What is Flyway ?

Flyway is an open-source database migration tool that helps you manage schema changes in a safe and repeatable way. It’s designed to be vendor-neutral, working across various database platforms like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and more. Flyway uses version control best practices to track and apply database migrations in a controlled and automated manner.
Here’s what Flyway offers:
- Versioned migrations: Each change to your database schema is represented as a migration script with a version number. This allows you to track the evolution of your database and easily roll back to previous versions if needed.
- Repeatable deployments: Flyway ensures that migrations are applied in the correct order consistently across different environments, like development, testing, and production. This helps avoid inconsistencies and potential issues.
- Automatic checksums: Flyway verifies the integrity of migration scripts before applying them, ensuring you’re applying the correct version and avoiding unexpected changes.
- Flexible scripting: You can write migration scripts in various languages like SQL, PL/SQL, and T-SQL, depending on your database platform.
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines: Flyway can be easily integrated into your continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline, allowing you to automate database schema changes along with code deployments.
Top 10 use cases of Flyway ?
Top 10 Use Cases of Flyway:
- Managing schema changes in complex applications: Flyway helps manage complex applications with frequent database schema changes, ensuring a controlled and organized evolution.
- Maintaining consistency across environments: Flyway ensures your database schemas are consistent across development, testing, and production environments, avoiding discrepancies and potential errors.
- Rolling back changes easily: If you encounter issues after a migration, Flyway allows you to easily roll back to a previous version, minimizing downtime and impact.
- Automating database deployments: Integrate Flyway with your CI/CD pipeline to automate database schema changes alongside code deployments, streamlining the process and reducing manual intervention.
- Collaboration and version control: Flyway promotes collaboration among developers by tracking changes and allowing for easy review and rollback of migrations.
- Improved database governance: Flyway helps enforce database schema versioning and change management policies, leading to better governance and control.
- Reduced risk of errors: By automating migrations and verifying checksums, Flyway helps minimize the risk of human errors and unexpected changes.
- Supports diverse database platforms: Flyway’s vendor-neutral approach provides flexibility to use it with different database platforms, avoiding vendor lock-in.
- Open-source and community-driven: Flyway is an open-source project with an active community, offering access to resources and support.
- Scalability and performance: Flyway is designed to handle large databases and complex migrations efficiently.
Whether you’re working on a small project or a large-scale enterprise application, Flyway can be a valuable tool to manage your database schema changes effectively and efficiently.
What are the feature of Flyway ?
Now, Let’s explore the features of Flyway, a popular database migration tool:
- Version Control for Databases:
- Flyway enables version control for your database schema.
- You can track changes over time, making it easier to manage and deploy updates.
- Simple and Reliable:
- Flyway follows the “plain old SQL” approach.
- No proprietary XML formats or complex configurations.
- It just works, with zero required dependencies.
- Convention Over Configuration:
- Flyway encourages convention over configuration.
- It simplifies the setup process and decreases boilerplate code.
- SQL and Java Migrations:
- Write migrations in plain SQL or Java.
- SQL migrations support database-specific syntax (e.g., PL/SQL, T-SQL).
- Automated Deployment Pipeline:
- Flyway integrates seamlessly into your deployment pipeline.
- From version control to continuous delivery, it automates database development.
- Change Reports and Drift Detection:
- Flyway provides change reports to track modifications.
- Detect drift between your database schema and expected state.
- Migration Script Auto-Generation:
- Flyway can generate migration scripts based on changes detected in your schema.
- Saves time and ensures consistency.
- Schema Comparison and Static Data Versioning:
- Compare schemas between databases.
- Version static data alongside schema changes.
- Built-in Git Client:
- Flyway includes a Git client for seamless integration with version control.
- Technical Support and Enterprise Features:
- Flyway offers different editions (Community, Teams, and Enterprise).
- Enterprise includes advanced features like migration script auto-generation, drift detection, and SQL code standard checks.
Flyway extends DevOps to your databases, accelerating software delivery while ensuring quality code! 🚀🗄️
How Flyway works and Architecture?
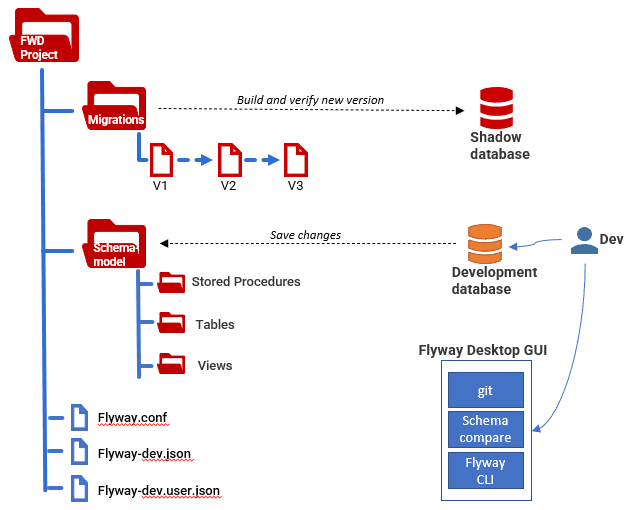
Flyway is a powerful database migration tool that simplifies managing and applying changes to your database schema. Let’s explore how it works and its architecture:
- Schema History Table:
- When you point Flyway to an empty database, it looks for its schema history table.
- If not found, Flyway creates it. This table tracks the state of the database.
- Scanning for Migrations:
- Flyway scans the filesystem or classpath for migration scripts (written in SQL or Java).
- Migrations are sorted by their version number and applied in order.
- Applying Migrations:
- Each migration is executed within a single database transaction.
- The schema history table is updated to reflect the applied migrations.
- Versioned vs. Repeatable Migrations:
- Versioned migrations have unique versions and are applied exactly once.
- Repeatable migrations are re-applied whenever their checksum changes.
- Upgrading to Newer Versions:
- Create a new migration with a higher version number.
- Flyway detects it and upgrades the database accordingly.
- Maven Plugin Integration:
- Use the Flyway Maven plugin to perform database migrations.
- Configure it via the
<configuration>tag in yourpom.xml.
- Other Configuration Options:
- Configure Flyway using Maven properties or an external
.conffile. - Specify database credentials, schemas, and other properties.
- Configure Flyway using Maven properties or an external
Flyway automates database evolution, making it easy to manage schema changes reliably! 🚀🗄️
How to Install Flyway it?
Now, Let’s find how to install Flyway, a powerful database schema change management tool:
- Download Flyway:
- Visit the official Flyway website to download the Flyway distribution.
- Select the accurate version for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
- Extract the Archive:
- Once downloaded, extract the Flyway archive to a local directory.
- You’ll find the Flyway executable and necessary files inside.
- Set Up Environment Variables (Optional):
- Add the Flyway installation directory to your system’s PATH environment variable.
- This step ensures you can run Flyway from any location in the command prompt or terminal.
- Verify Installation:
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Type
flyway --versionand press Enter. - If successful, you’ll see the Flyway version information.
That’s it! You’ve successfully installed Flyway. Now you’re ready to manage your database schema changes with ease. 🚀🗄️
Basic Tutorials of Flyway: Getting Started

This step-by-step guide will introduce you to Flyway’s basic functionalities through a simple example. We’ll focus on the Community Edition, but note that some features mentioned here might only be available in the Teams Edition.
1. Prerequisites:
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE): Download and install if not already present.
- Database: Choose a compatible database like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle. Set up your database and user credentials.
- Flyway download: Download the Flyway Community Edition from https://flywaydb.org/. Extract the downloaded archive.
2. Project Setup:
- Create a new project directory.
- Inside the project directory, create a file named
flyway.conf(configuration file). - In
flyway.conf, add the following basic configuration details:
# Database connection details
url=your_database_url
user=your_database_user
password=your_database_password
# Database schema
schemas=public
# Placeholders for migration scripts
locations=filesystem:migrations
Replace placeholders with your actual database details and desired location for migration scripts (usually a folder named migrations).
3. Create Initial Migration:
- Create a new folder named
migrationsunder your project directory. - Inside
migrations, create a file namedV1__create_users_table.sql. TheV1__prefix indicates the version number. - Add the following SQL script to create a
userstable:
SQL
CREATE TABLE users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
email VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL UNIQUE
);
4. Run Flyway Migration:
- Open a terminal and navigate to your project directory.
- Run the following command to execute the migration:
flyway migrate
Flyway will connect to your database, detect the migration script, and apply it. You can check your database to confirm the users table creation.
5. Add Another Migration:
- Create a new file named
V2__add_password_column.sqlwithin themigrationsfolder. - Add the following SQL script to add a
passwordcolumn to theuserstable:
SQL
ALTER TABLE users ADD password VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL;
- Run
flyway migrateagain to apply this new migration.
6. Additional Notes:
- You can add multiple migration scripts with unique version prefixes to manage schema evolution gradually.
- Flyway offers various commands for advanced tasks like checking migration status, rolling back changes, and more.
- Consider using a version control system like Git to track your migration scripts alongside your codebase for better management and collaboration.
This basic tutorial provides a starting point for using Flyway.

👤 About the Author
Rahul is passionate about DevOps, DevSecOps, SRE, MLOps, and AiOps. Driven by a love for innovation and continuous improvement, Rahul enjoys helping engineers and organizations embrace automation, reliability, and intelligent IT operations. Connect with Rahul and stay up-to-date with the latest in tech!
🌐 Connect with Rahul
-
Website: MotoShare.in
-
Facebook: facebook.com/DevOpsSchool
-
X (Twitter): x.com/DevOpsSchools
-
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/company/devopsschool
-
YouTube: youtube.com/@TheDevOpsSchool
-
Instagram: instagram.com/devopsschool
-
Quora: devopsschool.quora.com
-
Email: contact@devopsschool.com

