Step 1 – Download a file beat pacage
$ cd /opt
$ yum install wget -y
$ wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-8.3.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
$ tar -zxvf filebeat-8.3.3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
$ cd filebeat-8.3.3-linux-x86_64Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 2 – Configure input in filebeat.yml
# Each - is an input. Most options can be set at the input level, so
# you can use different inputs for various configurations.
# Below are the input specific configurations.
# filestream is an input for collecting log messages from files.
- type: filestream
# Unique ID among all inputs, an ID is required.
id: my-filestream-id
# Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true
# Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
- /var/log/*.log
#- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\*Code language: PHP (php)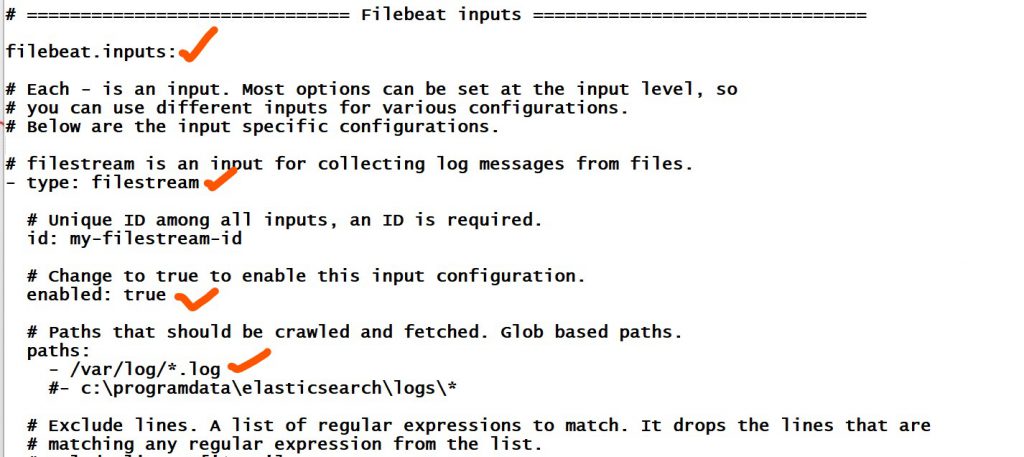
Step 3 – Configure output in filebeat.yml
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["https://172.18.0.2:9200"]
username: "elastic"
password: "qgWrZ8dzJtp*nB4HLIHZ"
ssl:
enabled: true
ca_trusted_fingerprint: "069dd4ec9161d86b6299a2823c1f66c5c7a1afd47550c8521bb07e6e0c4cf329" Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 4 – Configure Kibana in filebeat.yml
setup.kibana:
host: "172.18.0.3:5601"
username: "elastic"
password: "{qgWrZ8dzJtp*nB4HLIHZ}"Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 5 – To test your configuration file
$ ./filebeat test config -eStep 6 – Setup Assets
Filebeat comes with predefined assets for parsing, indexing, and visualizing your data. To load these assets:
$ ./filebeat setup -eCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 7 – Start the filebeat daemon
$ sudo chown root filebeat.yml
$ sudo ./filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I am working at Cotocus. I blog tech insights at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at I reviewed , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at PINTEREST
Rajesh Kumar at QUORA
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND

