
Continuous Monitoring is a practice in the field of information technology and cybersecurity that involves the ongoing, automated, and real-time observation and assessment of an organization’s systems, networks, applications, and digital assets to identify security threats, vulnerabilities, and performance issues. It is an essential component of an organization’s overall security and operational strategies and is crucial for maintaining the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of digital assets.
Key aspects of Continuous Monitoring include:
- Real-time Data Collection: Continuous Monitoring systems continuously collect and analyze data from various sources, including security logs, network traffic, system events, and application performance metrics.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: When anomalies, security threats, or performance issues are detected, Continuous Monitoring systems generate automated alerts and notifications to relevant personnel or teams, enabling timely response and remediation.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Continuous Monitoring includes regular vulnerability scanning to identify and assess vulnerabilities in systems and applications. It helps organizations prioritize and address security weaknesses promptly.
- Compliance Monitoring: Continuous Monitoring also includes monitoring for compliance with regulatory and security standards and policies, ensuring that organizations meet legal and internal requirements.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integration with threat intelligence feeds allows Continuous Monitoring systems to stay updated on emerging threats and vulnerabilities, enabling proactive defense measures.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous Monitoring assesses the performance of systems and applications, identifying bottlenecks and performance degradation issues that can impact user experience.
Why We need Continuous Monitoring?
- Early Threat Detection: Continuous Monitoring provides real-time visibility into security events and potential threats, allowing organizations to detect and respond to security incidents early, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Reduced Downtime: By continuously monitoring performance and detecting performance issues, organizations can proactively address system or application problems, minimizing downtime and service disruptions.
- Improved Security Posture: Continuous Monitoring helps organizations maintain a strong security posture by identifying vulnerabilities and non-compliance issues that need remediation.
- Compliance Assurance: Organizations subject to regulatory requirements can use Continuous Monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance with data protection and security standards. This reduces the risk of regulatory fines and penalties.
- Data Protection: Continuous Monitoring helps protect sensitive data by identifying unauthorized access attempts or data breaches as soon as they occur.
- Cost Savings: Early detection and resolution of issues through Continuous Monitoring can result in cost savings by avoiding the expenses associated with data breaches, downtime, and emergency response.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Continuous Monitoring allows organizations to proactively address security threats and vulnerabilities, reducing the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
- Enhanced Visibility: Continuous Monitoring provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s digital environment, enabling better decision-making and resource allocation.
- Scalability: As organizations grow and their digital footprints expand, Continuous Monitoring scales to accommodate additional assets and network segments, ensuring continuous protection.
- Incident Response Readiness: Continuous Monitoring enhances an organization’s incident response capabilities by providing real-time insights into security events and threats, facilitating faster and more effective incident response.
- Business Continuity: By identifying and mitigating performance issues, Continuous Monitoring helps ensure business continuity and uninterrupted service delivery to customers and users.
- User Experience Improvement: Monitoring application performance and user behavior allows organizations to improve user experience and customer satisfaction.
Continuous Monitoring is essential because it helps organizations maintain security, compliance, and operational efficiency by providing real-time insights into their digital environments. It allows organizations to detect and respond to security threats, vulnerabilities, and performance issues promptly, reducing risks and ensuring the reliability of digital services.
What is the Advantage of Continuous Monitoring?
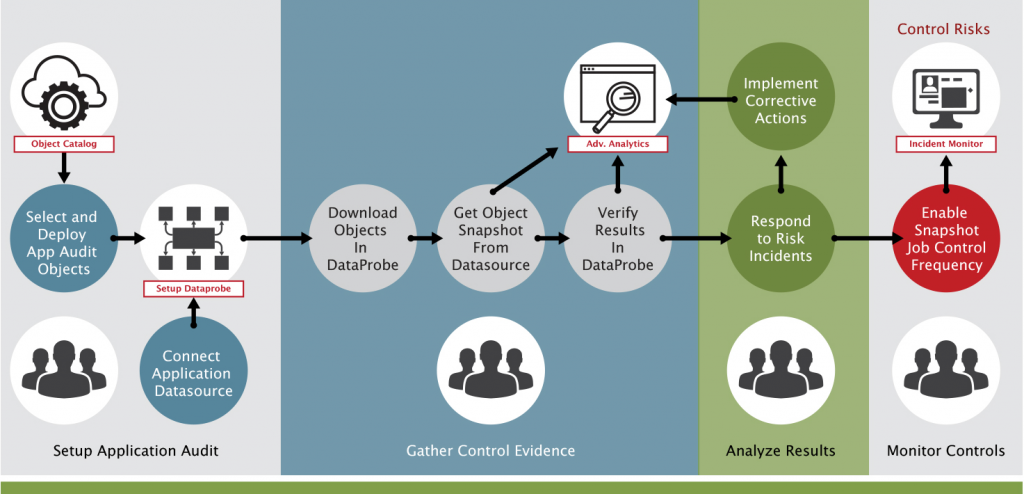
- Early Threat Detection: Continuous Monitoring provides real-time visibility into security events and potential threats, enabling organizations to detect and respond to security incidents early, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Reduced Downtime: By continuously monitoring performance and detecting performance issues, organizations can proactively address system or application problems, minimizing downtime and service disruptions. This leads to improved operational efficiency.
- Improved Security Posture: Continuous Monitoring helps organizations maintain a strong security posture by identifying vulnerabilities and non-compliance issues that need remediation. This proactive approach enhances the overall security of digital assets.
- Compliance Assurance: Organizations subject to regulatory requirements can use Continuous Monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance with data protection and security standards. This reduces the risk of regulatory fines and penalties while demonstrating commitment to data privacy.
- Data Protection: Continuous Monitoring helps protect sensitive data by identifying unauthorized access attempts or data breaches as soon as they occur. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding confidential information.
- Cost Savings: Early detection and resolution of issues through Continuous Monitoring can result in significant cost savings by avoiding the expenses associated with data breaches, downtime, and emergency response efforts.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: Continuous Monitoring allows organizations to proactively address security threats and vulnerabilities, reducing the likelihood of successful cyberattacks and minimizing potential damage.
- Enhanced Visibility: Continuous Monitoring provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s digital environment, enabling better decision-making, resource allocation, and the ability to identify areas for improvement.
- Scalability: Continuous Monitoring can scale to accommodate additional assets and network segments as organizations grow. It ensures that protection and visibility expand with the organization’s digital footprint.
- Incident Response Readiness: Continuous Monitoring enhances an organization’s incident response capabilities by providing real-time insights into security events and threats. This facilitates faster and more effective incident response, minimizing the impact of security incidents.
- Business Continuity: By identifying and mitigating performance issues, Continuous Monitoring helps ensure business continuity and uninterrupted service delivery to customers and users. It contributes to customer satisfaction and trust.
- User Experience Improvement: Monitoring application performance and user behavior allows organizations to make data-driven decisions for improving user experience and customer satisfaction. It helps deliver better services and products.
What is the feature of Continuous Monitoring?
- Real-time Data Collection: Continuous Monitoring systems continuously collect and analyze data from various sources, including security logs, network traffic, system events, and application performance metrics.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: Continuous Monitoring generates automated alerts and notifications when anomalies, security threats, or performance issues are detected, ensuring that relevant personnel can respond promptly.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Continuous Monitoring includes regular vulnerability scanning to identify and assess vulnerabilities in systems and applications, helping organizations prioritize and address security weaknesses.
- Compliance Monitoring: Continuous Monitoring monitors compliance with regulatory and security standards and policies, ensuring ongoing adherence to data protection and security requirements.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integration with threat intelligence feeds allows Continuous Monitoring systems to stay updated on emerging threats and vulnerabilities, enabling proactive defense measures.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous Monitoring assesses the performance of systems and applications, identifying bottlenecks and performance degradation issues that can impact user experience and business operations.
- Customizable Dashboards: Continuous Monitoring often provides customizable dashboards and reporting tools to visualize data, trends, and security-related information.
- Integration with SIEM: Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems allows for comprehensive security event correlation and analysis.
- Audit Trail and Reporting: Continuous Monitoring solutions often provide detailed audit trails and reporting capabilities to demonstrate compliance, investigate incidents, and track system changes.
- User Behavior Analytics: Some Continuous Monitoring systems incorporate user behavior analytics to detect abnormal user activities or insider threats.
Continuous Monitoring offers numerous advantages, including early threat detection, reduced downtime, improved security posture, compliance assurance, cost savings, and enhanced visibility. Its key features include real-time data collection, automated alerts, vulnerability scanning, compliance monitoring, threat intelligence integration, and customizable dashboards, all of which contribute to robust security and operational efficiency in today’s digital landscape.
What is the Top 10 Use cases of Continuous Monitoring?
Continuous Monitoring (CM) is the practice of monitoring systems and applications on an ongoing basis to identify and address problems as soon as possible. This can help to improve the performance, reliability, and security of systems and applications.
Here are the top 10 use cases of Continuous Monitoring:
- Identifying and resolving performance problems. CM can help to identify performance problems early on, before they impact users.
- Detecting and preventing security breaches. CM can help to detect security breaches early on, before they can cause damage.
- Ensuring compliance. CM can help to ensure that systems and applications are compliant with regulations.
- Improving the user experience. CM can help to improve the user experience by ensuring that systems and applications are performing as expected.
- Providing insights into system behavior. CM can provide insights into system behavior, which can help to identify and address problems.
- Automating tasks. CM can automate tasks, such as collecting logs and metrics, which can free up time for engineers to focus on other tasks.
- Providing a single view of the infrastructure. CM can provide a single view of the infrastructure, which can help to identify and resolve problems more quickly.
- Making predictions. CM can be used to make predictions about system behavior, which can help to prevent problems before they occur.
- Improving communication. CM can help to improve communication between teams by providing a central place to share information about system health.
- Providing a foundation for DevOps. CM is a key foundation for DevOps, as it provides the data and insights needed to automate and optimize the software delivery process.
How to Implement Continuous Monitoring?
The way to implement Continuous Monitoring depends on the specific needs of the organization. However, some common steps include:
- Identify the systems and applications that need to be monitored.
- Define the metrics that need to be collected.
- Select the tools and technologies that will be used for monitoring.
- Configure the monitoring tools and technologies.
- Collect data and generate reports.
- Analyze the data and identify problems.
- Take corrective action.
Continuous Monitoring is a complex undertaking, but it can be a very rewarding one. By implementing Continuous Monitoring, organizations can improve the performance, reliability, security, and user experience of their systems and applications.
Here are some additional considerations for implementing Continuous Monitoring:
- You need to have a clear understanding of your organization’s needs.
- You need to have the support of the organization’s leadership.
- You need to be willing to invest in the right tools and technologies.
How to Get certified in Continuous Monitoring?
- DevOpsSchool.com
- scmGalaxy.com
- BestDevOps.com
- Cotocus.com

There are currently no Continuous Monitoring (CM)-specific certification exams available. However, there are a number of certifications that can help you learn the fundamentals of CM, such as:
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP). This certification is offered by (ISC)² and covers the principles and practices of cloud security, including continuous monitoring.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP). This certification is also offered by (ISC)² and covers a wide range of security topics, including continuous monitoring.
- Certified Cloud Architect – Associate (CCA-A). This certification is offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) and covers the design and implementation of cloud architectures, including continuous monitoring.
- Certified Cloud Practitioner (CCP). This certification is also offered by AWS and covers the basics of cloud computing, including continuous monitoring.
In addition to certifications, there are a number of other resources that can help you learn CM, such as:
- Books. There are a number of books available on CM. These resources can help you learn about the concepts and practices of CM.
- Articles. There are a number of articles available on CM. These resources can help you learn about the latest trends in CM.
- Online courses. There are a number of online courses available on CM. These courses can teach you the fundamentals of CM and help you prepare for the certification exam.
- Workshops. There are a number of workshops available on CM. These workshops can help you learn about the latest trends in CM and get hands-on experience with the tools and technologies.
- Conferences. There are a number of conferences that cover CM. These conferences can be a great way to learn about CM from experts and network with other CM professionals.
How to Learn Continuous Monitoring?
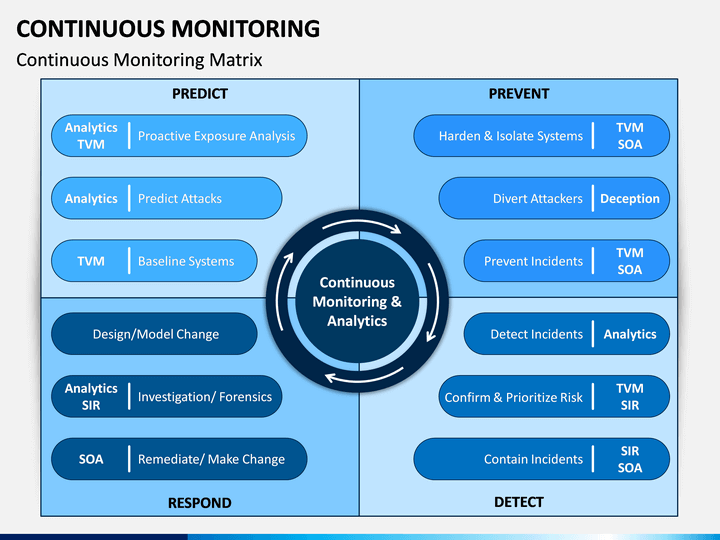
The best way to learn CM is to use a combination of these resources. Start by understanding the basics of cloud computing and security, and then focus on learning about the specific CM practices and technologies that are relevant to your organization.
Let’s have a look at some additional tips for learning CM:
- Get involved in the CM community. There is a growing community of CM professionals who are active on social media and in online forums. Get involved in this community to learn from others and stay up-to-date on the latest CM trends.
- Attend conferences and workshops. Attending conferences and workshops is a great way to learn about CM from experts.
- Get hands-on experience. The best way to learn CM is to get hands-on experience with it. You can do this by setting up a CM environment in the cloud or by working on a CM project at your job.
Continuous Monitoring is a rapidly growing field, and there is a high demand for CM professionals. By learning CM, you can position yourself for a successful career in this field.

👤 About the Author
Ashwani is passionate about DevOps, DevSecOps, SRE, MLOps, and AiOps, with a strong drive to simplify and scale modern IT operations. Through continuous learning and sharing, Ashwani helps organizations and engineers adopt best practices for automation, security, reliability, and AI-driven operations.
🌐 Connect & Follow:
- Website: WizBrand.com
- Facebook: facebook.com/DevOpsSchool
- X (Twitter): x.com/DevOpsSchools
- LinkedIn: linkedin.com/company/devopsschool
- YouTube: youtube.com/@TheDevOpsSchool
- Instagram: instagram.com/devopsschool
- Quora: devopsschool.quora.com
- Email– contact@devopsschool.com

