
Comments in PHP
Comments are those human-readable texts that we should add to make our code more understandable for other programmes. It is ignored by PHP and doesn’t affect your code.
Comment are of Two types.
i. One or Single-line Comment.
ii. Multi-line Comment.
i. One or Single-line Comment:- Single line Comment is used to comment one line at a time or used in one line.
There are two types of Single line Comment:-
- Starts with //
Ex- //this is home section. - Starts with #
Ex- # this is footer section.
ii. Multi-line Comment:- It is used to comment more than one line at a time or used in more than one line. It starts with /* and ends with */.
Ex – /* this is
a multi-line
Comment*/
String Interpolation
String Interpolation is a feature or a quick shortcut which allows popping the value of a variable into a double-quoted string.
Ex – {Without String Interpolation}
| <?php | |
| $num=10; | |
| echo "value is" . $num; | |
| ?> |
{With String Interpolation}
| <?php | |
| $num=10; | |
| echo "value is: $num"; | |
| ?> |
Constant Variable
It is a type of variable which can’t be modified. To create a constant variable define() function is used.
Syntax :- define(“constant_variable”,value,case-insensitive);
Ex – define(“pi”,3.1415,True); {Note:- If case-insensitive is not assigned then, its by default FALSE}
Rules of Constant Varible :-
- No need to start the constant varible with the $ sign.
- Name only starts with a letter and an underscore(_).
- Variable name can’t start with a number.
- Constants are automatically global and can be used in the entire script.
Arithmetic/Math Operators
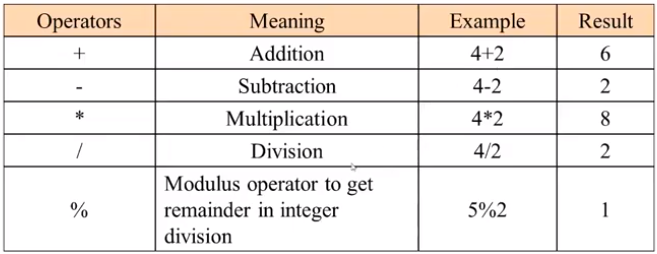
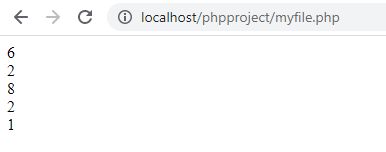
Sample Program
| <?php | |
| echo 4+2 . "<br />"; | |
| echo 4-2 . "<br />"; | |
| echo 4*2 . "<br />"; | |
| echo 4/2 . "<br />"; | |
| echo 5%2 . "<br />"; | |
| ?> |
Output
Maths Functions
There are predefined mathematical Functions available in PHP to do the mathematics calculations. See the below list:-
| abs() Returns the absolute (positive) value of a number | |
| acos() Returns the arc cosine of a number | |
| acosh() Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number | |
| asin() Returns the arc sine of a number | |
| asinh() Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number | |
| atan() Returns the arc tangent of a number in radians | |
| atan2() Returns the arc tangent of two variables x and y | |
| atanh() Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number | |
| base_convert() Converts a number from one number base to another | |
| bindec() Converts a binary number to a decimal number | |
| ceil() Rounds a number up to the nearest integer | |
| cos() Returns the cosine of a number | |
| cosh() Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number | |
| decbin() Converts a decimal number to a binary number | |
| dechex() Converts a decimal number to a hexadecimal number | |
| decoct() Converts a decimal number to an octal number | |
| deg2rad() Converts a degree value to a radian value | |
| exp() Calculates the exponent of e | |
| expm1() Returns exp(x) - 1 | |
| floor() Rounds a number down to the nearest integer | |
| fmod() Returns the remainder of x/y | |
| getrandmax() Returns the largest possible value returned by rand() | |
| hexdec() Converts a hexadecimal number to a decimal number | |
| hypot() Calculates the hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle | |
| intdiv() Performs integer division | |
| is_finite() Checks whether a value is finite or not | |
| is_infinite() Checks whether a value is infinite or not | |
| is_nan() Checks whether a value is 'not-a-number' | |
| lcg_value() Returns a pseudo random number in a range between 0 and 1 | |
| log() Returns the natural logarithm of a number | |
| log10() Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number | |
| log1p() Returns log(1+number) | |
| max() Returns the highest value in an array, or the highest value of several specified values | |
| min() Returns the lowest value in an array, or the lowest value of several specified values | |
| mt_getrandmax() Returns the largest possible value returned by mt_rand() | |
| mt_rand() Generates a random integer using Mersenne Twister algorithm | |
| mt_srand() Seeds the Mersenne Twister random number generator | |
| octdec() Converts an octal number to a decimal number | |
| pi() Returns the value of PI | |
| pow() Returns x raised to the power of y | |
| rad2deg() Converts a radian value to a degree value | |
| rand() Generates a random integer | |
| round() Rounds a floating-point number | |
| sin() Returns the sine of a number | |
| sinh() Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number | |
| sqrt() Returns the square root of a number | |
| srand() Seeds the random number generator | |
| tan() Returns the tangent of a number | |
| tanh() Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
Assignment Operators
This operator is used to assign value to the variables. For Ex –
$price=39.12 , $ram=$shyam=10 , $name=sushant
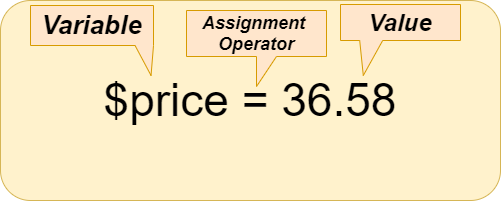
In the above example, Assignment operator (=) is used to assign the value (36.58) to the variable ($price).
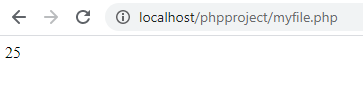
Combined Assignment Operator
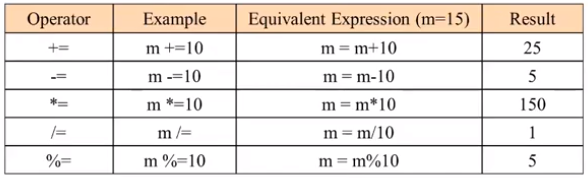
Sample Program

Output
To know more about Assignment Operator Click here – Assignment Operators
Click Here For Next Part – What are If, Nested if, if else and, Nested if else Statement in PHP?
With MotoShare.in, you can book a bike instantly, enjoy doorstep delivery, and ride without worries. Perfect for travelers, professionals, and adventure enthusiasts looking for a seamless mobility solution.

