Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients
Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients
 Difference Between Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients in Confluent Kafka
Difference Between Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients in Confluent Kafka
Confluent Kafka provides various tools for event streaming and real-time data processing. The key components include Topics, ksqlDB, Connectors, and Clients, each serving a distinct role.
 Topics (Core Kafka Component)
Topics (Core Kafka Component)
 What Are Kafka Topics?
What Are Kafka Topics?
- Kafka Topics are logical channels where messages (events) are published by producers and consumed by consumers.
- They act as distributed logs storing ordered events.
- Producers write data to a topic, and consumers read from it.
 Use Case of Topics
Use Case of Topics
- Used for event-driven applications.
- Acts as a buffer between producers and consumers.
- Example: A payment service publishes transactions to a "payments" topic, and a fraud detection service consumes those events.
 Key Features
Key Features
- Supports multiple partitions for parallelism.
- Retains messages based on retention policies (time-based or size-based).
- Enables real-time streaming and event sourcing.
 ksqlDB (Real-time SQL Processing on Kafka)
ksqlDB (Real-time SQL Processing on Kafka)
 What Is ksqlDB?
What Is ksqlDB?
- ksqlDB is a SQL engine for Kafka that allows users to query and process real-time streaming data without writing Java/Python code.
- It enables stateful stream processing on Kafka topics using SQL-like queries.
 Use Case of ksqlDB
Use Case of ksqlDB
- Real-time data transformation, aggregation, filtering, and joins across Kafka topics.
- Example: If a topic contains raw clickstream data, you can use ksqlDB to filter only clicks from India and write the output to another topic.
 Key Features
Key Features
- SQL-based stream processing (easier than Java/Python Kafka Streams API).
- Real-time analytics on Kafka events.
- Stateful computations (aggregations, windows, joins).
- Materialized views for fast querying.
 Example Query in ksqlDB
Example Query in ksqlDB
CREATE STREAM filtered_users AS
SELECT user_id, page_url FROM user_clicks
WHERE country = 'India'; Kafka Connectors (Data Integration Layer)
Kafka Connectors (Data Integration Layer)
 What Are Kafka Connectors?
What Are Kafka Connectors?
- Kafka Connect provides pre-built connectors to integrate Kafka with external systems (databases, cloud storage, etc.).
- Types:
- Source Connector → Brings data into Kafka from databases, APIs, etc.
- Sink Connector → Sends data from Kafka to databases, Elasticsearch, S3, etc..
 Use Case of Kafka Connect
Use Case of Kafka Connect
- Moves data from an external database to Kafka (CDC) or from Kafka to a data warehouse.
- Example:
- A JDBC Source Connector reads customer data from MySQL and sends it to a Kafka topic.
- A S3 Sink Connector stores Kafka topic data in Amazon S3.
 Key Features
Key Features
- Pre-built connectors for MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, AWS S3, Elasticsearch, etc.
- Scalable & distributed data movement.
- Fault-tolerant & auto-retry mechanisms.
 Example Connector Configuration (JDBC Source)
Example Connector Configuration (JDBC Source)
{
"name": "jdbc-source",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSourceConnector",
"connection.url": "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb",
"topic.prefix": "mysql-data-"
}
} Kafka Clients (Producers & Consumers)
Kafka Clients (Producers & Consumers)
 What Are Kafka Clients?
What Are Kafka Clients?
- Kafka Clients are the applications that produce or consume messages from Kafka topics.
- Clients use Kafka APIs to interact with topics.
 Use Case of Kafka Clients
Use Case of Kafka Clients
- Producers send data to Kafka topics.
- Consumers read data from Kafka topics.
- Example: A Python application writes stock prices to Kafka, and a Java application reads and processes them.
 Key Features
Key Features
- Available in multiple languages: Java, Python, Go, C++, .NET.
- Supports batch & real-time data processing.
- Uses consumer groups for parallel processing.
 Example Python Producer (Kafka Client)
Example Python Producer (Kafka Client)
from kafka import KafkaProducer
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092')
producer.send('stock-prices', key=b'TSLA', value=b'900') Example Java Consumer (Kafka Client)
Example Java Consumer (Kafka Client)
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("stock-prices"));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
System.out.println(record.value());
}
}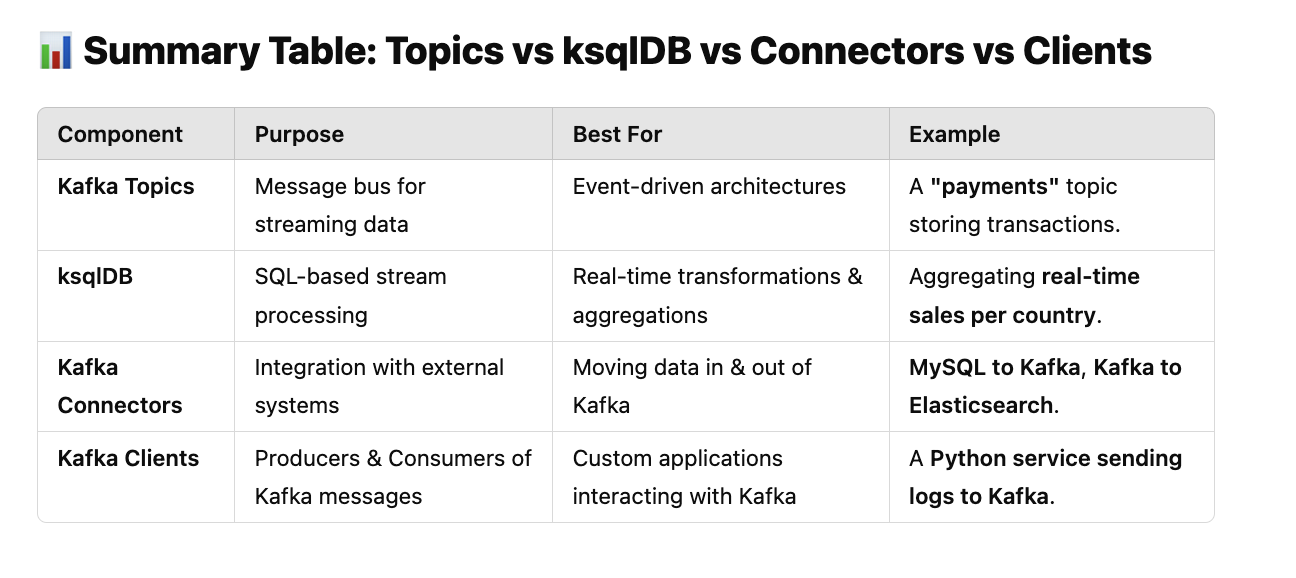
 Summary Table: Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients
Summary Table: Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients
| Component | Purpose | Best For | Example |
|--------------|------------|--------------|-------------|
| Kafka Topics | Message bus for streaming data | Event-driven architectures | A "payments" topic storing transactions. |
| ksqlDB | SQL-based stream processing | Real-time transformations & aggregations | Aggregating real-time sales per country. |
| Kafka Connectors | Integration with external systems | Moving data in & out of Kafka | MySQL to Kafka, Kafka to Elasticsearch. |
| Kafka Clients | Producers & Consumers of Kafka messages | Custom applications interacting with Kafka | A Python service sending logs to Kafka. |
 When to Use What?
When to Use What?
 Use Kafka Topics:
Use Kafka Topics:
- If you need a scalable message queue for real-time streaming.
 Use ksqlDB:
Use ksqlDB:
- If you want to process, transform, and filter Kafka streams using SQL.
 Use Kafka Connectors:
Use Kafka Connectors:
- If you need to move data between Kafka and databases/cloud storage.
 Use Kafka Clients:
Use Kafka Clients:
- If you need custom producers and consumers in Java, Python, etc.