What is apt-get?

apt-get is a command-line tool applied for package management in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu. It is part of the Advanced Package Tool (APT) suite, which includes several other utilities for managing software packages.
Top 10 use cases of apt-get?
Here are the top 10 use cases of apt-get:
- Package Installation:
- Use
apt-get installto download and install software packages from repositories. For example,apt-get install firefoxinstalls the Firefox web browser.
- Use
- Package Removal:
- Use
apt-get removeto uninstall software packages from the system. For example,apt-get remove firefoxremoves the Firefox web browser.
- Use
- Package Purging:
- Use
apt-get purgeto completely remove a package along with its configuration files. For example,apt-get purge firefoxremoves Firefox and its configuration files.
- Use
- Package Upgrades:
- Use
apt-get upgradeto upgrade installed packages to the latest available versions. This command updates all packages to their latest versions.
- Use
- System Update:
- Use
apt-get updateto update the local package index. This command downloads the latest package information from the repositories.
- Use
- Dependency Resolution:
apt-getautomatically resolves dependencies when installing or upgrading packages. It ensures that all required dependencies are installed along with the requested package.
- Repository Management:
apt-getmanages software repositories, including adding, removing, and enabling/disabling repositories. It uses configuration files in the/etc/apt/sources.list.d/directory.
- Package Search:
- Use
apt-cache searchto search for packages matching a given keyword. For example,apt-cache search text editorsearches for text editors available in the repositories.
- Use
- Package Information:
- Use
apt-cache showto display detailed information about a specific package. For example,apt-cache show firefoxdisplays information about the Firefox package.
- Use
- Dependency Resolution:
apt-getautomatically resolves dependencies when installing or upgrading packages. It ensures that all required dependencies are installed along with the requested package.
apt-get is a versatile and powerful package management tool that simplifies the process of installing, upgrading, and managing software packages on Debian-based Linux systems.
What are the feature of apt-get?
apt-get is a powerful package management tool for Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu. It offers several features that make it convenient for users to install, upgrade, remove, and manage software packages. Here are some of the key features of apt-get:
- Package Installation:
apt-getallows users to install software packages from repositories with a single command. It automatically resolves dependencies and installs the required packages.
- Package Removal:
- Users can remove installed packages using
apt-get remove. This command uninstalls the specified package while leaving configuration files intact.
- Users can remove installed packages using
- Package Purging:
apt-get purgeremoves a package along with its configuration files from the system. This ensures a complete removal of the package and its associated settings.
- Package Upgrades:
apt-get upgradeupgrades installed packages to their latest versions. It downloads and installs newer versions of packages available in the repositories.
- System Update:
apt-get updaterefreshes the local package index, ensuring that the system has the latest information about available packages and their versions.
- Dependency Resolution:
apt-getautomatically resolves dependencies when installing or upgrading packages. It ensures that all required dependencies are installed along with the requested package.
- Repository Management:
- Users can manage software repositories using
apt-get. This includes adding, removing, and enabling/disabling repositories to control which packages are available for installation.
- Users can manage software repositories using
- Package Search:
apt-cache searchallows users to search for packages based on keywords. It displays a list of packages matching the search criteria, making it easier to find and install software.
- Package Information:
apt-cache showprovides detailed information about a specific package, including its description, version, dependencies, and installed files. This helps users make informed decisions when installing or upgrading packages.
- Scriptable Operations:
apt-getcommands can be scripted and automated, making it easy to perform package management tasks in batch or in automated deployment scripts.
apt-get offers a comprehensive set of features for managing software packages on Debian-based Linux distributions. It simplifies the process of installing, upgrading, and removing packages while ensuring system stability and reliability.
How apt-get works and Architecture?
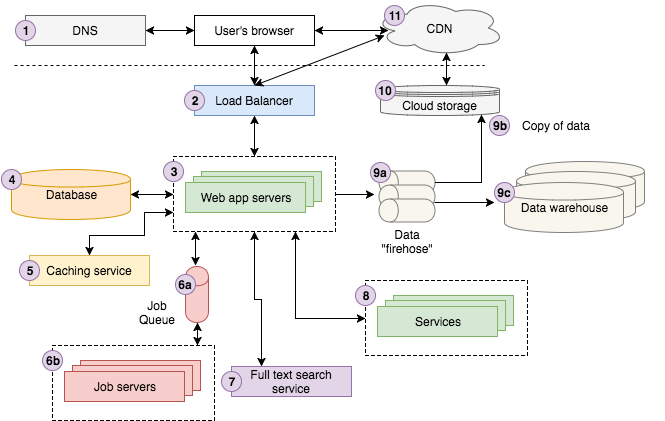
The workings and architecture of apt-get are closely tied to the underlying Advanced Package Tool (APT) system, which is a set of tools used for package management in Debian-based Linux distributions. Here’s an overview of how apt-get works and its architecture:
- Repository Configuration:
apt-getretrieves package information from software repositories configured on the system. These repositories contain metadata about available packages, including their names, versions, dependencies, and descriptions.
- Package Indexing:
- When
apt-get updateis executed, APT updates the local package index by fetching the latest package information from the configured repositories. This index is stored locally and used byapt-getto determine which packages are available for installation or upgrade.
- When
- Dependency Resolution:
- Before installing or upgrading packages,
apt-getperforms dependency resolution to ensure that all required dependencies for the requested packages are satisfied. It checks the local package index and downloads any missing dependencies from the repositories.
- Before installing or upgrading packages,
- Package Installation and Upgrade:
- When instructed to install or upgrade packages,
apt-getdownloads the corresponding package files from the repositories and installs them on the system. It also handles configuration file updates and post-installation tasks specified by the package maintainer scripts.
- When instructed to install or upgrade packages,
- Package Removal and Purging:
apt-get removeandapt-get purgecommands are used to uninstall packages from the system.apt-get removeremoves the package files while leaving configuration files intact, whileapt-get purgeremoves the package along with its configuration files.
- Dependency Handling:
- APT maintains a database of installed packages and their dependencies. It tracks dependencies between packages and ensures that packages are installed, upgraded, or removed in a consistent and reliable manner.
- Package Cache Management:
- APT maintains a cache of downloaded package files in the
/var/cache/apt/archives/directory. This cache helps to speed up subsequent package installations and upgrades by reusing locally stored package files whenever possible.
- APT maintains a cache of downloaded package files in the
- Plugin System and Hooks:
- APT provides a plugin system and hook mechanism that allows developers to extend its functionality and integrate with external tools and services. This enables customization and integration of
apt-getwith other package management systems or tools.
- APT provides a plugin system and hook mechanism that allows developers to extend its functionality and integrate with external tools and services. This enables customization and integration of
- Transaction Safety:
- APT ensures transaction safety by using a database-backed package management system. Package operations are performed atomically, ensuring that the system remains in a consistent state even in the event of failures or interruptions during package installation or upgrade.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI):
apt-getprovides a command-line interface for interacting with the APT system. Users can execute various commands and options to perform package management tasks such as installation, upgrade, removal, and repository management.
apt-get leverages the underlying APT system to facilitate package management operations on Debian-based Linux distributions. It provides a convenient and efficient way to install, upgrade, and manage software packages while ensuring system stability and reliability.
How to Install apt-get it?
apt-get is a powerful command-line tool for managing software packages on Debian-based Linux distributions, including Ubuntu. It allows you to install, upgrade, and remove packages with ease. Here’s how you can use apt-get:
- Updating the Package Database: Before installing or upgrading packages, it’s essential to update the package database. Run the following command to refresh the list of available packages:
sudo apt-get update - Installing Packages: To install a package, use the following syntax:
sudo apt-get install package_nameReplacepackage_namewith the name of the package you want to install. For example, to install the Firefox web browser, run:sudo apt-get install firefox - Upgrading Packages: To upgrade all installed packages to their latest versions, use:
sudo apt-get upgrade - Removing Packages: To remove a package (and its configuration files), use:
sudo apt-get remove package_name - Cleaning Up: After installing or removing packages, you can clean up any leftover files using:
sudo apt-get autoremove
Remember that apt-get is just one of the tools available for package management. There’s also apt, which is a newer and simpler version of apt-get. Both serve similar purposes, but apt provides a more user-friendly experience. If you’re using Ubuntu, you can also use apt directly by running:
sudo apt install package_nameBasic Tutorials of apt-get: Getting Started
Let’s dive into the basics of using apt-get for package management on Debian-based Linux distributions. Whether you’re new to Linux or looking to enhance your skills, understanding these commands will empower you as a proficient user.
- Update the Package Database:
- apt-get relies on a database of available packages. To ensure you have the latest information, run:
sudo apt-get updateThis command refreshes the package list, allowing your system to identify newer packages.
2. Upgrade Installed Packages:
- After updating the package database, you can upgrade your installed packages to their latest versions:
sudo apt-get upgrade This ensures that your system benefits from security patches and feature enhancements.
3. Search for Packages with apt-cache:
- apt-cache is a companion tool to apt-get. It helps you find new packages. For instance:
apt-cache search package_name Replace package_name with the software you’re interested in. It’ll display relevant packages.
4. Install New Packages:
- To install a package, use:
sudo apt-get install package_name
sudo apt-get install firefox 5. Remove Installed Packages:
- If you want to remove a package (including its configuration files), use:
sudo apt-get remove package_name 6. Clean Up:
- After installing or removing packages, clean up residual files with:
sudo apt-get autoremoveThis frees up disk space by removing unnecessary dependencies.
Always remember, apt-get is a powerful tool for managing software packages, and mastering it will enhance your Linux experience. 🐧📦🚀

👤 About the Author
Rahul is passionate about DevOps, DevSecOps, SRE, MLOps, and AiOps. Driven by a love for innovation and continuous improvement, Rahul enjoys helping engineers and organizations embrace automation, reliability, and intelligent IT operations. Connect with Rahul and stay up-to-date with the latest in tech!
🌐 Connect with Rahul
-
Website: MotoShare.in
-
Facebook: facebook.com/DevOpsSchool
-
X (Twitter): x.com/DevOpsSchools
-
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/company/devopsschool
-
YouTube: youtube.com/@TheDevOpsSchool
-
Instagram: instagram.com/devopsschool
-
Quora: devopsschool.quora.com
-
Email: contact@devopsschool.com

