What is Package Manager?
Package Manager contains many software package which is easy to install – remove and update. example of package manager includes yum, apt, nuget, chcoclate, play store, apple store.
What is Helm?
- Package Manager for installing kubernetes package
- kubernetes helm package is being called “CHART”
Helm is the best way to find, share, and use software built for Kubernetes.
Helm helps you manage Kubernetes applications — Helm Charts help you define, install, and upgrade even the most complex Kubernetes application.
Charts are easy to create, version, share, and publish — so start using Helm and stop the copy-and-paste.
Helm is a graduated project in the CNCF and is maintained by the Helm community.
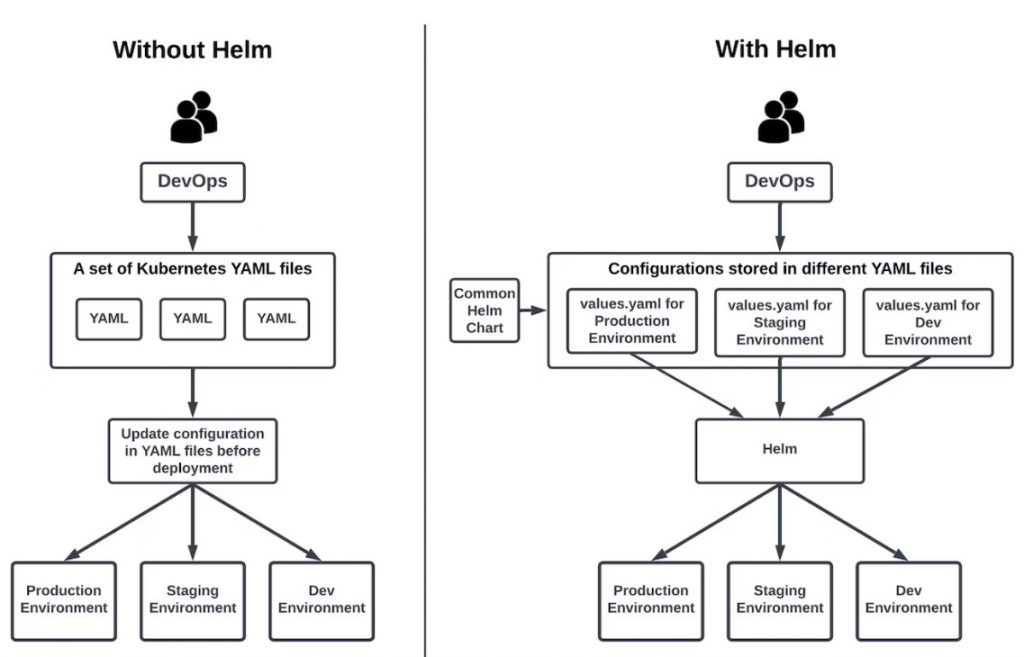
With and Without Helm
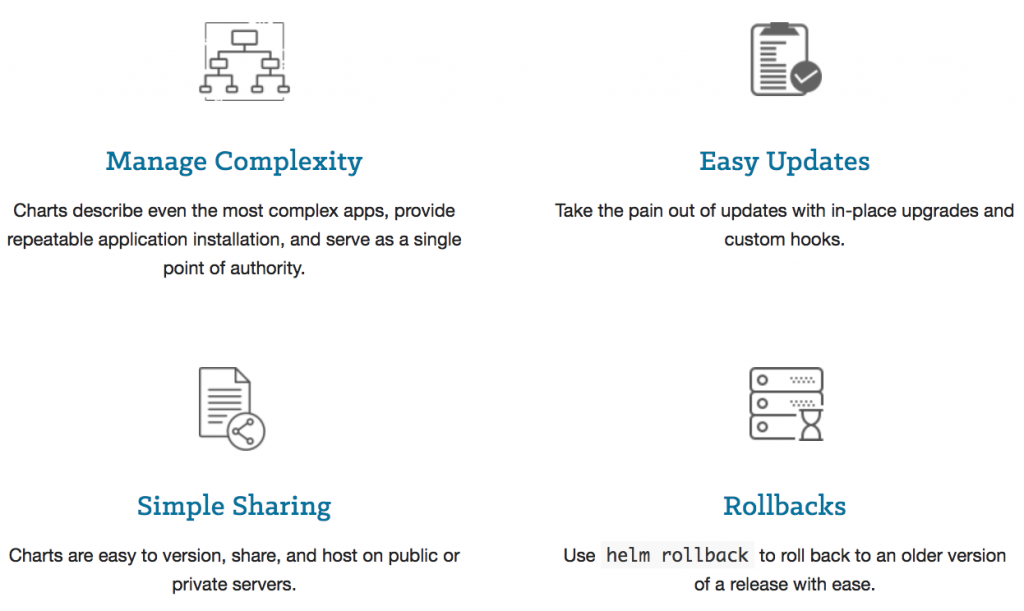
Feature of Helm?
What is kubernetes helm package?
kubernetes helm package is collection of kubernetes API resources yaml file which can be stored with certain structure for easy one click install-update-remove.
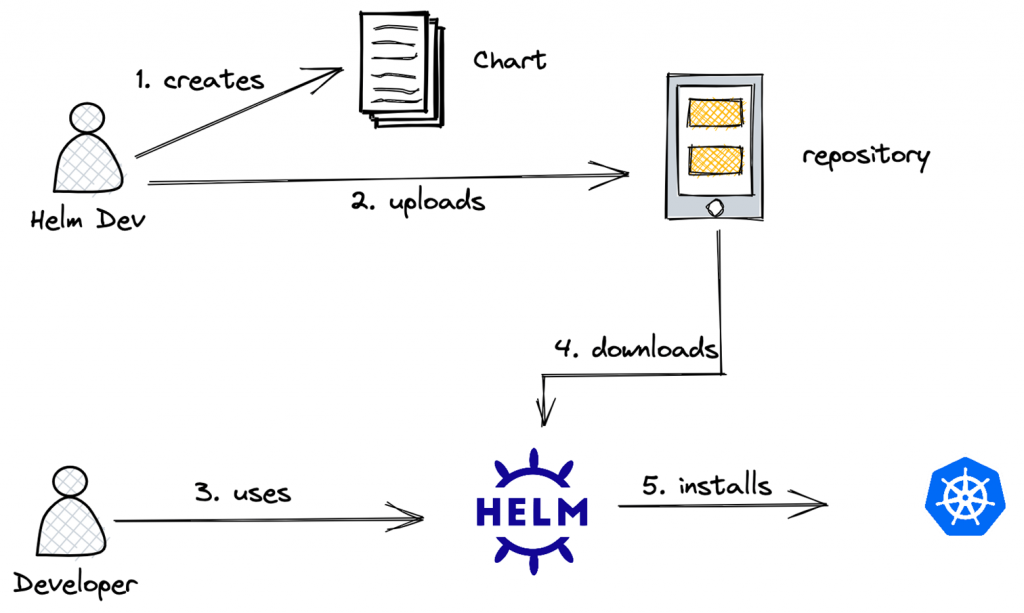
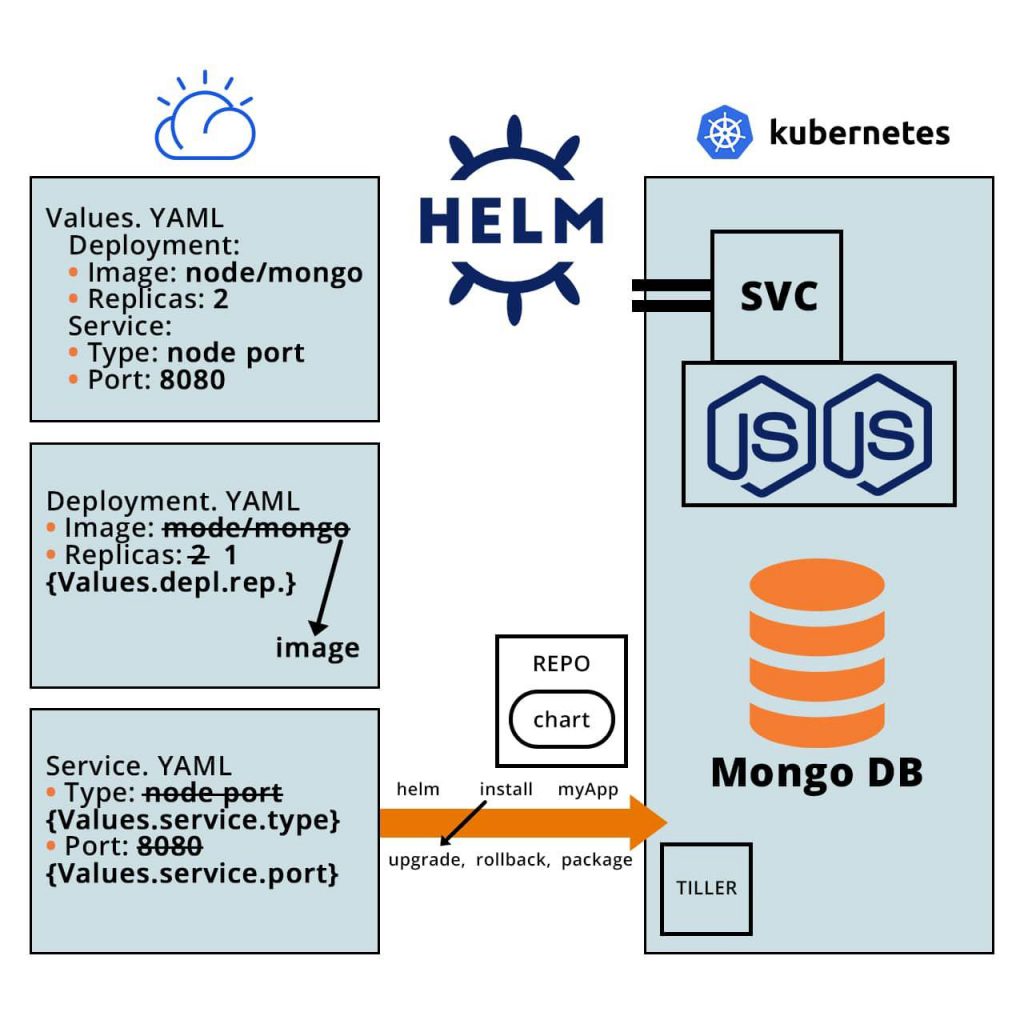
Helm Architecture
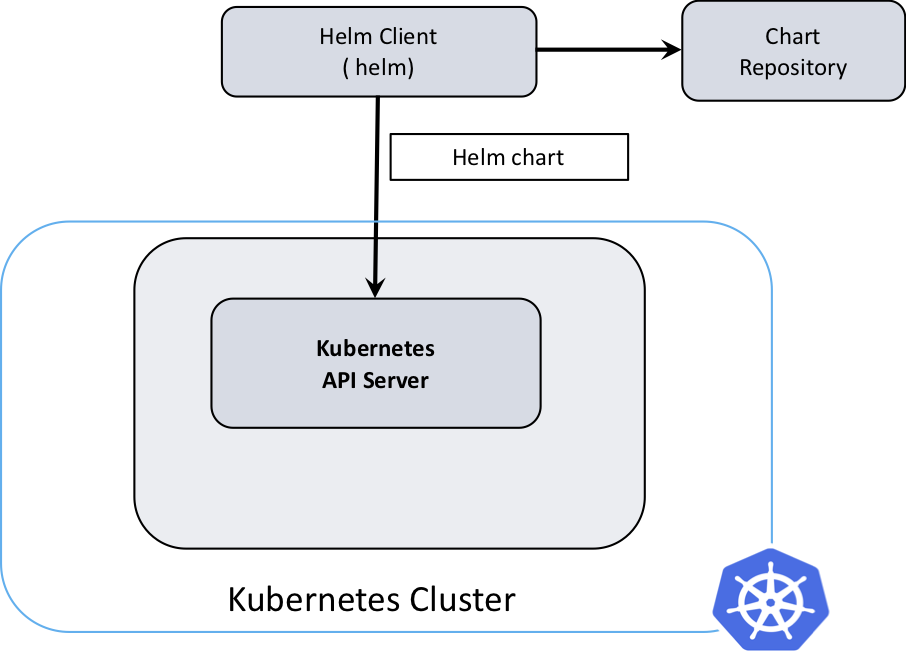
Helm Workflow
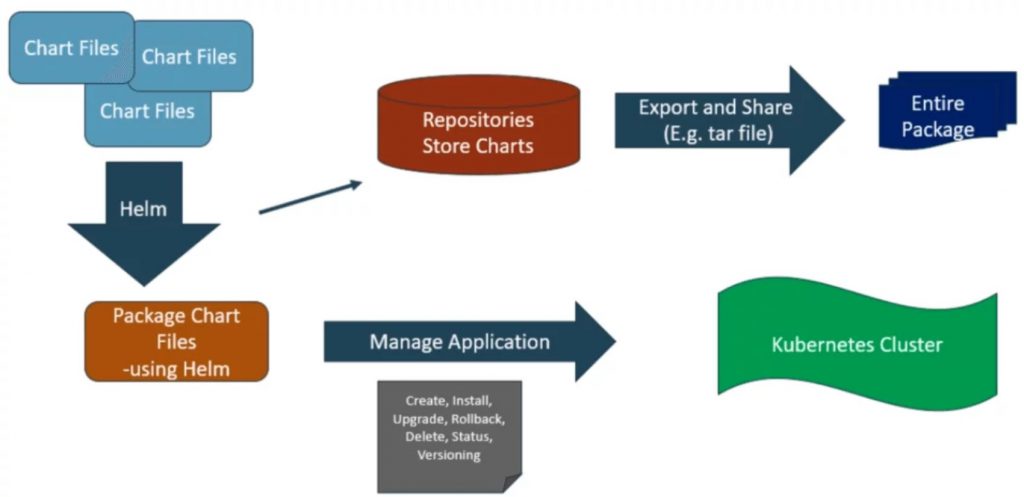
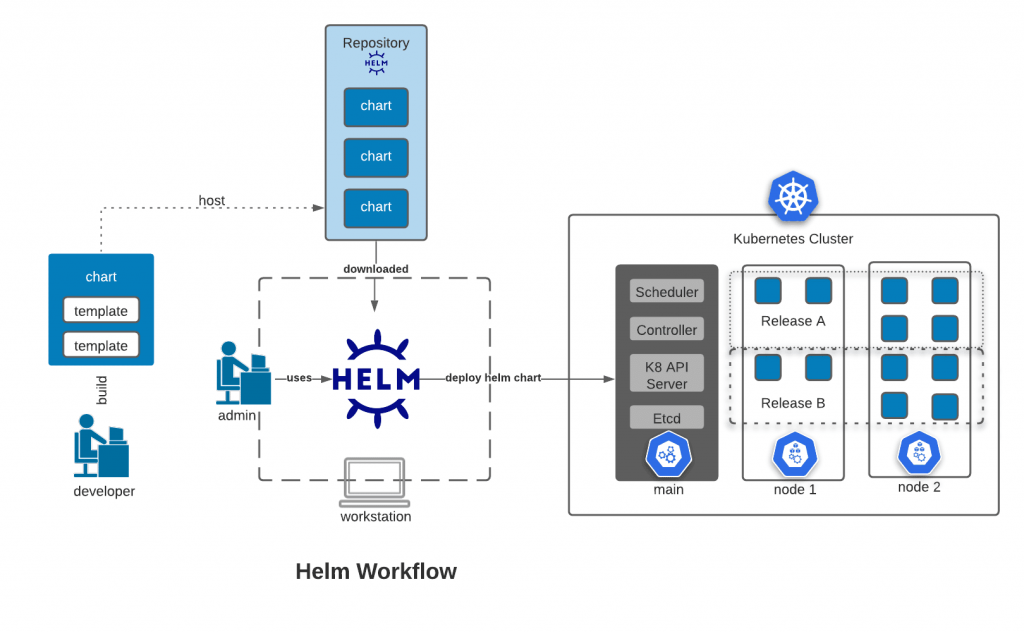
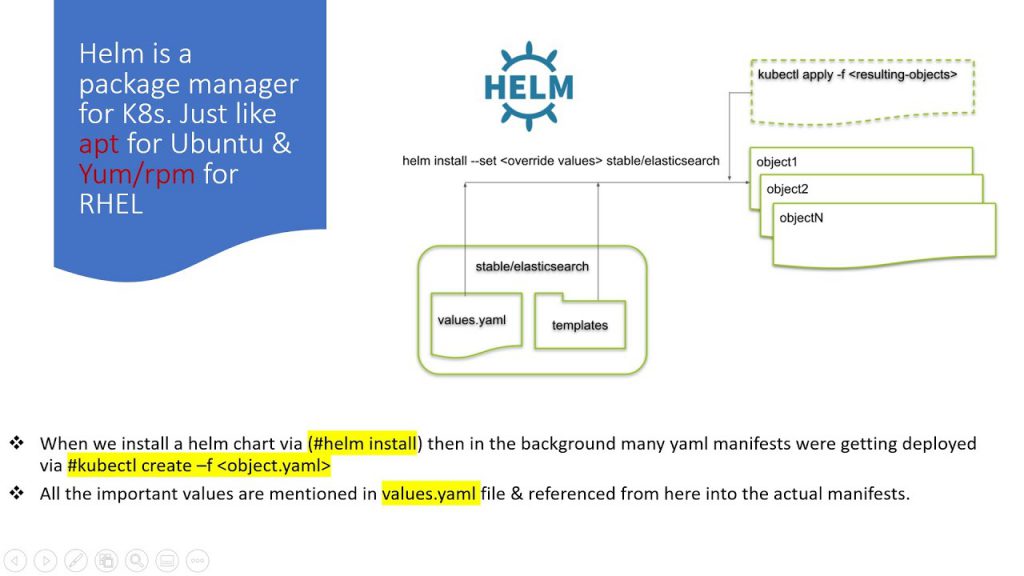
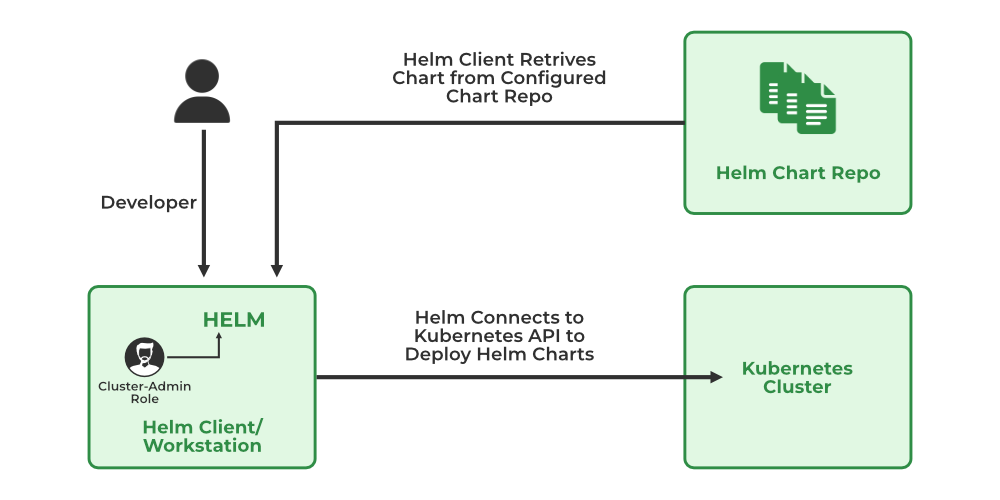
How Does Helm Work?
Helm Chart Anatomy
Helm Terminogy
- Chart: A Helm chart is a collection of files that describes a set of Kubernetes resources. It includes templates, values files, and other metadata required to deploy an application to a Kubernetes cluster.
- Release: A release is an instance of a chart deployed to a Kubernetes cluster. It represents a specific version of an application running in the cluster.
- Repository: A repository is a location where Helm charts are stored. It can be a local directory or a remote server accessible via HTTP(S), Git, or Amazon S3.
- Values: Values are parameters that can be customized when installing a Helm chart. They allow you to configure the deployment by providing specific values for variables defined in the chart.
- Template: Templates are files written in Go template language that define Kubernetes resource manifests. They allow you to dynamically generate YAML or JSON files based on the provided values.
- Release Namespace: A release namespace is the Kubernetes namespace in which a release is deployed. By default, Helm deploys releases to the same namespace as the Tiller (Helm’s server-side component) installation.
- Tiller: Tiller is the server-side component of Helm that interacts with the Kubernetes API server to manage releases. It has been deprecated in Helm 3, and Helm 3 no longer requires Tiller.
- Dependency: A Helm dependency is a chart that another chart depends on. It allows you to manage complex deployments by specifying and resolving dependencies between charts.
- Upgrade: Upgrading a release refers to updating the deployed version of a chart in a Kubernetes cluster. Helm provides commands to upgrade releases with new versions of charts or modify configuration values.
- Rollback: Rollback allows you to revert a release to a previous version. It is useful in case a new release version causes i
How to install helm?
- helm client must be installed in kubectl workstation
- Download your desired version
- Unpack it (tar -zxvf helm-v3.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz)
- Find the helm binary in the unpacked directory, and move it to its desired destination (mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm)
https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/
Commands in Linux?
$ wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.6.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ tar -zxvf helm-v3.6.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ cd linux-amd64
$ echo $PATH
$ mv helm /usr/local/bin
$ helm
$ helm versionCode language: PHP (php)How to use helm for Install – updating – removing a helm package called “CHART”?
Step 1 - Visit a helm.sh --> https://artifacthub.io/
Step 2 - Search & Identify a desire chart which you want to install in k8 cluster?
Step 3 - Add helm repo e.g tomcat chat
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
Step 4 - Install chart eg. tomcat
$ helm install my-release bitnami/tomcat
Step 5 - Verify
$ helm list
Step 6 - Remove
$ helm uninstall my-releaseCode language: PHP (php)How to create custom helm chart?
$ helm create scmgalaxy
How to install Local chart?
$ helm install scmgalaxy ./scmgalaxy Helm Help info
[root@rajesh k8]# helm
The Kubernetes package manager
Common actions for Helm:
- helm search: search for charts
- helm pull: download a chart to your local directory to view
- helm install: upload the chart to Kubernetes
- helm list: list releases of charts
Environment variables:
| Name | Description |
|------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| $HELM_CACHE_HOME | set an alternative location for storing cached files. |
| $HELM_CONFIG_HOME | set an alternative location for storing Helm configuration. |
| $HELM_DATA_HOME | set an alternative location for storing Helm data. |
| $HELM_DEBUG | indicate whether or not Helm is running in Debug mode |
| $HELM_DRIVER | set the backend storage driver. Values are: configmap, secret, memory, postgres |
| $HELM_DRIVER_SQL_CONNECTION_STRING | set the connection string the SQL storage driver should use. |
| $HELM_MAX_HISTORY | set the maximum number of helm release history. |
| $HELM_NAMESPACE | set the namespace used for the helm operations. |
| $HELM_NO_PLUGINS | disable plugins. Set HELM_NO_PLUGINS=1 to disable plugins. |
| $HELM_PLUGINS | set the path to the plugins directory |
| $HELM_REGISTRY_CONFIG | set the path to the registry config file. |
| $HELM_REPOSITORY_CACHE | set the path to the repository cache directory |
| $HELM_REPOSITORY_CONFIG | set the path to the repositories file. |
| $KUBECONFIG | set an alternative Kubernetes configuration file (default "~/.kube/config") |
| $HELM_KUBEAPISERVER | set the Kubernetes API Server Endpoint for authentication |
| $HELM_KUBECAFILE | set the Kubernetes certificate authority file. |
| $HELM_KUBEASGROUPS | set the Groups to use for impersonation using a comma-separated list. |
| $HELM_KUBEASUSER | set the Username to impersonate for the operation. |
| $HELM_KUBECONTEXT | set the name of the kubeconfig context. |
| $HELM_KUBETOKEN | set the Bearer KubeToken used for authentication. |
Helm stores cache, configuration, and data based on the following configuration order:
- If a HELM_*_HOME environment variable is set, it will be used
- Otherwise, on systems supporting the XDG base directory specification, the XDG variables will be used
- When no other location is set a default location will be used based on the operating system
By default, the default directories depend on the Operating System. The defaults are listed below:
| Operating System | Cache Path | Configuration Path | Data Path |
|------------------|---------------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------|
| Linux | $HOME/.cache/helm | $HOME/.config/helm | $HOME/.local/share/helm |
| macOS | $HOME/Library/Caches/helm | $HOME/Library/Preferences/helm | $HOME/Library/helm |
| Windows | %TEMP%\helm | %APPDATA%\helm | %APPDATA%\helm |
Usage:
helm [command]
Available Commands:
completion generate autocompletion scripts for the specified shell
create create a new chart with the given name
dependency manage a chart's dependencies
env helm client environment information
get download extended information of a named release
help Help about any command
history fetch release history
install install a chart
lint examine a chart for possible issues
list list releases
package package a chart directory into a chart archive
plugin install, list, or uninstall Helm plugins
pull download a chart from a repository and (optionally) unpack it in local directory
repo add, list, remove, update, and index chart repositories
rollback roll back a release to a previous revision
search search for a keyword in charts
show show information of a chart
status display the status of the named release
template locally render templates
test run tests for a release
uninstall uninstall a release
upgrade upgrade a release
verify verify that a chart at the given path has been signed and is valid
version print the client version information
Flags:
--debug enable verbose output
-h, --help help for helm
--kube-apiserver string the address and the port for the Kubernetes API server
--kube-as-group stringArray group to impersonate for the operation, this flag can be repeated to specify multiple groups.
--kube-as-user string username to impersonate for the operation
--kube-ca-file string the certificate authority file for the Kubernetes API server connection
--kube-context string name of the kubeconfig context to use
--kube-token string bearer token used for authentication
--kubeconfig string path to the kubeconfig file
-n, --namespace string namespace scope for this request
--registry-config string path to the registry config file (default "/root/.config/helm/registry.json")
--repository-cache string path to the file containing cached repository indexes (default "/root/.cache/helm/repository")
--repository-config string path to the file containing repository names and URLs (default "/root/.config/helm/repositories.yaml")
Use "helm [command] --help" for more information about a command.Code language: PHP (php)I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

