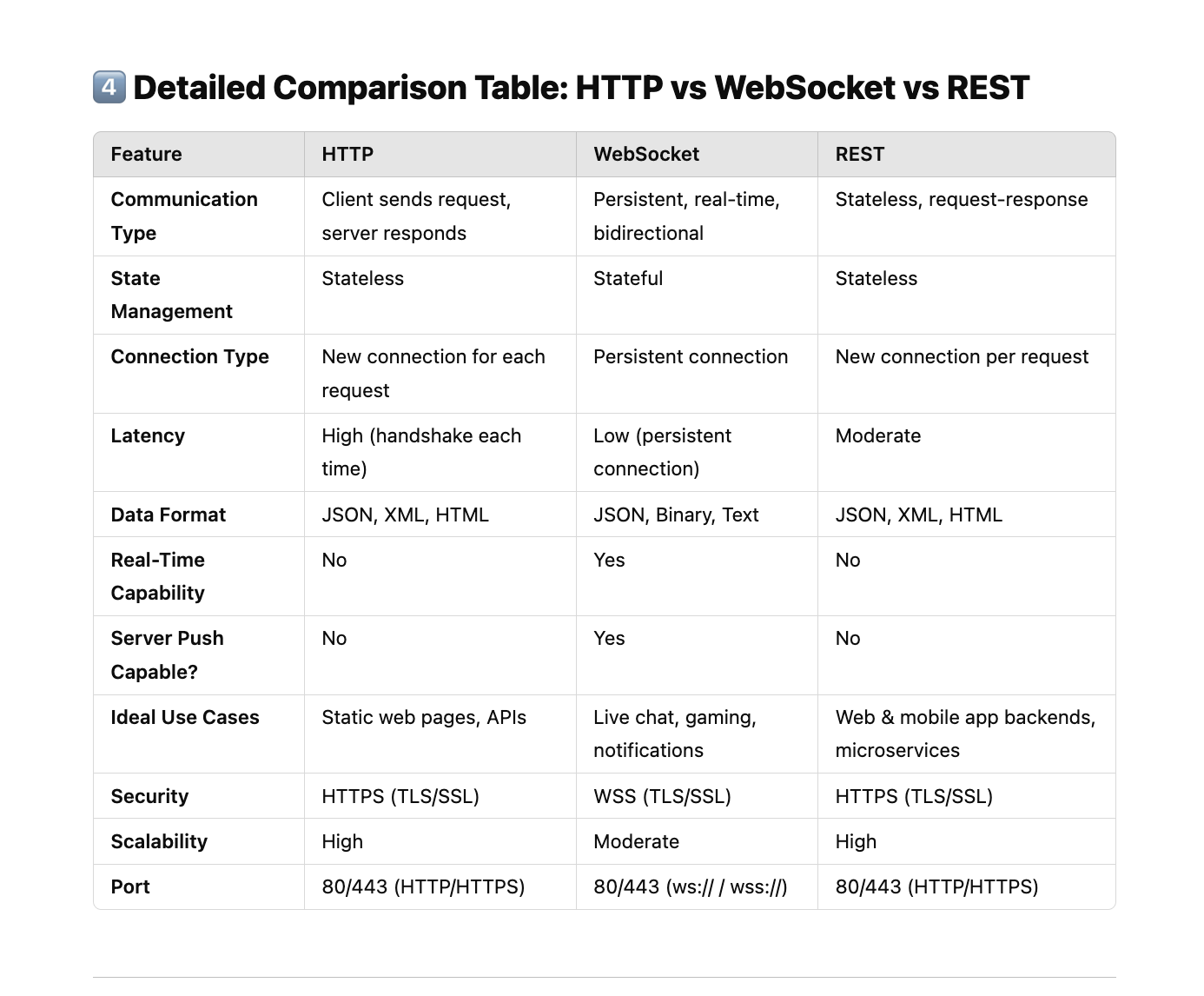
 Detailed Comparison Table: HTTP vs WebSocket vs REST
Detailed Comparison Table: HTTP vs WebSocket vs REST
| Feature | HTTP | WebSocket | REST |
|---------|---------|--------------|---------|
| Communication Type | Client sends request, server responds | Persistent, real-time, bidirectional | Stateless, request-response |
| State Management | Stateless | Stateful | Stateless |
| Connection Type | New connection for each request | Persistent connection | New connection per request |
| Latency | High (handshake each time) | Low (persistent connection) | Moderate |
| Data Format | JSON, XML, HTML | JSON, Binary, Text | JSON, XML, HTML |
| Real-Time Capability | No | Yes | No |
| Server Push Capable? | No | Yes | No |
| Ideal Use Cases | Static web pages, APIs | Live chat, gaming, notifications | Web & mobile app backends, microservices |
| Security | HTTPS (TLS/SSL) | WSS (TLS/SSL) | HTTPS (TLS/SSL) |
| Scalability | High | Moderate | High |
| Port | 80/443 (HTTP/HTTPS) | 80/443 (ws:// / wss://) | 80/443 (HTTP/HTTPS) |
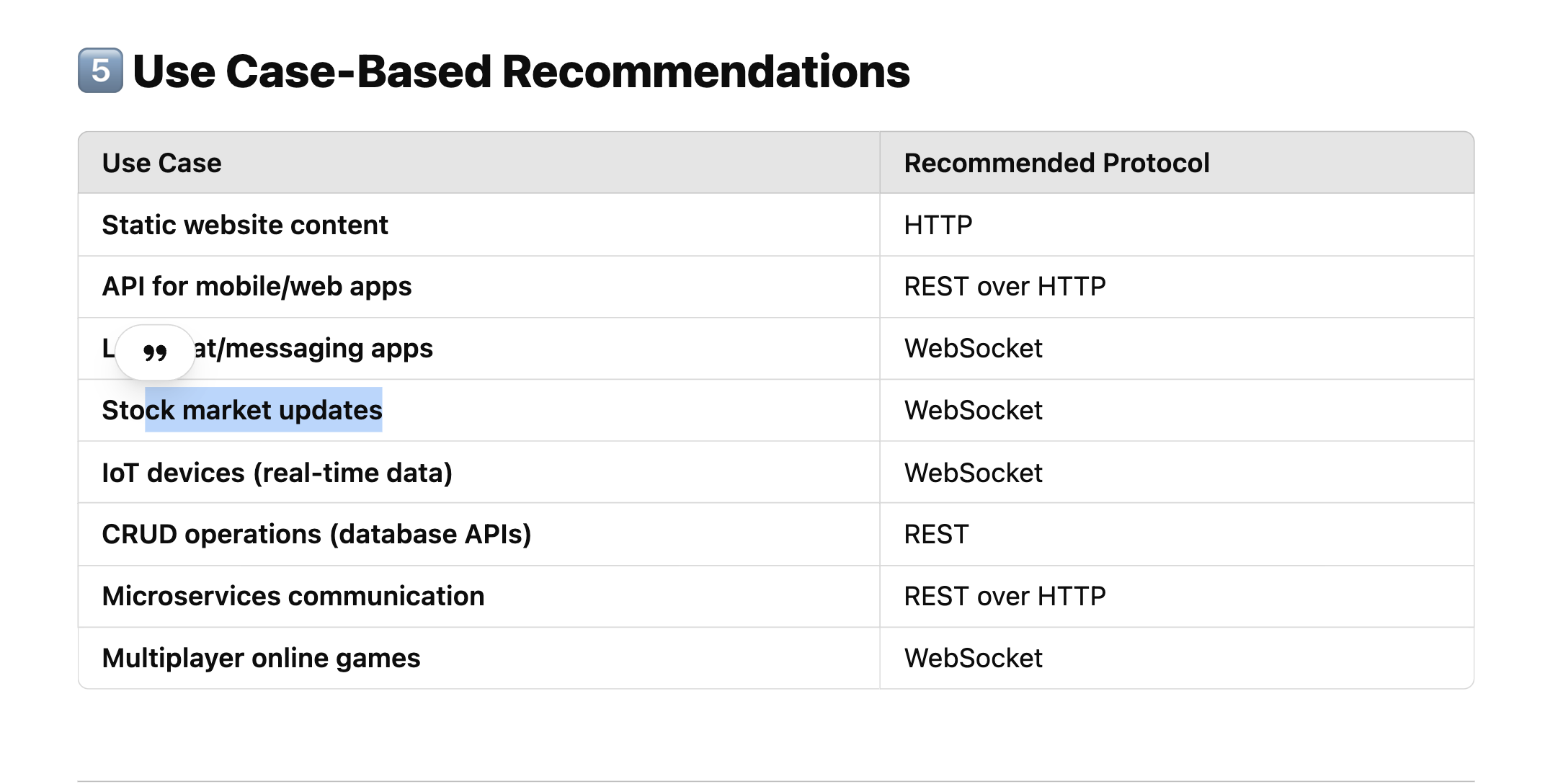
 Use Case-Based Recommendations
Use Case-Based Recommendations
| Use Case | Recommended Protocol |
|----------|------------------|
| Static website content | HTTP |
| API for mobile/web apps | REST over HTTP |
| Live chat/messaging apps | WebSocket |
| Stock market updates | WebSocket |
| IoT devices (real-time data) | WebSocket |
| CRUD operations (database APIs) | REST |
| Microservices communication | REST over HTTP |
| Multiplayer online games | WebSocket |
 Summary & Conclusion
Summary & Conclusion
| Criteria | Best Choice |
|-------------|--------------|
| Best for Static Content Delivery | HTTP |
| Best for API Communication | REST |
| Best for Real-Time Communication | WebSocket |
 Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Use HTTP for general web communication (e.g., website browsing).
- Use WebSockets for real-time applications (e.g., chat apps, live notifications).
- Use REST for scalable web APIs (e.g., backend services).