Ansible most asked FAQ’s and interview questions:-
Q1) what is Ansible?
Ansible is developed in Python language. It is a software tool. It is useful while deploying any application using ssh without any downtime. Using this tool one can manage and configure software applications very easily.
Q2) Ansible Playbooks vs Roles
Roles Playbooks
Roles are reusable subsets of a play. Playbooks contain Plays.
A set of tasks for accomplishing a certain role. Mapps among hosts and roles.
Example: common, webservers. Example: site.yml, fooservers.yml, webservers.yml.
Q3) what are the advantages of using Ansible?
The main three advantages of using this tool are,i.e. Ansible
Agentless
Very low overhead
Good performance
Q4) Compare Ansible VS Puppet
Ansible Puppet
Simplest Technology Complex Technology
Written in YAML languag Written in Ruby language
Automated workflow for Continuous Delivery Visualization and reporting
Agent-less install and deploy Easy install
No support for Windows Support for all major OS’s
GUI -work under progress Good GUI
CLI accepts commands in almost any language Must learn the Puppet DSL
Q5) How does Ansible Works?
There are many similar automation tools available like Puppet, Capistrano, Chef, Salt, Space Walk, etc, but Ansible categorizes into two types of servers: controlling machines and nodes.
The controlling machine, where Ansible is installed and Nodes are managed by this controlling machine over SSH. The location of nodes is specified by the controlling machine through its inventory.
The controlling machine (Ansible) deploys modules to nodes using SSH protocol and these modules are stored temporarily on remote nodes and communicate with the Ansible machine through a JSON connection over the standard output.
Ansible is agent-less, which means no need for any agent installation on remote nodes, so it means there are no background daemons or programs are executing for Ansible when it’s not managing any nodes.
Ansible can handle 100’s of nodes from a single system over an SSH connection and the entire operation can be handled and executed by one single command ‘ansible’. But, in some cases, where you required to execute multiple commands for a deployment, here we can build playbooks.
Q6) what’s the Use of Ansible.
Ansible can be used in IT Infrastructure to manage and deploy software applications to remote nodes. For example, let’s say you need to deploy a single software or multiple software to 100’s of nodes by a single command, here ansible comes into the picture, with the help of Ansible you can deploy as many applications to many nodes with one single command, but you must have a little programming knowledge for understanding the ansible scripts.
We’ve compiled a series on Ansible, title ‘Preparation for the Deployment of your IT Infrastructure with Ansible IT Automation Tool‘, through parts 1-4 and covers the following topics.
Q7) Explain Ansible architecture?
Ansible automation engine is the main component of Ansible, which interacts directly with the configuration management database, cloud services, and various users who write playbooks to execute it.
The following are the components of the Ansible Automation engine:
Modules: Ansible works effectively by connecting nodes and pushing out scripts called “Ansible modules”. It helps to manage packages, system resources, files, libraries, etc.
Inventories: These are the lists of nodes or hosts containing their databases, servers, IP addresses, etc.
APIs: These used for commuting public or private cloud services.
Plugins: Plugins augment Ansible’s core functionality. Also offers extensions and options for the core features of Ansible – transforming data, connecting to inventory, logging output, and more.
Playbooks: Describes the tasks that need to be executed. They are simple code files written in YAML format and can be used to declare configurations, automating tasks, etc.
Hosts: Hosts are node systems that are automated by Ansible on any machine like Linux, RedHat, Windows, etc.
Networking: Ansible can be used to automate multiple networks and services. It uses a secure and simple automation framework for IT operations and development.
Cloud: A system of remote servers that allows you to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server.
CMDB: It is a type of repository which acts as a data warehouse for IT installations.
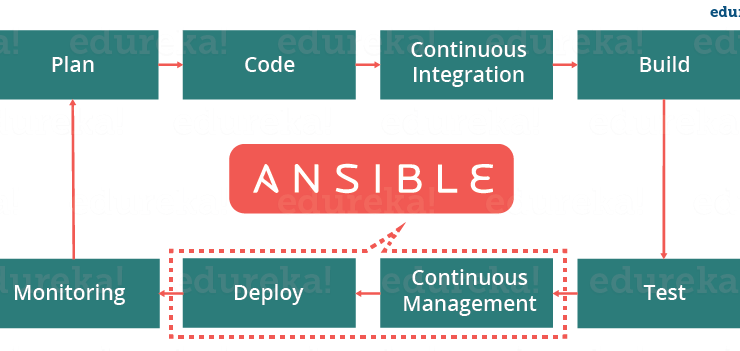
Q8) What is CI/CD? And how Ansible is related to it?
CI/CD is one of the best software development practices to implement and develop code effectively. CI stands for Continuous Integration, and CD stands for continuous delivery. Continuous Integration is a collection of practices that drive developers to implement and check-in code to version control repositories. Continuous delivery picks up where continuous Integration ends. This process builds software in such a way that software will be released into production at any given time.
Ansible is an excellent tool for CI/CD processes, which provide a stable infrastructure to a provision target environment and then deploy the application to it.
Q9) Can you create reusable content with Ansible?
Yes, Ansible has the concept of roles that helps to create reusable content. To create a role, you need to follow Ansible’s conventions of structuring directories and naming files.
Q10) Is Ansible a Configuration management tool?
Configuration management is the practice to handle updates and manage the consistency of a product’s performance over a particular period of time. Ansible is an open-source IT Configuration Management tool, which automates a wide variety of challenges in complex multi-tier IT application environments.
Q11) What are the differences between the variable name and environment variables?
Variable Names Environment Variables
By adding strings, we can build variable names By accessing existing variables, we can access environment variables
Supports adding more strings The advanced playbooks section sets the environment variables.
Use the IPV4 address for variable names. Use {{ansible_env.SOME_VARIABLE}} for remote environment variables
Q12) How to create an empty file with Ansible?
To create an empty file, Ansible uses a file module. For this, we need to set up two parameters.
Path – This place represents the location where the file gets created, either the relative or an absolute path. Also, the name of the file includes here.
State – For creating a new file, this parameter should be set to touch.
Q13) How will you set the environment variable or any path for a task or entire playbook?
To set the environment variables, we use the environment keyword. We’ll use it at the task or other levels in the play:
environment:
PATH: “{{ ansible_env.PATH }}:/thingy/bin”
SOME: value
Q14) How would you describe yourself in terms of what you do and how you’d like to be remembered?
Obviously, I’d like to be remembered as a master of prose who forever changed the face of literature as we know it, but I’m going to have to settle for being remembered as a science fiction writer (and, more and more, critic) who wrote the occasional funny line and picked up a few awards.
Q15) Why are you attracted to science and science fiction?
Early imprinting, maybe, for the science fiction. When I was quite small a family friend let me read his 1950s run of ‘Galaxy’ magazine. My favorite aunt pressed John Wyndham’s ‘The Day of the Triffids’ on me; a more terrifying great-aunt gave me G.K. Chesterton’s fantastic novels; and so on.
The incurable addiction had begun. Meanwhile, science classes just seemed to be the part of a school that made the most sense, and I fell in love with Pelican pop-maths titles – especially Kasner’s and Newman’s ‘Mathematics and the Imagination’ and all those books of Martin Gardner’s ‘Scientific American’ columns.
Q17) Describe your newsletter Ansible and who it’s aimed at.
It appears monthly and has been called the ‘Private Eye’ of science fiction, but isn’t as cruel and doesn’t (I hope) recycle old jokes quite as relentlessly. Though I feel a certain duty to list some bread-and-butter material like conventions, award winners, and deaths in the field, ‘Ansible’ skips the most boring SF news – the long lists of books acquired, books published, book sales figures, major new remainders – in favor of quirkier items and poking fun at SF notables. The most popular departments quote terrible lines from published SF/fantasy and bizarre things said about SF by outsiders (‘As Others See Us’). All the back issues of ‘Ansible’ since it started in 1979 can be read online.
Q18) So how does Ansible work? Please explain in detail?
Within the market, they are many automation tools like Puppet, Capistrano, Chef, Salt, Space Walk, etc.
When it comes to Ansible, this tool is categorized into two types of servers:
1. Controlling machines
2. Nodes
Ansible is an agentless tool so it doesn’t require any mandatory installations on remote nodes. So there are no background programs that are executed while it is managing any nodes.
Ansible is able to handle a lot of nodes from a single system over an SSH connection.
Playbooks are defined as a bunch of commands where they are capable of performing multiple tasks and they are in YAML file format.
Q19) What does Ansible offer?
Ansible offers:
Security and Compliance policy integration
Automated workflow for Continuous Delivery
Simplified orchestration
App deployment
Configuration management
Streamlined provisioning
Q20) Can we manage Windows Nano Server using Ansible?
No, it is not possible to manage Windows Nano Server using Ansible as it doesn’t have full access to the .Net framework, which is primarily used by internal components and modules.
Q21) Do we have any Web Interface/ Rest API etc fo
Yes, Ansible Inc makes a great efficient tool. It is easy to use.
Q22) What is Ansible Tower?
Ansible is classified as a web-based solution which makes Ansible very easy to use. It is considered to be or acts like a hub for all of your automation tasks. The tower is free for usage till 10 nodes.
Q23) What are the features of the Ansible Tower?
Features of the Ansible Tower are:
Ansible Dashboard
Real-time job status updates
Multi-playbook workflows
Who Ran What Job When
Scale capacity with tower clusters
Integrated notifications
Schedule ansible jobs
Manage and track inventory
Remote command execution
REST API & Tower CLI Tool
Q24) How do change the documentation and submit it?
Usually, the documentation is kept in the main project folder in the git repository. For complete instructions on this can be available in docs.
Q25) How do you access Shell Environment Variables?
If you are just looking to access the existing variables then you can use the “env” lookup plugin.
For example:
Accessing the value of Home environment variable on management machine:
local_home:”{{lookup(‘env’,’HOME’)}}”
Q26) How can you speed up management inside EC2?
It is not advised to manage a group of EC2 machines from your laptop. The best way is to connect to a management node inside Ec2 first and then execute Ansible from there.
Q27) Is it possible to increase the Ansible reboot module to more than 600 seconds?
Yes, it is possible to increase the Ansible reboot module to specific values using the below syntax:
– name: Reboot a Linux system
reboot:
reboot_timeout: 1000
Q28) How can you use docker modules in Ansible?
Docker modules require docker-py installed on the host running Ansible.
$ pip install ‘docker-py>=1.7.0’
The docker_service module also requires docker-compose
$ pip install ‘docker-compose>=1.7.0’
Q29) Explain how you will copy files recursively onto a target host?
The copy file in Ansible has a recursive parameter. If you have to copy files for a large number of files, then the synchronizing module is the best choice for it.
– synchronize:
src: /first/absolute/path
dest: /second/absolute/path
delegate_to: “{{ inventory_hostname }}”
Q30) How can you disable cowsay?
If cowsay is installed then executing your playbooks within Ansible is very smooth.
Even if you think that you want to work in a professional cow free environment, then you will have two options:
Uninstall cowsay
Setting up value for the environment variable, like below
Export ANSIBLE_NOCOWS=1
Q31) How can you access a list of Ansible_Variables?
By default, Ansible gathers facts under machines under management. Further, these facts are accessed in Playbooks and in templates. One of the best ways to view a list of all the facts that are available in a machine, then need to run the setup module in the ad-hoc way:
Ansible- m setup hostname
Once this statement is executed, it will print out a dictionary of all the facts that are available for that particular host. This is the best way to access the list of Ansible_variables.
Q32) How can you see all the variables specific to my host?
To see all the host-specific variables, that include all facts and other resources are:
Ansible – m debug- a “var=hostvars[‘hostname’]” localhost
Q33) How do you access a variable name programmatically?
By adding strings together, the variables names are built programmatically like below format:
{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname][‘ansible_’ + which_interface][‘ipv4’][‘address’] }}
‘inventory_hostname’ is a variable that represents the present host you are looping over.
Q34) How to configure a jump host for accessing servers that have no direct access?
We should set a ProxyCommand in the ansible_ssh_common_args inventory variable. For connecting to the relevant host, arguments defined in this variable are added to scp/ssh/sftp command line.
For example,
[gatewayed]
foo ansible_host=192.0.2.1
bar ansible_host=192.0.2.2
With the following contents, create the group_vars/gatewayed.yml
ansible_ssh_common_args: ‘-o ProxyCommand=”ssh -W %h:%p -q user@gateway.example.com”‘
When connecting to any hosts in the group gatewayed, Ansible will append these arguments to the command line.
Q35) Explain how you can generate encrypted passwords for the user module?
Ansible ad-hoc command is the easiest option:
ansible all -i localhost, -m debug -a “msg={{ ‘mypassword’ | password_hash(‘sha512’, ‘mysecret’) }}”
The mkpasswd utility available on the Linux systems is also the best option:
mkpasswd –method=sha-512
Q36) Can you keep data secret in the playbook?
Yes. If any task that you want to keep secret in the playbook when using -v (verbose) mode, the following playbook attribute will be helpful:
– name: secret task
shell: /usr/bin/do_something –value={{ secret_value }}
no_log: True
It hides sensitive information from others and provides the verbose output.
Q37) What is idempotency?
Idempotence is an essential feature of Ansible, which helps you to execute one or more tasks on a server as many times as needed, but without changing the result beyond the initial application.
Q38) Can you create encrypted files with Ansible?
Yes, using the ‘ansible-vault create’ command, we can create encrypted files
$ ansible-vault create filename.yaml
Q39) What is the difference between a playbook and a play?
A playbook is a list of plays. A play is a set of tasks and roles that run on one or more managed hosts. Play includes one or more tasks.
Q40) How will you get access to the ansible host when I delegate a task?
We can access it through host variables and even works for all the overridden variables like ansible_port, ansible_user, etc.
original_host: “{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname][‘ansible_host’] }}”
Q41) Explain the Ansible Tag’s usage?
A tag is an attribute that sets the ansible structure(plays, tasks, roles). When there’s an extensive playbook needed, it’s more useful to run just a part of it as opposed to the entire thing. That’s where tags usage is required.
Q42) How can you filter out tasks in tags?
Use –tags or –skip-tags options on the command line
Use the TAGS_RUN and TAGS_SKIP options, If you’re in Ansible configuration settings.
Q43) What are handlers?
In Ansible, handlers are just like normal tasks in a playbook but run when tasks include the notify directive and also indicate that it changed something. It runs only once after all the tasks executed in a particular play. It automatically loads through roles/<role_name>/handlers/main.yaml.
They are used to trigger the status of a service, such as restarting or stopping a service.
Q44) How will you upgrade Ansible?
Using the command “sudo pip install ansible==<version-number>”, we can easily upgrade Ansible.
Q45) Ansible vs Chef?
Ansible Chef
Ansible is easier to set up and provides faster performance Compared to Ansible, Chef is not very easy to set up
Ansible uses YAML (Python) for managing configurations Chef uses DSL (Ruby) for managing configurations
Highly scalable Highly scalable
Ansible charges annually $10,000 Chef Automate charges an annual fee of $13700
Q46) Why don’t you ship in X format?
They are several reasons for not shipping in X format. In general, it caters to maintainability. Within the market, they are tons of different ways to ship software and it is very tedious to support all of them.
Q47) What is Ansible can do?
Ansible can do the following for us:
Configuration management
Application deployment
Task automation
IT orchestration
Q48) Please define what is Ansible Galaxy?
Ansible Galaxy refers to the website Galaxy where the users will be able to share all the roles to a CLI ( Command Line Interface) where the installation, creation, and managing of roles happen
Q49) Can you explain how to handle various machines requiring different user accounts or ports to log in?
Just by setting inventories in the inventory file, we can handle various machines requiring different user accounts or ports to log in.
For example, the following hosts have different ports and usernames:
[webservers]
asdf.example.com ansible_port=5000 ansible_user=alice
jkl.example.com ansible_port=5001 ansible_user=bob
You can specify the connection type to be used by:
[testcluster]
localhost ansible_connection=local
/path/to/chroot1 ansible_connection=chroot
foo.example.com ansible_connection=paramiko
File them in a group_vars/<group-name> file.
Q50) Do you know what language Ansible is written in?
Ansible is written in Python and PowerShell
Q51) Please explain what is Red Hat Ansible?
Ansible and Ansible Tower by Red Hat, both are an end to end complete automation platforms which are capable of providing the following features or functionalities:
Provisioning
Deploying applications
Orchestrating workflows
Manage IT systems
Configuration of IT systems
Networks
Applications
All of these activities are dealt with by Ansible where it can help the business to solve real-time business problems.
Q52) Is Ansible is an open-source tool?
Yes, Ansible is an open-source tool that is a powerful automation software tool that one can use.
Q53) Why you have to learn Ansible?
Ansible is more a tool for servers but does it have anything for networking. If you closely look into it, there is some support available in the market for networking devices. Using this tool, it will give you an overall view of your environment and also knowledge of how it works when it comes to network automation.
It is one of those tools where it is considered to be good to explore a new tool.
Q54) What are Ansible server requirements?
You need to have a virtual machine with Linux installed, which has Python 2.6 version or higher.
Q55) How to install Ansible on CentOS?
Step 1: Update your Control Node
yum update
Step 2: Install the EPEL Repository
yum install epel-release
Step 3: Install Ansible
yum install Ansible
Q56) How can you connect to other devices within Ansible?
Once, Ansible is installed and the basic setup has been completed, an inventory is created. This would be the base and one can start testing ansible. To connect to a different device then you have to use “Ping module”. This can be used as a simple connection test.
Ansible – m ping all
Q57) Can you build your own modules with Ansible?
Yes, we can create or own modules within Ansible.
It is an open-source tool that primarily works on Python. If you are good at programming in Python you can start creating your own modules in few hours from scratch and you don’t need to have any prior knowledge of the same.
Q58) How can you find information in Ansible?
After completing the basic setup, one has to make sure to find out the module called the “setup” module. Using this setup module, you will be able to find out a lot of information.
Q59) What does Fact mean in Ansible?
The term “Facts” is commonly used in an Ansible environment. They are described in the playbook areas where it displays known and discovered variables about the system. Facts are used to implement conditionals executions and also used for getting ad-hoc information of information.
You can see all the facts via:
$ ansible all- m setup
So if you want to extract only a certain part of the information then you can use the “setup” module where you will have an option to filter out the output and just get hold of the fact that you are in need of.
Q60) What is ask_pass in ansible?
The ask_pass is controlled in Ansible Playbook.
This controls whether ansible-playbook prompts a password by default. Usually, the default behavior is no:
It is always set to ask_pass=True
If you are using SSH keys for authentication purposes then you really don’t have to change this setting at all.
Q61) Explain What is ask_sudo_pass
This control is very similar to ask_pass
The ask_sudo_pass controls the Ansible Playbook to prompt a Sudo password. Usually, the default behavior is no:
ask_sudo_pass= True
One has to make sure and change this setting where the sudo passwords are enabled most of the time.
Q62) Explain what is ask_vault_pass?
Using this control we can determine whether Ansible Playbook should prompt a password for the vault password by default. As usual, the default behavior is no
ask_vault_pass= True
Q63) Explain Callback_plugin in Ansible?
Callbacks are explained as a piece of code in ansible environments where to get is used to call a specific event and permit the notifications.
This is more sort of a developer-related feature and allows low-level extensions around ansible so that they can be loaded from different locations without any problem.
Q64) Explain Module utilities in Ansible?
Ansible provides a wide variety of module utilities that help the developers while developing their own modules. The basic.py is a module that provides the main entry point for accessing the Ansible library and using those as basics one can start off working.
Q65) Where is the unit testing is available in Ansible?
Unit tests for all the modules are available in .test/units/modules. Firstly you have to set up your testing environment
Q66) Explain in detail ad-hoc commands?
Well, ad-hoc commands are nothing but a command which is used to do something quickly and it is more sort of one-time use. Unlike, the playbook is used for a repeated action which is something that is very useful in the Ansible environment. But there might be scenarios where we want to use ad-hoc commands which can simply do the required activity and it is a nonrepetitive activity.
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

