
Analyzing Machine Data with Datadog
by DevOpsSchool.com
Rajesh Kumar
(Senior DevOps Manager & Principal Architect)

-
DevOps@RajeshKumar.xyz
www.rajeshkumar.xyz
/RajeshKumarLog
/RajeshKumarIN
/RajeshKumarIN
Rajesh Kumar — an award-winning academician and consultant trainer, with 15+ years’ experience in diverse skill management, who has more than a decade of experience in training large and diverse groups across multiple industry sectors.
Outline
Module 1: Introducing NewRelic Logs
Module 2: NewRelic Components
Module 3: Installing NewRelic
Module 4: Getting Data In
Module 5: Basic Search

Prerequisite
Basic Windows Administration
Basic Linux Administration
Windows Environment Linux
Environment

Common Mistakes

Huge mistake!!!
“Well there’s usually enough money in the bank, so who needs to plan and budget?”







What is Log?
Log = record related to whatever activities occurring on an information system
Also: alert, "event", alarm, message, record, etc

Log Data Sources
- IDS
- Firewalls/IPS
- Anti-maleware
- Proxies
- Network Infrastructure
- Servers
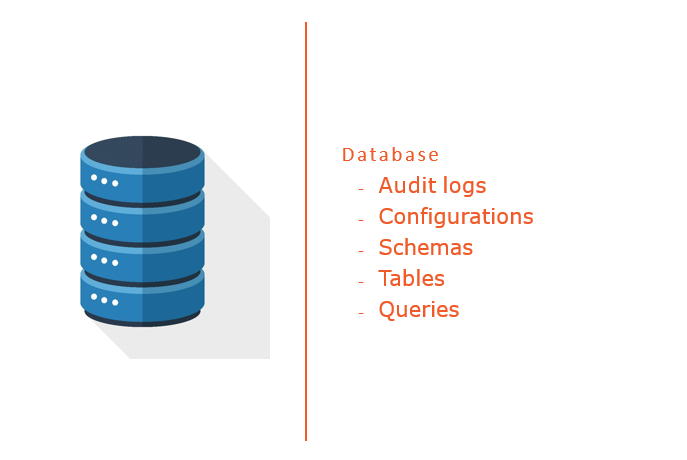
- Databases
- Application
Machine Data & Log
Data generated by machines, computer processing, applications and sensor data.




Analyzing Log Data: Why It’s Important?
- Production Monitoring and Debugging
- Resource Usage
- HTTP Errors
- Slow Queries
- Rogue Automated Robots
- Security Issues
Analyzing Log Data: Why It’s Important
- Tracking Your Site’s/Platform’s Visitors
- Situational awareness and new threat discovery
- Getting more value out of network and security infrastructures
- Extracting what is really actionable automatically
- Measuring security (metrics, trends, etc)
- Compliance an regulations
- Incident response (last, but not least)
What to look for in Logs?
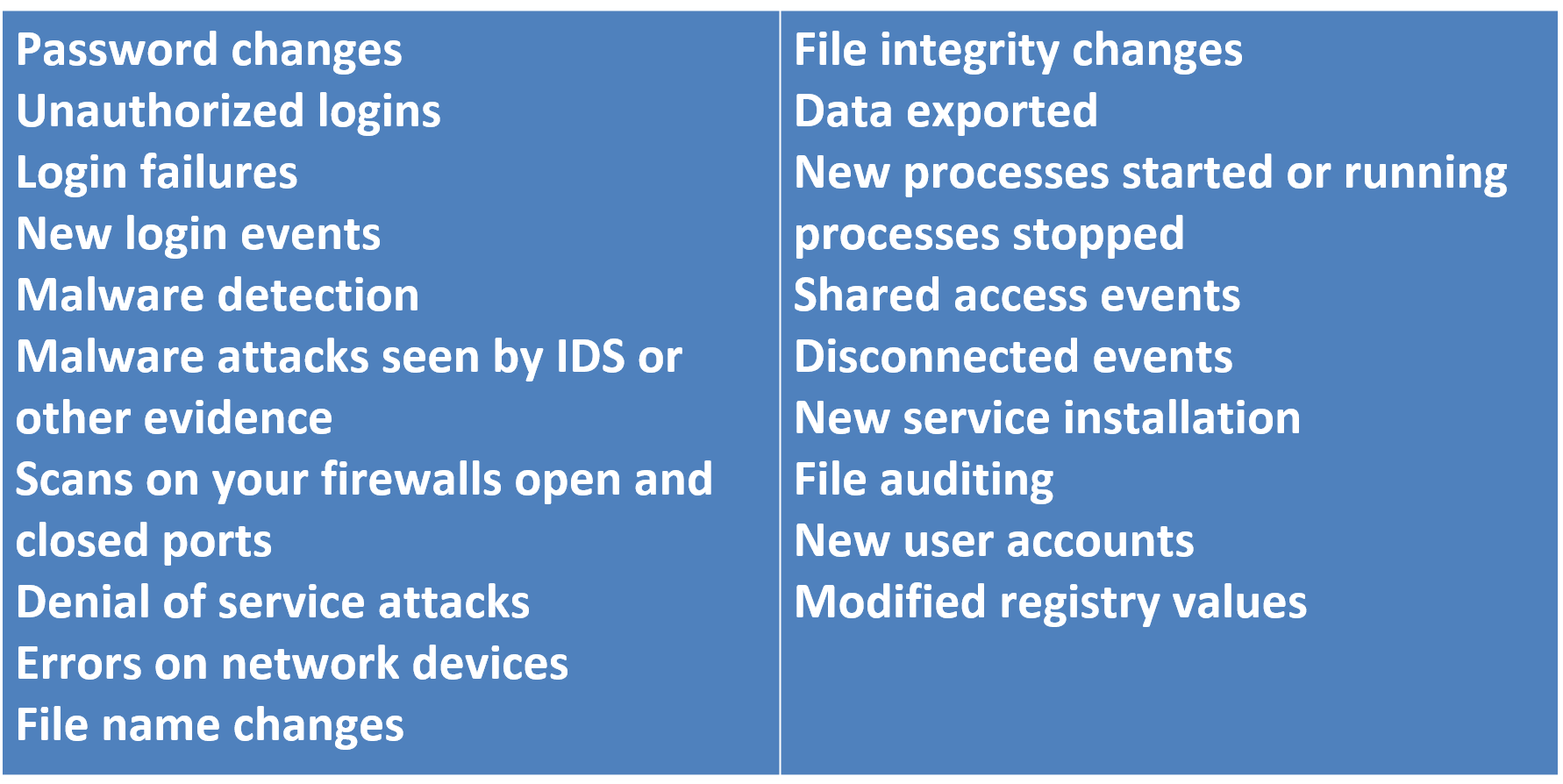
Common Fields in Log
Time
Source
Destination
Protocol
Port(s)
User name
Event/Attach type
Bytes exchanged
Best Practices For Log Analysis
Pattern detection and recognition: to filter messages based on a pattern book.
Normalization: to convert different log elements such as dates to the same format.
Tagging and classification: to tag log elements with keywords and categorize them into a number of classes so you can filter and adjust the way you display your data.
Correlation analysis: to collate logs from different sources and systems and sort meaningful messages that pertain to a particular event. This helps discover connections between data not visible in a single log. For instance, if you have just experienced a cyber attack, correlation analysis would put together the logs generated by your servers, firewalls, network devices, & other sources, and find the messages that are relevant to that particular attack.
Artificial ignorance: a machine learning process to identify and “ignore” log entries that are not useful and detect anomalies.
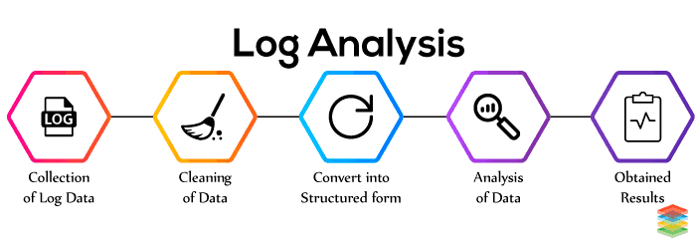


Datdog Workflow

Analyzing Log Files

What Data?
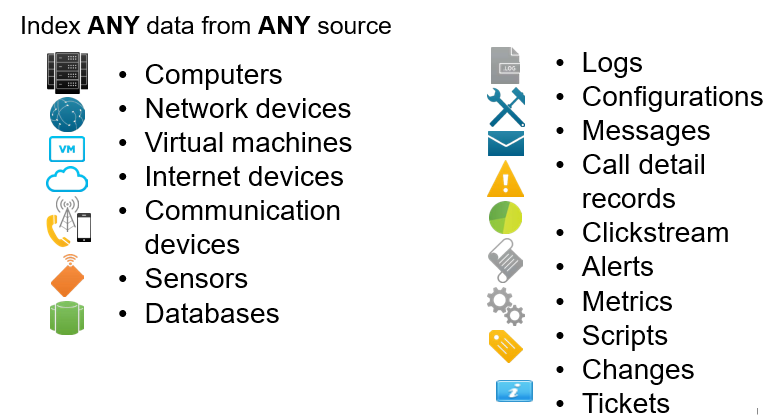
Get started log management with Datadog
Datadog Log Management: Rapid Troubleshooting
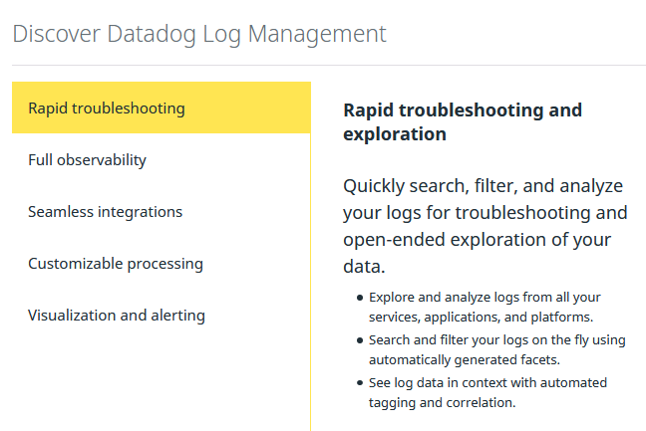
Datadog Log Management: Full observability

Datadog Log Management: Seamless Integration
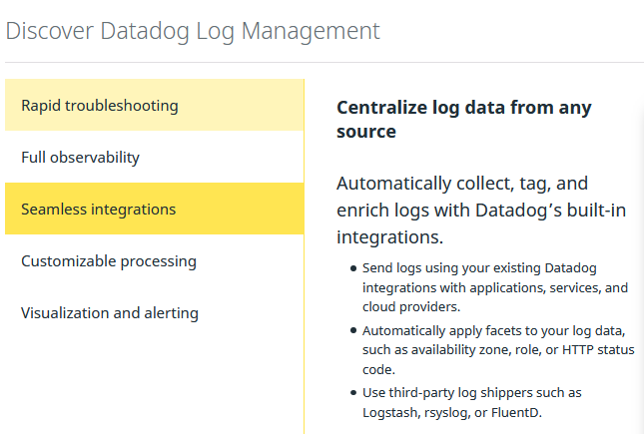
Datadog Log Management: Customizable Processing

Datadog Log Management: Visualization and Alerting

Sending Logs to Datadog
- Sending logs manually
- Send logs from a file
Sending Logs to Datadog: Sending logs manually
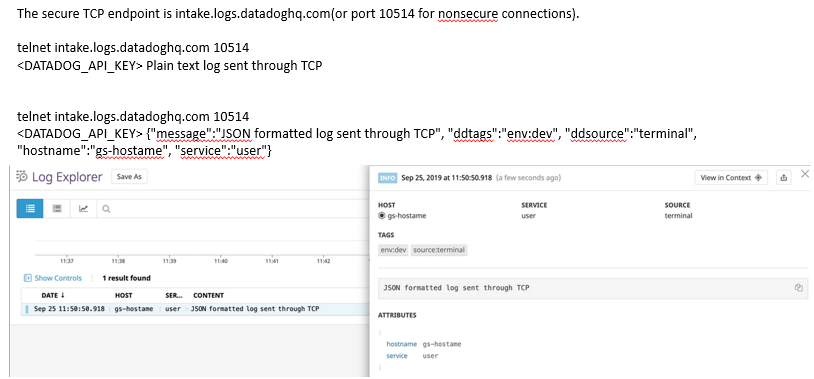
Sending Logs to Datadog: Send logs from a file

DevOpsSchool Community Networks
These platforms provide you the opportunity to connect with peers and industry DevOps leaders, where you can share, discuss or get information on latest topics or happenings in DevOps culture and grow your DevOps professionals network.
 |
|---|
| DevOps |
| Build & Release |
 |
|---|
| DevOps |
| Build & Release |
 |
|---|
| DevOpsSchool |
| DevOps Group |
 |
|---|
| BestDevOps.com |

Any Questions?

Thank You!
DevOpsSchool — Lets Learn, Share & Practice DevOps
Connect with us on
contact@devopsschool.com | +91 700 483 5930Next up:

Datadog Course
Datadog APIs Key Tokens
